| Admissions | Accreditation | Booksellers | Catalog | Colleges | Contact Us | Continents/States/Districts | Contracts | Examinations | Forms | Grants | Hostels | Instructors | Lecture | Librarians | Membership | Professional Examinations | Recommendations | Research Grants | Researchers | Students login | Schools | Search | Study Center/Centre | Universities | Volunteer |
State department of water.
| For whom are these training programs meant in the state or outside the state around the world? |
| Drinking Water Treatment & Distribution System Operators |
| Hydraulic Engineer |
| Plumber |
| Mechanical engineers |
| Chemical engineers |
| Plumbers/Pipe Layers |
| Administrative Positions |
| Chief Engineer |
| Aditional Secretary |
| Assistant Director (Plg) |
| Commissioner Secretary |
| Dy. Secretary ( HRM Cell) |
| FA/CAO |
| Joint Director (Plg) |
| Under Secretary (G) |
| Under Secretary (NG) |
Drinking Water Treatment & Distribution System Operators
|
Public Water System Self-Assessment Has your system had a violation of the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) requirements in the last year? Yes____ No____ Not Sure____ Is the person in charge clearly defined? Yes____ No____ Not Sure____ Are your water system documents and records stored in an organized manner? Yes____ No____ Not Sure____ What is a Water Treatment Plant Operator? The Water Plant Operator controls and maintains treatment plant equipment to clarify and disinfect water for human consumption. Performs laboratory tests for operational strategy and adjusts chemical feed rate settings to ensure compliance with ______ Primary/Secondary Drinking Water Standards. What does a Water Treatment Plant Operator do? Operates and controls electric motors, pumps, and valves to regulate flow of water source into treatment plant and monitors all operational gauges to ensure proper plant operation. Tests water samples to determine pH, iron, manganese, free chlorine, and turbidity, using pH meter, colorimeter, and turbidimeter. Records data, such as water flow meters, chlorine feed rate settings, turbidity, and other lab tests. Injects specified amounts of chemicals, such as chlorine and potassium permanganate into water and makes necessary feed rate adjustments as water quality changes. Starts agitators to mix potassium permanganate and replenishes solution barrels when necessary. Pumps clarified and disinfected water into water storage tanks and distribution mains. Monitors panel board and adjusts controls to regulate flow rates and water storage tank levels. Backwashes filters when head loss is 6 10 psi differential or at a minimum every 96-hours. Repairs and lubricates machines and equipment using hand and power tools. Operates portable water-purification plant to supply drinking water during emergency contingencies. Performs related work as assigned. What is the workplace of a Water Treatment Plant Operator like? Here are further guidelines. | |||
| Drinking water Emergencies | |||
| Food and Waterborne disease | |||
|
Public Drinking Water Systems
How many total residents of the state are there up to today? How many residents of the state have tap water supply within their building or house? How many residents of the state do not have tap water supply within the building or house? What is the location of those who do not have tap water supply within the building or house? Was any water-related illness reported from any location in the state from past 10 years? What are the dimensions of the state? Does the state have population more than 10 million? What are the most common reported complaints of tap water in the last 10 years in the state? What is the location of these complaints? What are recommendations to improve tap water supply in the state? What are the locations of water filtration and purification plants in the state? How many workers have duty at these locations? What are the essential daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly work activities at the plant? What are the locations of tap water pipe manufacturing plants in the state? How many workers have duty at these locations? What are the essential daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly work activities at the plant? What materials are utilized for tap water pipe manufacturing in the state? | |||
| |||
|
