Pilots
Flying an airplane is fun. Getting paid to do it is even better. For some people, it's the perfect job: an office that travels, a view that's constantly changing and challenges that are exhilarating. It has been said that a pilot's job is hours of boredom punctuated with seconds of sheer terror. This is perhaps hyperbole, but sometimes not all that far from the truth.
A person who takes a multimillion dollar machine, casually flies it off the ground and then safely returns it, fascinates people. They wonder what it's like to be responsible for hundreds of lives or goods worth millions. When passengers peek inside a cockpit, they are amazed. They stare at the multitude of dials and ask incredulously, "Do you really know what they all do?"
Pilots are the focal point and end operator in a huge team of highly trained professionals. They are the movie stars of the air transportation show, because they are the most visible people to the public, while most of the other team members remain "behind the scenes." But movie stars rarely die or cause others to die because of an on-the-job mistake. All pilots run that risk. Piloting is a serious business.
Myths, Stereotypes and Reality
The longtime stereotype of airline pilots is that they are male, fearless, perfectly fit, good at math, trained in the military, blessed with perfect vision, all paid like super senior 747 captains (regardless of what they really fly) and only at work three days every other month.
In the 1950s, some of these notions were accurate.
To be a pilot for hire, you need a commercial pilot certificate. You earn your certificate by passing commercial pilot ground school and logging at least 250 flight hours, with allotted time dedicated to certain conditions and maneuvers. After you have logged your hours and passed your written ground school test, you will need to pass a check-ride. A check-ride is something like the driving test we take to get our driver's licenses. A Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) examiner asks you to plan a flight, quizzes you on aviation matters and then accompanies you on a flight. As in a driver's license test, the examiner requests that you execute certain maneuvers and directs your flying throughout the entire flight. If everything goes well, the examiner issues you a commercial pilot's certificate.
Additionally, a commercial pilot needs an up-to-date first- or second-class medical certificate, an instrument rating and a multi-engine rating. For you to receive a medical certificate, an Aviation Medical Examiner must verify that you meet the health and fitness requirements to be a pilot. You need to get an instrument rating to fly with low visibility (in adverse weather and in clouds). You receive an instrument rating by passing instrument ground school, logging a specified amount of instrument flight time (flying without visibility) and passing an instrument rating check-ride. To fly planes with multiple engines (most of the planes in commercial use), you need to have some lessons and pass a multi-engine check-ride. At some point, most airline pilots also get an airline transport pilot certificate. This highest pilot certificate allows you to be the pilot in command (the captain) of a large commercial aircraft. It requires that you pass a written test, have a first-class medical certificate, are a high school graduate and have logged 1,500 flight hours including 250 hours as the pilot in command.
Rest Assured
A pilot certificate lasts forever, but to exercise particular flight privileges (to fly particular planes and to fly in particular conditions), a pilot must have certain experience or endorsements. This means that if you haven't flown a type of airplane for a while, you can't just hop in and take it for a ride. You must have flown a certain number of hours within a certain period of time or had a designated instructor evaluate you and sign you off as qualified. It's a very regulated industry, so don't worry: The person in the pilot's seat must be qualified to be there.
To be hired, you need flight experience. Your level of experience is based on the number and complexity of aircraft you have flown, the quantity and complexity of the flying you did (jet or propeller, day or night, local or cross-country, flying with visibility or flying using only instruments, etc.) and which crew positions you've held. Briefly, in the late 1960s, some airlines hired people without certificates or flight time and trained them from the ground up. This was an abnormal practice, and it is unlikely to recur. These days, a major airline hiring a pilot with a freshly minted commercial pilot's certificate (only 250 flight hours) is virtually unheard of. Most successful pilot applicants at major airlines have thousands of flight hours. Secondary airlines (regional or commuter) may have lower requirements.
