|
|
| Fuselage |
The fuselage holds the structure together and accommodate
passengers and/or cargo. Modern aircraft fuselage may accommodate up to
800 passengers in economy class (e.g. A380) and up to 112,700kg cargo
(e.g. B747-400ER). (Image: fuselage of a Boeing 737, blinking —embedded from Wikipedia on 23 March 2010) |
 |
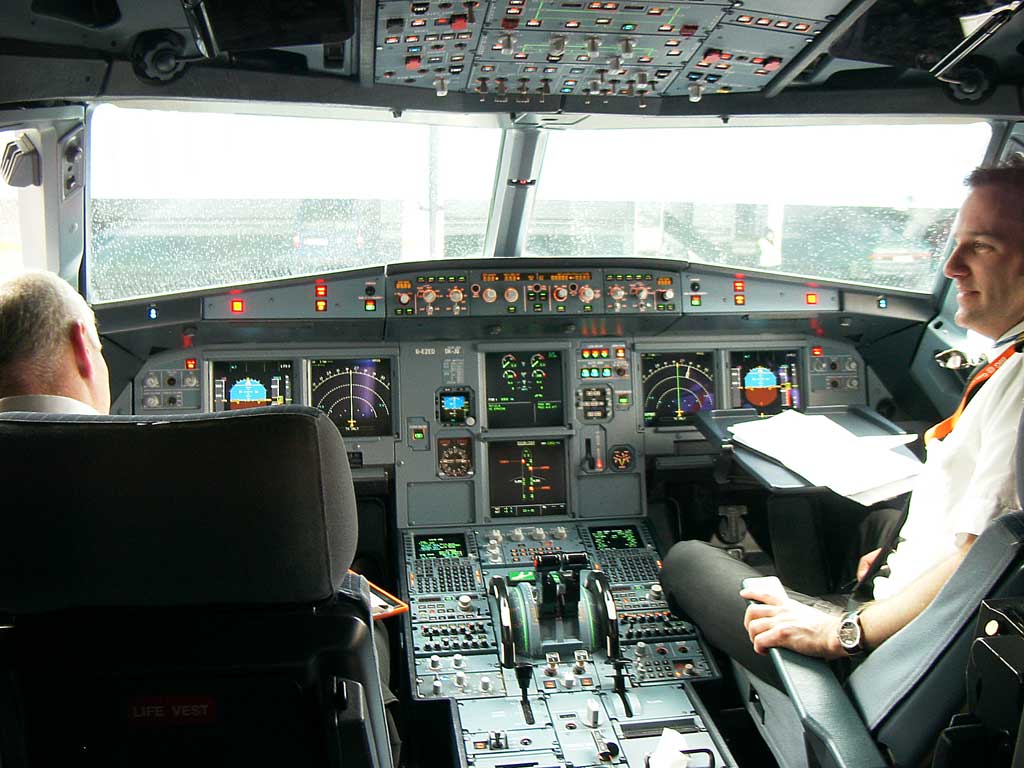
| Cockpit |
The cockpit holds the command and control section of an airplane.
Modern aircraft cockpits have a number of vital instruments for
controlling the airplane on the ground as well as when flying. (Image: cockpit of Airbus 319 —embedded from Wikipedia on 23 March 2010) |
 |
| Powerplant and undercarriage |
| Powerplant (engines) |
Engines generate thrust and provide hydraulic and electric power.
Modern aircraft are employed with different types of engines, although
jet engines are favoured with by most commercial airliners. (Image: JAL Cargo Boeing 747-400 with its four engines —embedded from Wikipedia on 23 March 2010) |
 |
| Undercarriage (landing gear) |
The undercarriage, also known as landing gear, provides a platform
for the aircraft to stand as well as plays an important obvious role in
landing and take-off. (Image: undercarriage —embedded from Wikipedia on 23 March 2010) |
 |
| Wings |
| Wing |
Wings generate lift and control the airflow while flying. Wing
design is a crucial factor in aviation: a wing is designed to reduce
drag at the leading edge, generate lift by its crescent and manage
airflow using the rear edge. Furthermore, while gliding (i.e. without
engine power), the wings allow the pilot to increase and decrease the
descent rate. (Image: left wing of an Airbus 319 —embedded from Wikipedia on 23 March 2010) |
 |
| Slat |
Slats adjust the angle of attack of the wings, increasing lift.