Q: What resources, products, and services are required for uninterrupted safe tap water supply? 1. Original sources like river water, lake water, or sea water are identified. 2. State planning and development is taken into consideration. 3. A water supply scheme is designed. 4. Vehicles for excavation and for other services. 5. Materials for construction of filtration plant and equipment to establish filtration plant. 6. Various purification methods like bleaching powder and chlorination. 7. Laboratory equipment to test water for safe human consumption. 8. Water tanks, pipes, and plumbing supplies are required. Q: Can any city or municipality or service manufacture or provide all products and services required to establish uninterrupted safe tap water supply even if river or lake is located in a city? A: No, they cannot. For all practical purposes, workers get products and service involved in this work from other areas of the state. In some regions, city municipality workers do operations and distribution of water. For all practical purposes, they are state workers. Q: Do products and services for water filtration, water tanks, vehicles, pipes, plumbing, maintenance, electricity, clothes, building materials, or food items for workers get produced from within the city area? A: No, they don't. Q: What workers, services, and vendors are required for tap water supply? A: Mechanical engineers, plumbers, and fitters; water tank, pipe, and plumbing product manufacturers; vehicle manufacturers and operators; bleaching powder manufacturers' filtration plant equipment and material manufacturers; and guides for workers. Are there any other workers that need to be included? | |||
| Mechanical engineers | |||
| Chemical engineers | |||
| Plumber and fitter training | |||
| Pipes | |||
|
Tube well water
Q: Can a tube well or any well be utilized for a regular pure tap water supply from ground water everyday? A: Experience has proven that a tube well can supplement other water resources, but it is not sufficient for a regular tap water supply. Tube well water can be utilized for occasional drinking water, bathing, and irrigation. People will face hardship if they try to utilize tube well water for everyday. | |||
Water Filtration Plant | |||
| Water Chemistry | |||
| Water Conservation | |||
| Water Saving Products | |||
| Preventive Health Measures | |||
Water Pressure
| |||
| Maintenance Exercise | |||
| Bottled water-Project Report | |||
|
Water source What is a source water assessment? Where does drinking water come from? What are the threats to source water? How much assessment work has been done? Is more assessment work needed? Does my state have a source water assessment program? Is source water protection required? What is a Public Water System? What are the different types of public water systems? Where do public water systems get the drinking water? What is a source water assessment area for surface water? What is a source water assessment area for ground water? What does a Potential Contaminant Source Inventory consist of? Here are important guidelines. | |||
Oceans, Seas, & Bays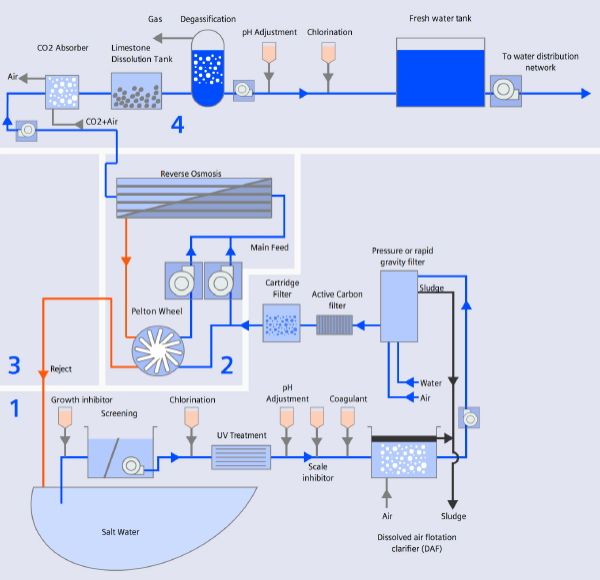
| |||
| Rivers | |||
Lakes
Saline | |||
Ground water
Saline | |||
|
How many total districts/counties are there? How many Water Filtration Plant/Water Treatment Plants are there? Why we need to build another Water Filtration Plant/Water Treatment Plants? What's the best way to build another Water Filtration Plant/Water Treatment Plants? (A-1) = Name of the Water Filtration Plant/Water Treatment Plant. What are the demographics of the PHE's/city's (A-1) service area? What are the water sources for the (A-1) Water Treatment Plant? How are Water Systems Monitored? How are Treatment Techniques used to monitor drinking water? What was the capacity of the old (A-1) Water Treatment Plant? What is the capacity of the new (A-1) Water Treatment Plant? Is the project on budget? Impacts on Community Large-scale construction projects will always have activities that will impact the surrounding neighborhood. (For Example: Road detour etc.) | |||
|
What specific water purification methods are there? How do specific water purification methods work? | |||
Maintenance Exercise
Who is responsible for the repair and the maintenance? Who should be contacted? What is their contact information? What are the procedures involved? | |||
|
Water Quality Control
Public Health Engineering/water works/etc, through technical monitoring, surveillance, and enforcement action, is responsible for assuring that quality of drinking water, as distributed by public supply or obtained commercially as bottled water, is in full compliance with Federal, State, and local standards. This task is accomplished by surveillance sampling and performance of water treatment facility inspections. | |||
|
The PHE also assures that the quality of waters used for recreational purposes, at pools and beaches, are constructed and operated in compliance which protect the public health and safety.