Timing is everything. You could be the world's most qualified pilot, but if there are no openings for pilots when you enter the job market, a good job will be very hard to find. It's that simple. Unfortunately, timing is something we have almost no control over. There are no guarantees in the airline business. You won't know how your career went until you retire and can look back at it. Boom-to-bust cycles in the economy are magnified in the aviation industry.
Education
While there is no college requirement to be a pilot, most airlines look for some college time and prefer an earned degree. College shows that you are trainable and that you can stick to a challenging curriculum and succeed -- qualities an airline would like to know that you have before it spends a lot of money to train you. There are two major career paths to being hired as an airline pilot: civilian or military. Each has its advantages and disadvantages.
In the civilian career path, you can attend a college that offers a two- or four-year degree (some universities even offer advanced degrees in aviation) along with flight training toward various pilot certificates. Several universities in the United States and Canada offer courses along with flight training so that you graduate with a bachelor's or associate's degree in aviation along with a commercial pilot certificate and multi-engine and instrument ratings. There are also technical schools that offer flight training toward a certificate, often in less time. In both types of programs, you often graduate with an instructor's rating, and you've built up some flight time teaching others.
An alternative to a professional school or college is to get your flight training piecemeal from a local flight school. It will take longer, and the level of instruction might not be as rich, but all commercial certificates are equal in the eyes of the FAA. The agency doesn't care where or how they were earned.
Civilian training costs a lot of money. Basic flying lessons start at about $80 an hour, and you'll need at least 250 hours before you have your commercial rating. It also costs a lot to rent large, complex airplanes for instruction. I like to think of the expense as an investment in a rewarding career that will pay dividends for years to come. Scholarships (full and partial) do exist, but most pilots will end up investing a lot of money in flight training.
In the military, you commit to many years of service after your one year of pilot training (10 years of commitment in the Air Force). You must also meet other requirements, such as college course work, good health and adequate physical ability. There are no guarantees that you'll pass the military flight training on the service's rigid time schedule, or that you'll get to fly a specific airplane. In exchange for these compromises, the military pays you to train, and you get the best training in the equipment that an airline pilot would fly (complex jets).
A military pilot lives a military life, follows orders, risks bodily harm and uses lethal weapons. These aren't things to take lightly, so if you are considering the military (and that is a wide field that includes the Coast Guard), then explore it thoroughly and see if the timing is right for you and your career needs. It is an excellent experience for many people. Some pilots even make the military their career.
After a pilot is certified, he or she will have to get more experience and flight hours before an airline will hire him or her. Because of the military's service commitment, a military pilot will probably get a lot of flying experience before he or she leaves to join an airline. A civilian pilot, or a military pilot who needs more flight hours, may work as a flight instructor, then perhaps move to a charter company. From there, he or she might move to a regional airline and then on to a major airline.
Training
Once hired, regardless of your background, the airline will train you based on its procedures and its FAA-approved training curriculum. Even though all airlines fly the same kinds of airplanes, each airline has slightly different methods and procedures. The goal of an airline is to train you to be qualified in your position and to be standard. Standardization is one of the pillars of a safe airline. The concept is that, within the airline, cockpit behavior and procedure will be the same in every flight, no matter which pilots are at the controls, to prevent confusion and misunderstanding.
The initial training at an airline takes about 10 weeks. Basic indoctrination lasts a week or so. Training on general subjects, which include regulations and company-specific procedures, takes another week. You will spend two weeks on aircraft systems specific to the equipment you'll operate. Pilots will usually specialize in one type of airplane, such as 727s or MD-80s, until they move to a seat on a different airplane. After systems, you'll pair off with a training partner and have two or more weeks of simulator training. In the simulator, you'll experience just about every emergency and anomaly imaginable. You'll focus particularly on crew coordination and successful landing. All maneuvers are practiced until they are satisfactorily completed.
Once the pre-checks, oral examinations and final check-rides are over, you will have completed the airplane training. But you're not ready just yet. Next you'll fly with a special instructor pilot and get initial operating experience. This experience, which includes at least 25 hours of flight time, will teach you to integrate your newfound technical skills with the daily requirements of the job.