Slats are fitted at the leading edges of the wings, and deploying them
increases the angle of attack of the wings, allowing the pilot to
increase the lift generated by the wing. (Image: slats extended —embedded from Wikipedia on 23 March 2010) |
 |
| Flap |
Flaps adjust the camber of the wings, increasing lift. Flaps are
normally fitted at the trailing edge of the wings. Extending the flaps
increase the camber of the wings airfoil, thus increasing lift at lower
speeds, an important feature for landing. (Image: flaps fully extended —embedded from Wikipedia on 23 March 2010) |
 |
| Spoiler |
Spoilers adjust the camber of sections of the wings, decreasing
lift. Spoilers are fitted on top of the wings, and are used to reduce
lift on a section of the wing in a controlled manner. Spoilers are
useful for decreasing lift without increasing the airspeed of the
airplane or without increasing drag significantly. (Image: spoilers deployed after touchdown —embedded from Wikipedia on 23 March 2010) |
 |
| Aileron |
Ailerons increase or decrease lift asymmetrically, in order to
change roll and, thus, move the aircraft left or right while flying.
Ailerons are hinged sections fitted at the rear of each wing. Ailerons
work asymmetrically as a pair: as the right aileron goes up, the left
one comes down and viceversa, thus making the aircraft roll right or
left, respectively. (Image: ailerons in action to control the airplane's rolling motion —embedded from NASA on 23 March 2010) |
 |
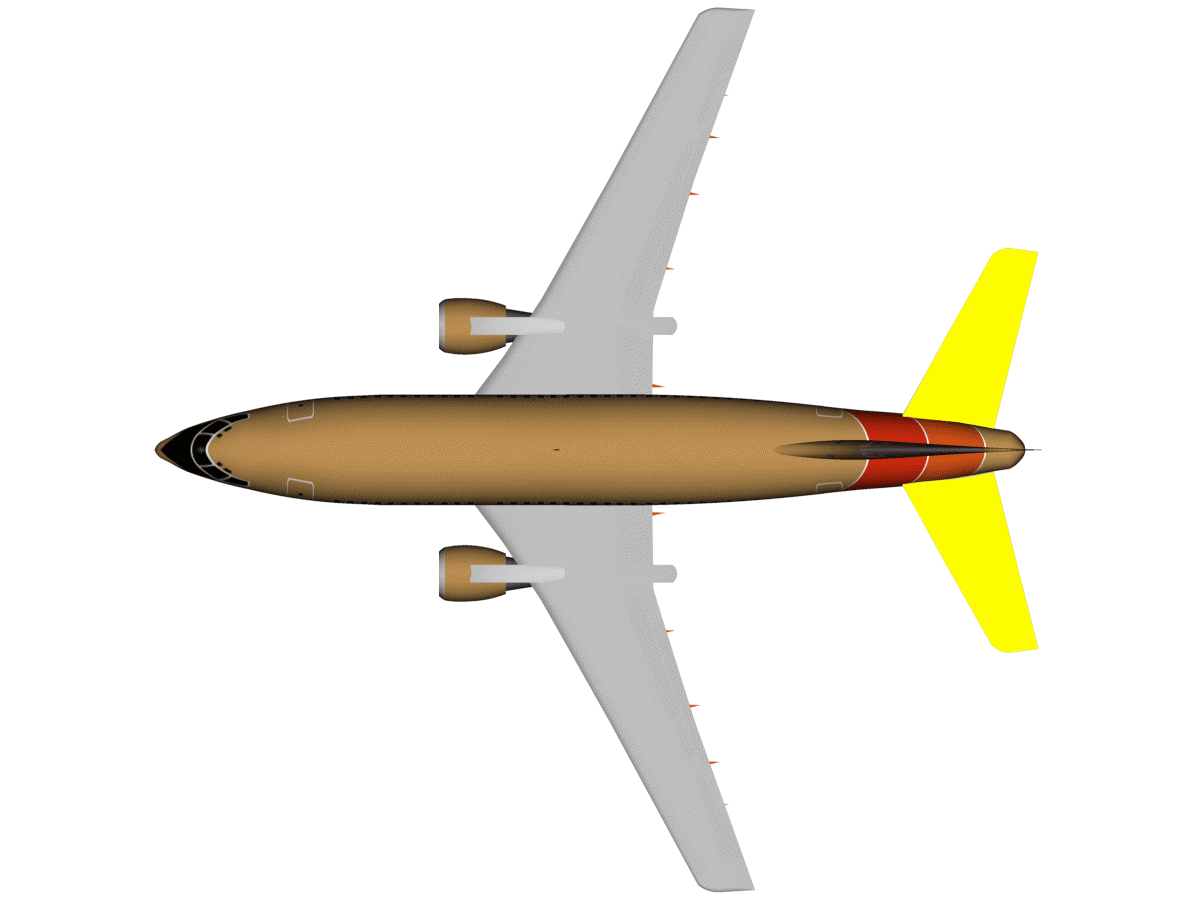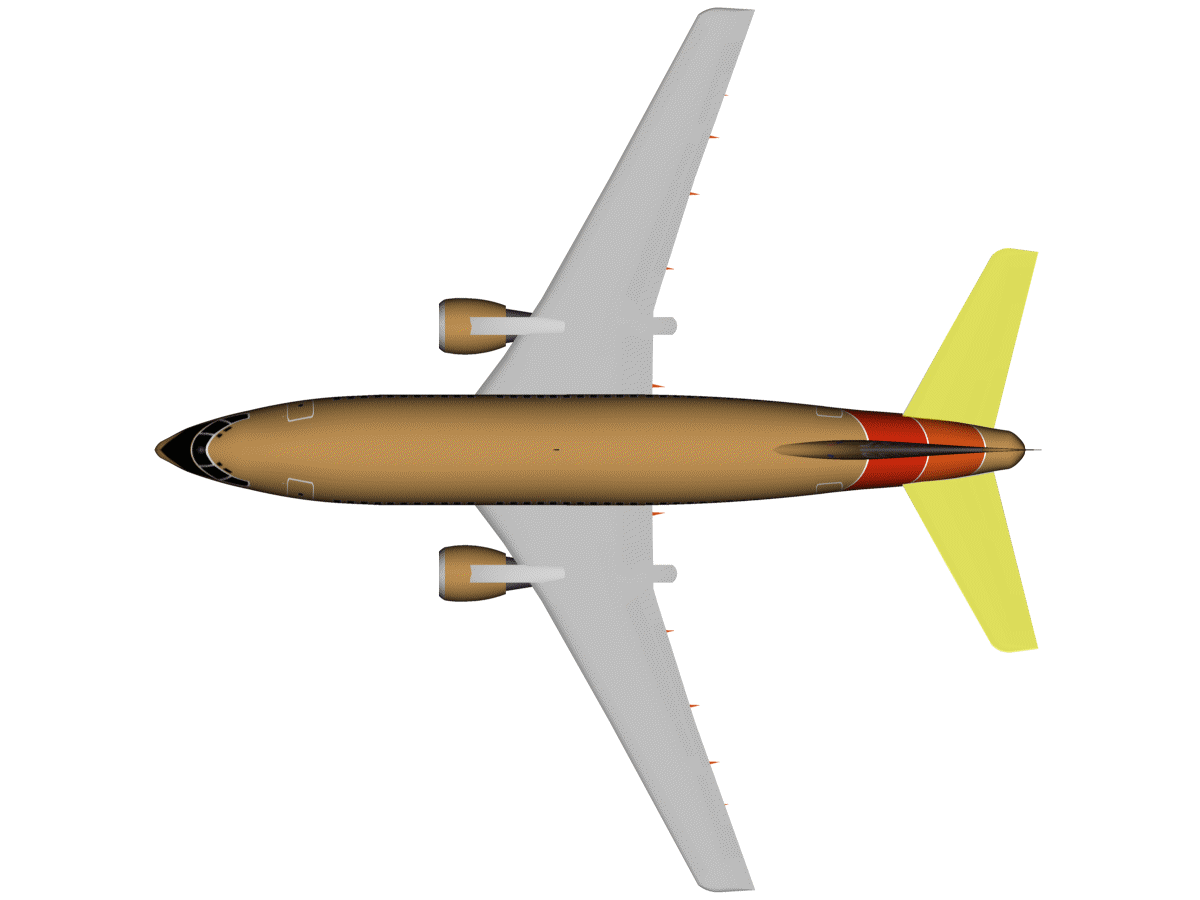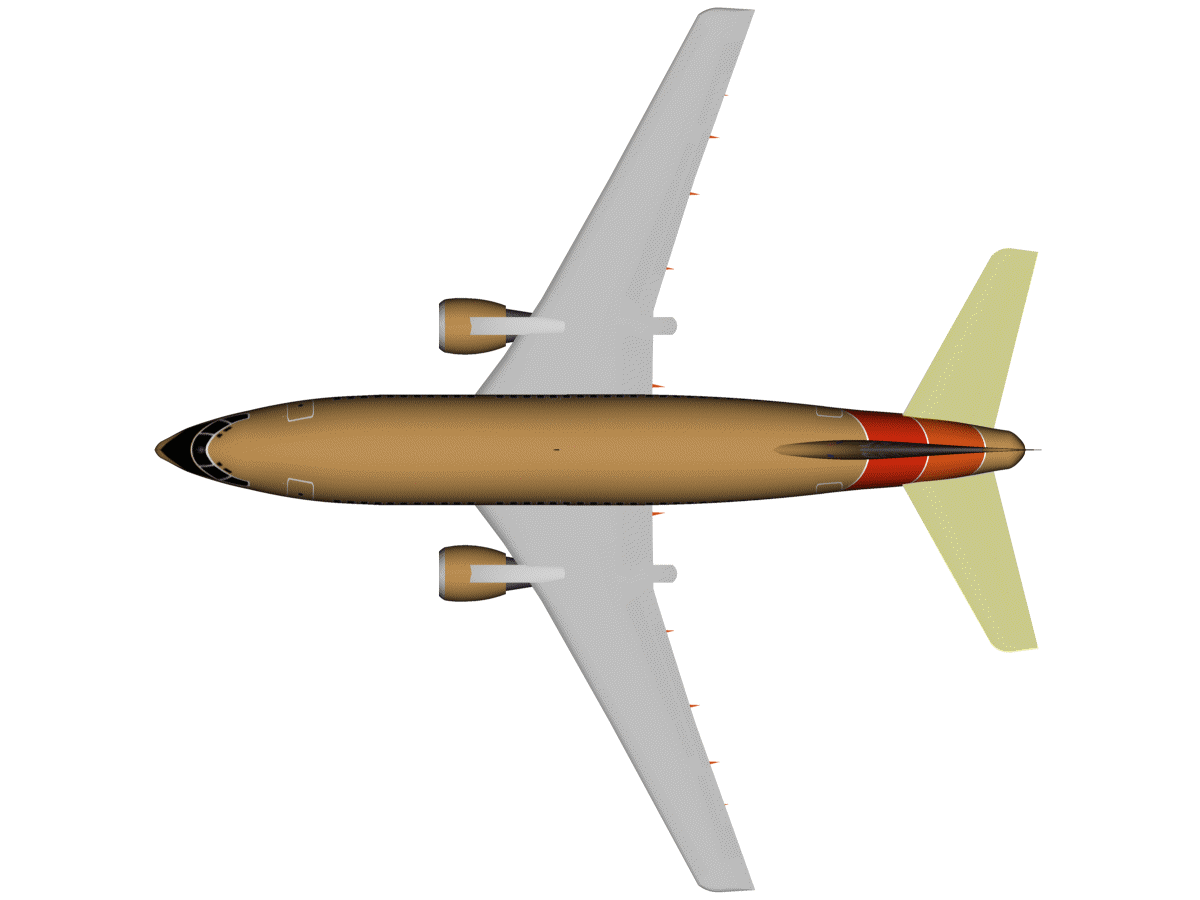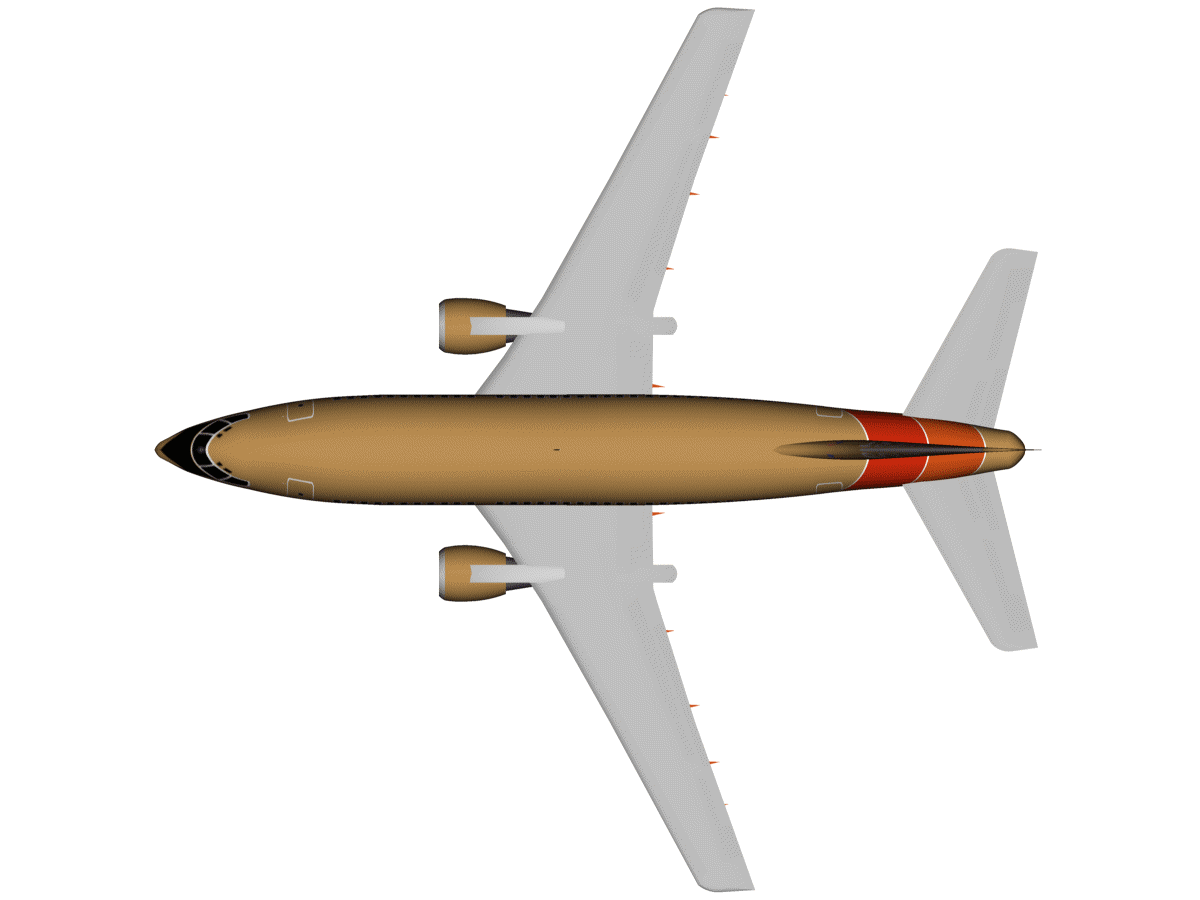
| Tail |
| Horizontal stabiliser |
The horizontal stabiliser helps maintain an airplane's equilibrium
and stability in flight. It does so by providing a mini wing at a
certain distance from the main wings (typically at the back, although
it can also be positioned at the from of the aircraft). This smaller
wing produces enough lift to control the pitch of the aircraft and
maintain its stability. Although an aircraft without a horizontal
