|
What is Thrust? What are the types of rocket propulsion? How does propulsion work? How do engineers use this knowledge of the mass flow rate? |
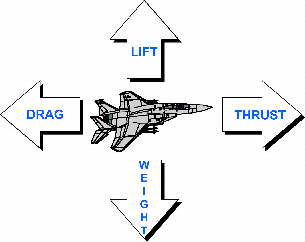 What is Thrust? THRUST is one of the four forces acting on an aircraft. Thrust (measured in pounds or newtons) provides the velocity required for an aircraft's wings to produce LIFT. Thrust is the force necessary to move the aircraft forward and lift is the force acting in the upward direction required to keep the aircraft aloft. Opposing thrust is DRAG or the force produced by air resistance. The last force is the WEIGHT of the airplane, the downward acting force, and is produced by gravity. You might have read where the F-15 can accelerate while flying straight up. A F-15E can accomplish this when the weight of the F-15E is less than the 58,200 pounds of thrust produced by the engines (commonly referred to as a thrust-to-weight ratio of greater than 1.0). Thrust is a measurement of force. Force is addressed by Newton's second law of motion and is represented by the formula Force = Mass x Acceleration 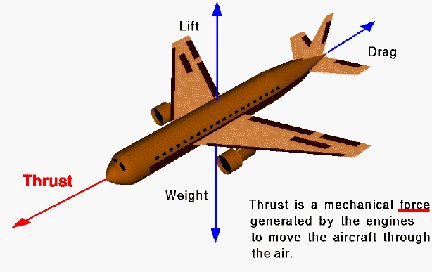 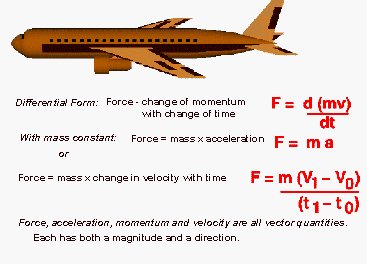 How does propulsion work? Propulsion moves things like spacecraft or jet planes forward by pushing something out of the back. Think of a balloon that you blow up and then release. The air rushing out of the back pushes the balloon forward. This happens because of a phenomenon described by Sir Issac Newton: "every action has an equal and opposite reaction." How do engineers use this knowledge of the mass flow rate? The thrust depends directly on the mass flow rate through the propulsion system. |
|
How does a jet engine work? What goes on inside a turbofan engine? What is reverse thrust during landing? How does a super-heavy jet get off the ground? What do you need to know in order to explain the phenomenon of "flying"? |