After initial operating experience, you face another flight test, called a line check. After you pass the line check, you are released to operate scheduled flights as a crew member. Airlines are now required to set up 100 hours of flying for you after a line check, so you can get immediate experience. After all that,you'll want a vacation.
Pilot Positions
On an airliner, the captain is the pilot in the left seat. He or she flies the airplane, makes all the command decisions and is responsible for the flight's safety. The captain's job is a big responsibility. It calls for tough decisions and requires more than just the technical skill involved in flying the airplane. The captain is a team leader and must establish an effective crew atmosphere, with good communication and resource management. A captain must pass many written and practical tests and have his or her performance evaluated regularly. A pilot must have high seniority (time in service) to hold the position of captain and, as a general rule, captains are the most senior (and therefore most experienced) of the pilots at an airline. As we will see in the next section, seniority plays a major role in the career of an airline pilot.
The cornerstone of aviation safety is redundancy. So, in addition to two (or more) engines, radios, sets of flight instruments, etc., there are always at least two flying pilots. The first officer sits in the right seat and acts as a co-pilot. He or she has an independent set of controls and instruments to operate the aircraft and flies the plane about half the time, usually swapping duties with the captain each flight leg. The first officer assists the captain in preflight duties by reviewing paperwork and performing aircraft preflight checks. The first officer must pass many practical and written exams and must have a certain amount of seniority. As a rule, first officers have less seniority than their captains.
Some planes have a third position in the cockpit for a flight engineer, also called a second officer. The flight engineer is a usually a pilot but doesn't actually fly the airplane. He or she performs the bulk of aircraft preflight checks, operates and monitors the aircraft's systems during flight and makes aircraft performance calculations, such as determining takeoff and landing speeds, engine power settings and fuel management. The flight engineer position is also an apprenticeship of sorts, as it is the best position for observing the flying pilots. This job is now a rarity in the business: The positions are mostly in airplanes built before the mid-1980s. As older airplanes are retired, they are replaced with planes in which more advanced or automated systems perform the flight engineer's duties. The position will someday be "extinct," like the navigator and radio operator positions of airplanes from the 1930s and 1940s.
Life at Work
Ideally, your first job at a major airline will be the job you retire from. Many folks make their piloting careers at regional airline jobs or in corporate flight departments, and they have their reasons. Usually, lifestyle and seniority issues compel them to stay. Still, major airlines are considered the apex of the career ladder. This is because the pay, job stability, work rules and airplanes are usually the best in the business. As a general rule, the larger the airline, the greater the opportunities, but some small airlines have unique cultures that are particularly appealing to some pilots. Whatever makes you happy, go for it.
As a junior on the bottom of the seniority list, you will most likely be on reserve. You are the backup if things don't go according to plan. In the airline business, unplanned things happen all the time. Pilots get sick at the last minute, for instance. There are reserve pilots for every position an airline has. Reserve pilots have varying windows of "on call" duty, usually in 12-hour blocks. If their pagers go off in this time, they must dash to the airport for their assignment. Reserve pilots need to be near the airport they fly from and they need their uniform and luggage on hand, because at a moment's notice they may have to go to work. They don't know where they might go, or for how long, so they have to pack for all contingencies. Their family lives can be put on hold in an instant. If they are watching their children, they need a solid backup who can quickly step in. Most reserve pilots are expected to be ready to fly at the airport 60 to 90 minutes from when they are first paged.
A reserve pilot might have a few days of reserve alternating with a couple of days off, or the reserve days may be together in a long stretch followed by a long stretch of days off. Depending on a huge range of factors, a reserve pilot could fly every day of reserve, or not fly at all for weeks on end. Some pilots don't mind being on reserve, especially if they live in the city they are based in (called a domicile). To me -- and many share my opinion on this -- reserve is not a pleasant experience. This is especially true if you don't live in your domicile. Then you are called a commuter and likely maintain a "crash pad," usually with other away-from-home pilots.