Technical Assistance Plumbing Swimming Pool Reviews Public Facility Reviews Institutional Reviews Grants Evaluations Highway Right of Way Approvals Coastal Management and Waterway Approvals | |||
Bottled water-Project Report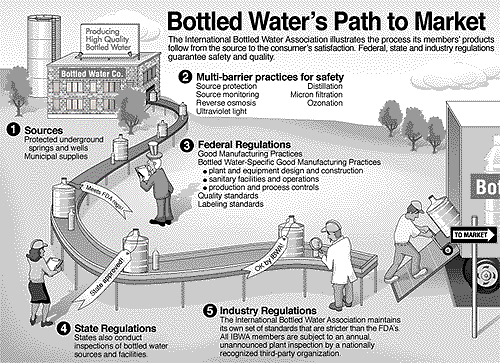
What is bottled water? What are the different types of bottled water? Is bottled water regulated differently from tap water? How long can I store bottled water? What is the difference between bottled water and tap water? |
|
Human Water Requirement Calculator Without perspiration, the normal daily turnover of water in adults is about 4% of body weight, which is 2.8 lit for a 70kg person. Body Weight Pounds 165.347 Kilograms 75 Exercise Time 0, 20, 40, 60 Number Of Minutes Of Daily Exercise Environmental Conditions
Normally Warm Environment Normally Cool Environment Extreme Cold - At, Near or Below Freezing (Surrounding Climate) 2550 (Mililiters Of Water) Approximate Glasses Of Water 10.778 |
|
|
How much water should you drink every day? Nobody knows for sure and different people have different views. Experts say that you should drink at least eight glasses of water every day; a glass of water is about 8 ounces or about .236 milliliters. How much water should you drink each day? People more than 18 years of age should drink at least 1.5 to 2 liters of water daily. Water consumption for children How much drinking water do children need every 24 hours? How much formula? For the first 6 months your baby should be taking 150-200 mls of formula per 1 kg (or 70-90 mls per lb). For example, a baby weighing 5 kg should take 750-1000 mls in 24 hours (150/200 mls multiplied by 5). It is normal for some babies to take slightly more than this, some a little less. Commonly, babies have 6-7 feeds every 24 hours - researchers/pediatrician recommend you feed your baby whenever she/he is hungry. About 20 minutes is the right length of time for a feed but some babies are slow feeders and others fast. A slow feed could last up to one hour and a fast feed may be finished in 10 minutes. The flow of milk from the teat and wind are two factors that may affect your baby's feeding. Formula will provide a healthy baby with all the fluid needed in the first 6 months of life. It's only when your baby is unwell or very thirsty e.g. during hot weather, that additional drinks are needed. For a thirsty baby, cooled, boiled tap water is the best drink to offer. An unwell baby with diarrhoea needs to be given an oral reyhdration solution. What nutrients are in infant formulas? Baby formulas contain energy-providing nutrients (protein, carbohydrate and fat) as well as water (an essential nutrient) and appropriate vitamins and minerals. The energy nutrients provide the calories necessary to maintain bodily functions, support activity, and promote growth. They also support desirable immune functions as an outcome of overall nutrition. Protein provides the building blocks necessary to form and repair tissue. Vitamins and minerals are essential in the metabolism of energy nutrients. Minerals play an important part in bone structure, regulate certain body functions and, together with water, help maintain the body's water balance. Standard iron-fortified baby formulas are nutritionally complete foods for normal infants. When a physician recommends a formula not fortified with iron, another source of iron should also be recommended. A physician may recommend fluoride supplementation to infants at least 6 months of age only if the water supply is severely depleted of fluoride. Here are further guidelines. How can you tell if children are dehydrated? If your child has fever, diarrhea, or vomiting, or is sweating a lot on a hot day or during intense physical activity, watch for signs of dehydration, which can include: * Irritability (more crying, fussiness with inconsolability) * No tears when the child cries * Dry or sticky mucous membranes (the lining of the mouth or tongue) * Lethargy (less than normal activity) * Lack of urine or wet diapers for 6 to 8 hours in an infant (or only a very small amount of dark yellow urine) * Lack of urine for 12 hours in an older child (or only a very small amount of dark yellow urine) * Fatigue or dizziness in an older child * Sunken eyes * Sunken soft spot on the front of the head in babies (called the fontanel) Here are further guidelines. |
| Bath | A full tub is about 36 gallons. |
| Shower | 2 gallons per minute. Old shower heads use as much as 5 gallons per minute. |
| Teeth brushing | <1 gallon, especially if water is turned off while brushing. Newer bath faucets use about 1 gallon per minute, whereas older models use over 2 gallons. |
| Hands/face washing | 1 gallon |
| Face/leg shaving | 1 gallon |
| Dishwasher | 4 to 10 gallons/load, depending of efficiency of dishwasher |