stabiliser could, in principle, fly with wings only, controlling its
pitch and airspeed would be difficult, as pitch and, subsequently,
airspeed can be easily disturbed by air conditions: as soon as the
aircraft pitches up, the tendency is to continue pitching up even
further and decrease airspeed; and as soon as the aircraft pitches
down, the tendency then is to continue pitching down even further and
increase airspeed. An aircraft with a horizontal stabiliser, however,
could be flown hand-offs (once correctly trimmed) without affecting its
pitch and speed. (Image: the horizontal stabiliser, blinking —embedded from Wikipedia on 25 March 2010) |
 |
| Elevator |
Elevators increase or decrease lift on the horizontal stabiliser
symmetrically in order to control the pitch motion of an airplane.
Elevators are hinged surfaces fitted at the rear of the horizontal
stabiliser. They work symmetrically as a pair: when the elevators are
up, the aircraft ascends; when the elevators are down, the aircraft
descends, and when the elevators are horizontal, the aircraft flies
straight. (Image: elevators in action to control the airplane's pitching motion —embedded from NASA on 25 March 2010) |
 |
| Vertical stabiliser |
The vertical stabiliser prevents lateral movements of the airplane.
Without a vertical stabiliser, most aircraft would lose lateral
control, tend to slip, increase drag and become uncontrollable. (Image: the vertical stabiliser, blinking —embedded from Wikipedia on 25 March 2010) |
 |
| Rudder |
The rudder controls the yaw motion of an airplane. The rudder is a
hinged surface fitted to the vertical stabiliser. When the rudder is
turned to the left, the aircraft turns to the left in the horizontal
plane; when the rudder is turned to the right, the aircraft turns to
the right. The rudder is used to turn the aircraft left or right on the
ground. In the air, however, the rudder is primarily used to coordinate
left and right turns (the turns themselves are done with the ailerons)
or to counter adverse yaw (e.g. when crosswinds pushes the airplane
sideways).
|