With a little seniority, you'll rise above reserve to hold a line. A line is a pilot's defined flying schedule. In order of seniority, each pilot in a position chooses his or her line. Different lines of flying will have certain layover cities in them, certain days off or other distinctions. Depending on these factors, as well as the airline, the nature of its business and its working agreement with its pilots, some lines are more desirable than others. Again, seniority is your leverage in making your life more livable.
For most pilots, either on reserve or holding a line, time away from home is a given. Depending on the specifics of the airline and the pilot's personal situation, a pilot could be away from home only during the day or only at night, or might be on the other side of the world for 14 days or more! It takes a special family to cope with the regular absence of one (or both) of its members. Pilots often joke that they're gone so much they've actually been married for only half the time since their wedding date.
A pilot's work day, or duty day, varies depending on a number of factors, such as the number of pilots a plane needs and whether the flight is international or domestic. A long duty day can last 16 hours or, on international flights, have no limit at all. Fortunately, most pilots' working agreements limit duty days to something less than the legal maximum. Scheduled flight time is limited to 8 hours for domestic flights and 12 hours for international flights, unless the crew is augmented with additional relief pilots. The actual flight time is often longer than these limits.
Pilots have a stressful job and follow a difficult career path, but most of them wouldn't be as happy doing anything else. Most pilots have wanted to be a pilot from a very early age. Very rarely does someone without a deep passion for airplanes and their history become a pilot. Lots of people think it would be neat to fly, but those who make it to the cockpits are extremely dedicated to getting there. There are many hurdles, obstacles and patience-testing situations on the road to becoming a pilot.
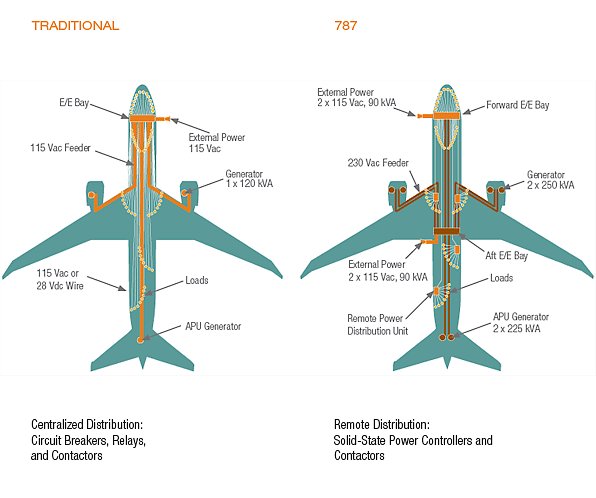
Boeing 787 / Electrical System Distribution
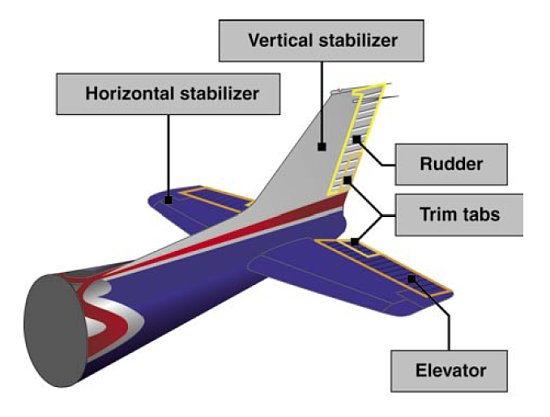
Tail, Rudder, Rear Fuselage
Aircraft Roll
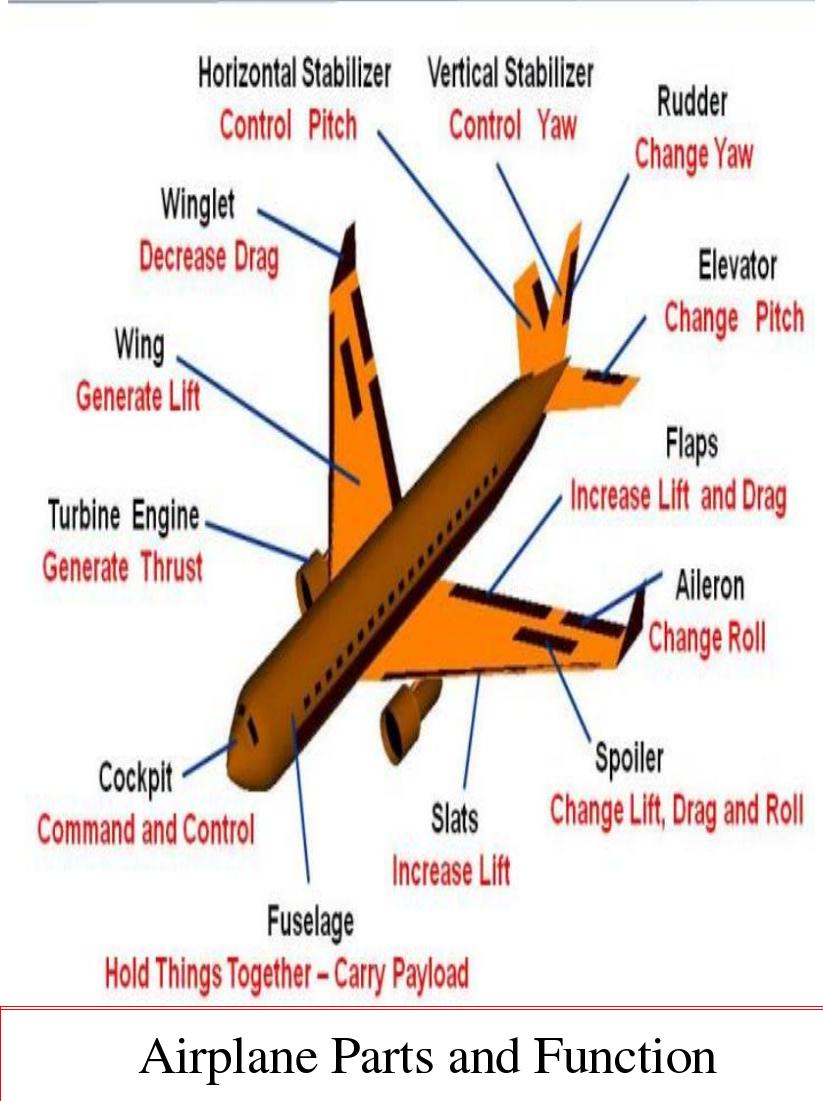
Airplane Parts and Function
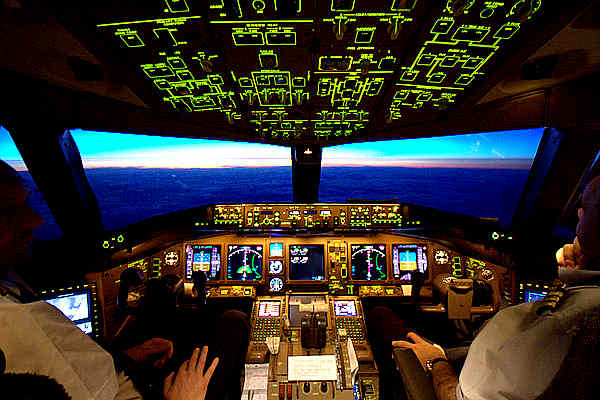

Boeing 777 Cockpit – in flight
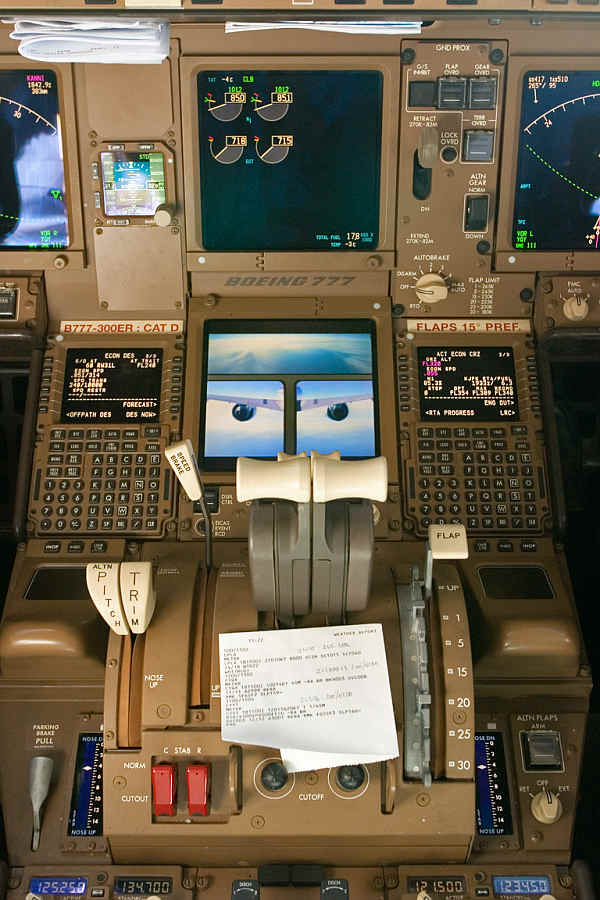

Boeing 777-300ER Cockpit
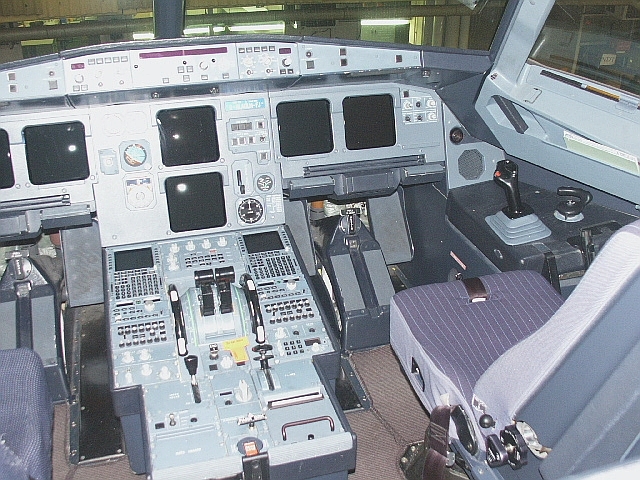

Airbus A321 Cockpit
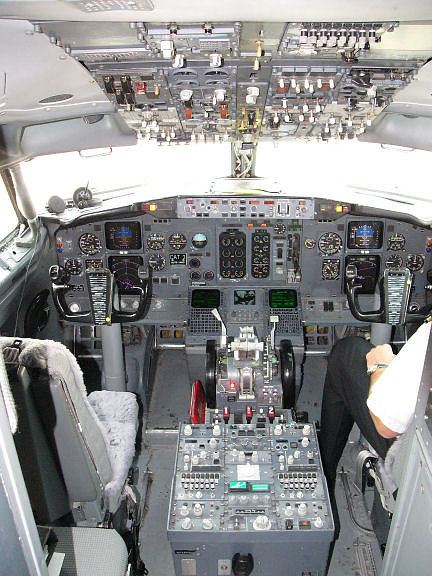

Boeing 737-700 – Overhead Panel
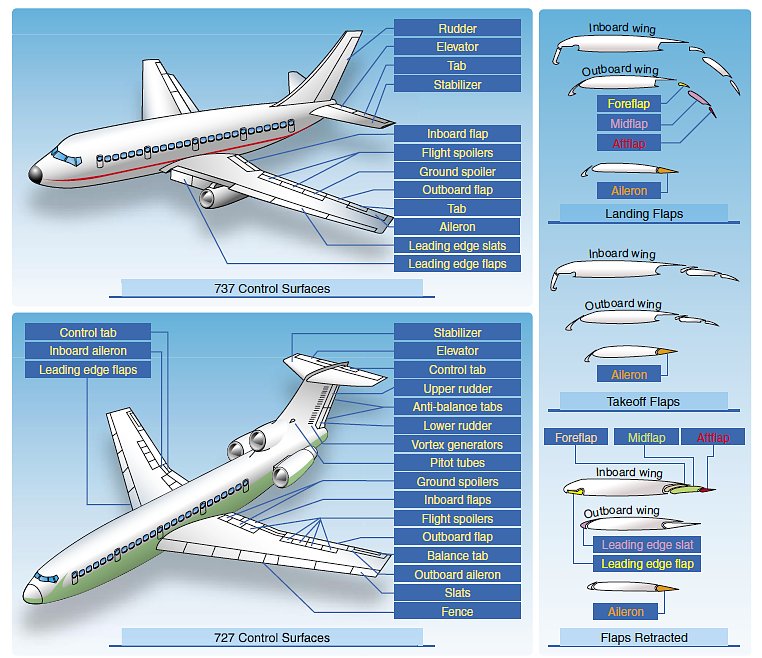
Aircraft Control Surfaces
|
|
What do you think poses the greatest threat to Airline security today?
What would you do if you lost an engine on take off?
Why do airliners have swept wings?
Airline pilot
Typical work activities
The job of a pilot comes with heavy responsibility and personal commitment. Stringent training courses have to be passed followed by recurrent training every six months in order to maintain the relevant licence required for the job.
