What is Electricity?
Electricity is a flow of charged particles, which may be electrons or ions.
(If you are not sure what electrons or ions are,
see GCSE Chemistry at electrons or ions).
In chemistry, ions which are free to move will conduct electricity
during electrolysis.
In physics, we are dealing with electricity as a flow of electrons.
A cell uses chemical reactions to make electricity.
In the circuit below, electricity will flow from the cell (or battery),
through the lamp (light bulb) and back to the cell.
Cell and Battery
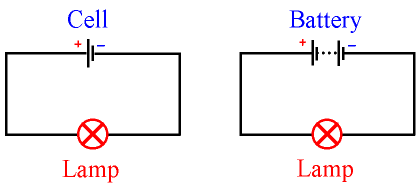
There is a difference between a cell and a battery.
In every-day life, we use the word "battery".
In physics, one "battery" on its own is called a cell.
Two or more cells which are joined together are called a battery.
The cells of a battery are joined together in series.
The positive side of one cell is joined to the negative side of the next cell.
The word "battery" is used to mean "collection".
A collection of cells is called a battery of cells.
