Geographic coordinate system
| Latitude and Longitude Quiz |
| Plotting Coordinates: |
| Measurement |
| Latitude and Longitude |
| Converting Addresses to/from Latitude/Longitude/Altitude in One Step |
|
What are geographic coordinate systems? A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on the Earth to be specified by a set of numbers or letters, or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents vertical position, and two or three of the numbers represent horizontal position. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. A point is referenced by its longitude and latitude values. One of the most common coordinate systems in use is the Geographic Coordinate System, which uses degrees of latitude and longitude to describe a location on the earth’s surface. Lines of latitude run parallel to the equator and divide the earth into 180 equal portions from north to south (or south to north). The reference latitude is the equator and each hemisphere is divided into ninety equal portions, each representing one degree of latitude. 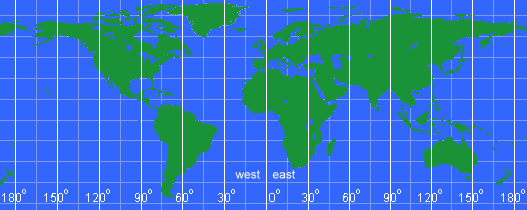 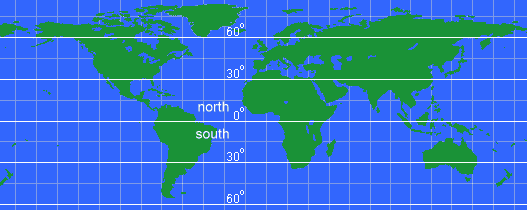  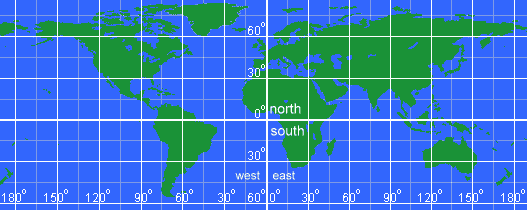
|
|
List of largest power stations in the world Latitude and Longitude Coordinates |
|
Latitude and Longitude Coordinates
Take a look at this map:  Obviously, that is a map of the earth. You can find the continents and can probably make a good try at pointing to where you live. But, how could you tell someone else where you live so they could quickly find it on their own map? That is where a coordinate system helps. What is the Equator? The equator is an imaginary line that divides the Earth into the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere. Its length is about 24,901.5 miles (40,075 kilometers). The geographical areas surrounding it are known as the equatorial regions, and they have a particular type of climate. Latitude and Longitude The location of any point on the Earth can be defined by its latitude and longitude, given in degrees (°). Lines of longitude all run from pole to pole, and they are all roughly the same length but are not parallel, as they converge towards the poles. Lines of latitude run at right angles to the longitude lines and are parallel, but they diminish in length towards the poles. The equator is at 0° latitude and is the longest such line, representing the circumference of the Earth. When a latitude for a location not on the equator is given, it is necessary to specify whether it is north or south of this line. Day Length and Seasons Due to the fact that the Earth wobbles slightly on its axis through the year, the higher latitudes experience summer and winter seasons, as well as variations in day length. At the equator, however, the effects of this wobbling are minimal. As a result, the region experiences 12 hours of daylight throughout the year and does not have clearly defined seasons, at least in terms of temperature. Average daily maximum temperatures are typically about 80 to 90°F (27 - 32°C), but this is affected by altitude, with higher areas being cooler. Annual rainfall generally varies from about 98 inches (249 cm) to about 138 inches (350 cm). There is normally not a great deal of variation in temperature through the year, but rainfall often has a seasonal aspect, as it is affected by ocean currents and factors beyond the region. The rainy and dry seasons vary from place to place, with some areas experiencing high to very high rainfall all year round, and others having distinct relatively dry periods. The high temperatures and abundant moisture found in most equatorial areas have led to the growth of rainforests with a great diversity of plant and animal life. Drawing those latitude lines onto a map would look like this:  Drawing those longitude lines onto a map would look like this:  For example, Seattle, Washington, North America is at latitude 47.6° North and longitude 122.33° West. From the center of the earth, look up 46.6° from the equator and turn right (west) 122.33° from the Prime Meridiean and you will be looking right at Seattle. Latitude and Longitude Grid Combining latitude and longitude results in a grid that covers the globe. Every point can be defined by a north/south degree and an east/west degree. And, the complete grid on a map looks like: 
|
Latitude and Longitude Quiz
Plotting Coordinates:
|
Latitude and Longitude Quiz What are latitude and longitude lines? A: imaginary lines that divide the Earth B: visible lines that divide the Earth C: long and short lines that divide the Earth A: imaginary lines that divide the Earth What are latitude and longitude lines also called? A: latitudinal lines B: meridian lines C: long lines of latitude B: meridian lines True or False? The equator is the main line of longitude. A: True B: False Explanation: The equator is the main line of latitude. This is the main line of longitude. A: equator B: northern hemisphere C: prime meridian C: prime meridian _______________ lines run from east to west. They measure distances north and south of the equator. A: Longitude B: Latitude C: Primary B: Latitude Which line cuts the world into north and south latitude? A: equator B: prime meridian C: longitude A: equator This marks the location of the equator on Earth. A: 90 degrees B: 20 degrees C: 10 degrees D: 0 degrees D: 0 degrees Longitude lines run from __________ to ___________, pole to pole. A: east, west B: north, south C: east, south D: west, north B: north, south True or False? The prime meridian cuts the world into west and east longitudes. A: True B: False A: True The intersection of the Earth's latitude and longitude lines form a _________. A: grid B: map C: hemisphere A: grid Explanation: All of the lines have degree markings. If you know the degrees of latitude and longitude of a certain place, you can easily find it on a map. |
|
Directions: For questions 16- 20, use a Red marker to plot the points of these given coordinates using the provided map.
Each question is worth 1 point. 16. 40 degrees S, 40 degrees E 17. 80 degrees N, 60 degrees W 18. 20 degrees S, 100 degrees W 19. 10 degrees N, 20 degrees E 20. 40 degrees N, 100 degrees W |