There is more to the role than just flying the plane, which has to be done safely and economically, and tasks can typically include:
•ensuring all information on the route, weather, passengers and aircraft is received;
•using that information to create a flight plan which details the altitude for the flight, route to be taken and amount of fuel required;
•ensuring the fuel levels balance safety with economy and supervising the loading and fuelling of the aircraft;
•ensuring all safety systems are working properly;
•briefing the cabin crew before the flight and maintaining regular contact throughout the flight;
•carrying out pre-flight checks on the navigation and operating systems;
•communicating with air traffic control before take-off and during flight and landing;
•ensuring noise regulations are followed during take off and landing;
•understanding and interpreting data from instruments and controls;
•making regular checks on the aircraft's technical performance and position, on weather conditions and air traffic during flight;
•communicating with passengers using the public address system;
•reacting quickly and appropriately to environmental changes and emergencies;
•updating the aircraft logbook and writing a report at the end of the flight noting any incidents or problems with the aircraft.
First officer
As a newly qualified first officer you would work alongside a captain, usually on short-haul flights to provide you with experience of a lot of take-offs and landings. Once you had achieved 1,500 hours of flying time (500 of which must be in a plane which requires more than one crew to operate it) your ATLP will become ‘unfrozen’ and you will be issued with a full ATPL. This is what is required to go on to become a captain.
All pilots have to pass certain examinations every six months in order to keep their licence and so it is important that the pilot takes control of their studies and ensures they are up to speed with the necessary information. It is also good to keep up to date with any developments in new instruments or technology relating to aviation.
Can you explain pressurized airplane cabins?
The atmosphere is about 50 miles "deep," and at sea level it exerts 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi). Our bodies think 14.7 psi is completely normal.
When you blow up a tire on a car or a bike, you use a pump to increase the pressure inside a closed space. A car tire typically runs at 30 psi, and a bike tire might run at 60 psi. There is no magic here -- the pump simply stuffs more air into a constant volume so the pressure rises.
A plane flies at about 30,000 feet. The air pressure at 30,000 feet is significantly lower than at sea level (4.3 psi versus 14.7 psi). High-pressure air is used to "pump up" the cabin in much the same way that a tire is pumped up. The high-pressure air on most planes comes from the compression stage of the jet engines.
|
|