| Dishwashing by hand: | 20 gallons. Newer kitchen faucets use about 2.2 gallons per minutes, whereas older faucets use more. |
| Clothes washer | 25 gallons/load for newer washers. Older models use about 40 gallons per load. |
| Toilet flush | 3 gallons. Most all new toilets use 1.6 gallons per flush, but many older toilets used about 4 gallons. |
| Glasses of water drunk | 8 oz. per glass (did you remember to drink your 8 glasses of water today?) |
| Outdoor watering | 5 to 10 gallons per minute |
| Irrigation water requirements |
Plumber
|
What is a Plumber? According to one dictionary, a plumber is someone that fits and repairs water pipes. When you find out what a plumber does, it is much more complex than that. They also install and repair water systems as well as waste disposal and drainage for a home. Plumbers also install plumbing fixtures, sinks, bathtubs and toilets. You may also call in a plumber to install that new dishwasher. When all of a sudden you are taking a cold shower, it may be time to call in a plumber to install a new water heater. When that toilet wont unclog, find a plumber. 
Plumbing Tools Pliers (tongue and groove) Basin Wrench Compression Sleeve Puller Pipe Wrench Adjustable wrench Screw Drivers Allen Wrench Set Hacksaw Plumber's Putty Plumbers need many tools to get the plumbing work done right. A plumber that shows up at your door will usually have a truck stocked with tools and equipment for anything they might run into. A successful plumber knows that having the right tools can speed up the time it takes to finish a job. Most homeowners would not imagine the amount of money a plumber invests in tools and equipment. Using saws, pipe bending machines, pipe cutters and video camera inspection are just a few of the tools a plumber may need on a service call. We take for granted when everything is working right, but when the basement is flooded and you need a sump pump installed, what are you going to do? Find a plumber. You may have a slab leak or a hidden water leak behind a wall. A good plumber is like any other trade. Once you find a plumber you trust, you have the peace of mind knowing that your homes plumbing is in good hands in the case of an emergency. Do you need to findaplumber? RESPONSIBILITIES (Major responsibilities and target accomplishments expected of the position including the typical problems encountered in carrying out the responsibilities.) 1. Install, repair and maintain plumbing systems and components Main Activities Review building plans and specifications to determine the layout for plumbing and related materials Identify required tools and special equipment Select the type and size of pipe required Locate and mark positions for connections and fixtures Install supports and hangers for pipe, fixtures and equipment Assemble and install valves and fittings Install, repair and maintain water treatment equipment, piping and controls Install, repair and maintain underground storm sanitary and water piping systems Install, repair and maintain sinks, tubs and toilets Install, repair and maintain water heaters and conditioners Install, repair and maintain plumbing fixtures, appliances and trim Test pipe systems and fixtures for leaks 2. Maintain all building codes, installation requirements and relevant legislation Main Activities Perform scheduled maintenance service on plumbing systems and fixtures Apply all codes to installations, repairs and maintenance Ensure all requirements as specified by the manufacturer of systems and fixtures are met Ensure all installations, repairs and maintenance are properly sized, aligned, supported and graded Ensure all installations, repairs and maintenance meet the requirements of the appropriate codes Ensure all installations, repairs and maintenance meet environmental protection requirements 3. Administer and schedule work Main Activities Prepare orders of supplies Keep daily reports Schedule work in cooperation with other trades and suppliers 4. Perform other related duties as required Some needed skills, interests, and values Reading drawings, and specifications to determine layout of water supply, waste, and venting systems Detecting faults in plumbing appliances and systems, and correctly _______ their causes Installing, repairing and maintaining ________ plumbing fixtures and systems Locating and marking positions for pipe connections, passage holes, and fixtures in walls and floors Measuring, cutting, bending, and threading pipes using hand and power tools or machines Joining pipes and fittings together using soldering techniques, compression fittings, threaded fittings, and push-on fittings. Testing pipes for leaks using air and water pressure gauges Awareness of legal regulations and safety issues Ensuring safety standards and build regulations are met. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. |
