| Admissions | Contact Us | Examinations | Grants | Instructors | Lecture | Membership | Students login | Schools | Colleges | Universities | Professional Examinations | Recommendations | Research Grants | Search | Librarians | Forms | Booksellers | Continents/States/Districts | Contracts | Volunteer |
|
What is Astronomy? What does an Astronomer do? What is Astronomy? Astronomy is the study of the universe, namely the objects we observe, like the Moon, Sun, and planets in our Solar System; stars; our Milky Way Galaxy, and other galaxies; and, a host of other celestial objects and phenomena, like nebulae, and black holes! What does an Astronomer do? Astronomers make observations, perform experiments, and collect data. Astronomers use physics and other sciences to interpret the data they collect. Astronomers are interested in the evolution of our universe and how it was created. They want to understand the objects in our Solar System and elsewhere in the cosmos, and how these objects and phenomena will change over time. Astronomers use many tools to observe and interpret celestial objects and phenomena. These tools include: ?Telescopes, to collect light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation, and resolve images. ?Electronic detectors like CCDs (charge-coupled devices) to catch photons and produce images. ?Spectroscopic methods to observe and analyze the emission and absorption spectra from light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation. ?Photometry to measure the changes in the brightness of stars over time. ?Computers and specialized software to perform calculations and data analysis. Astronomy is broken down into a number of subfields, allowing scientists to specialize in particular objects and phenomena. Cosmology is the study of the origins and eventual fate of the universe. Religious cosmology (or mythological cosmology) is a body of beliefs based on the historical, mythological, religious, and esoteric literature and traditions of creation and eschatology. Galactic astronomers study our galaxy, the Milky Way, while extragalactic astronomers peer outside of it to determine how these collections of stars form, change, and die. Planetary astronomers, for instance, focus on the growth, evolution, and death of planets, while solar astronomers spend their time analyzing a single star—our sun. Stellar astronomers turn their eyes to the stars, including the black holes, nebulae, white dwarfs, and supernova that survive stellar deaths. Astrometry, the most ancient branch of astronomy, is the measure of the sun, moon, and planets. The precise calculations of these motions allows astronomers in other fields to model the birth and evolution of planets and stars, and to predict events such as eclipses, meteor showers, and the appearance of comets. Is there a web server in Kashmir? What is the location? 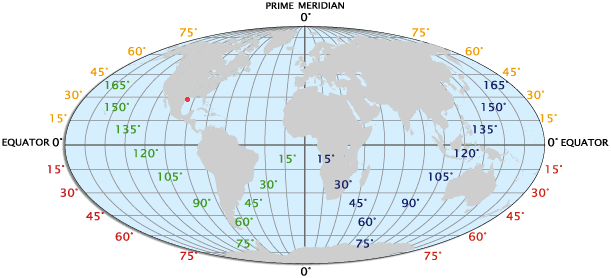 Earth Science: Astronomy
Earth Science: Astronomy
Purpose: To explain the seasons of the year and the phases of the moon. Students often have many misconceptions about Earth's motion in space, the phases of the moon, and the causes of seasonal changes. 1. What causes night and day? 2. What causes the seasons? 3. Why are the seasons in the Southern Hemisphere opposite to those in the Northern Hemisphere? 4. Why are the days longer in the summer than in winter? 5. What causes the apparent changes in the sun’s position during the year? 6. Why does the moon go through phases? 7. Why does the moon rise a little later each day? 8. What causes the tides? 9. What causes lunar eclipses? 10. What causes solar eclipses? 11. What causes the difference between a sidereal day and a solar day? 12. What causes the difference between the sidereal period and the synodic period? 13. What is space? 14. Where does space begin? 15. How big is the universe? 16. Will the universe ever end? 17. Why does the moon shine? 18. How many stars can you see at night? 19. Why do some stars twinkle? 20. What would happen to the planets if the Sun suddenly wasn't there? 21. What is the moon's mass and density? Also how was it named, and what's it's gravity? 22. Is it possible for the new planet that we discovered, outside of Pluto's orbit, to be part of a space ripple sending a new galaxy to collide with ours? 23. How did the universe begin? 24. What color is each planet? 25. Is the Moon moving away from the Earth? 26. How far is each planet from Earth? 27. How do you measure the distance between Earth and the Sun? 28. How many stars are there in our Galaxy (Milky Way)? 29. What is the largest star? 30. Do all objects in the universe exert force on all other objects? 31. Do the orbits of any of our planets change, or do the planets always follow the same paths? 32. Are the planets in our solar system likely to be destroyed when the sun finally burns out, and will they be destroyed by a nuclear explosion or just drift off without the sun's gravitational pull? |
|
Discussion Questions
What are longitude and latitude? What is latitude and longitude used for? 1.The measure of how far north or south a place is from the equator is Latitude Longitude Prime Meridian 2. The measure of how far east or west of the Prime Meridian a place is located is Latitude Longitude Equator 3.The latitude line at 0 degrees latitude is The equator The Prime Meridian The Tropic of Cancer 4. The line at 0 degrees longitude is The equator The Prime Meridian The Tropic of Capricorn 5. How far a location is from the equator effects The time zone the place is in The climate of the area When it is day and when it is night 6. The longitude of a place or how far it is from the Prime Meridian effects The time zone a place is in How much rainfall a place receives The climate of the area 7. The closer to the equator a place is The colder it is The hotter it is 8. Latitude and longitude are measured in Degrees Pounds Acres |
