|
What is the solar system? What's in our Solar System? Where does the solar system end? What is a Planet? How big is our solar system? Where can I find information about Earth science? What is the solar system? 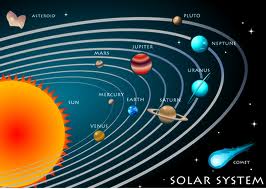 1.Our solar system is made up of the sun and everything that travels around it. This includes eight planets and their natural satellites such as Earth's moon; dwarf planets such as Pluto and Ceres; asteroids; comets and meteoroids 2.The sun is the center of our solar system. It contains almost all of the mass in our solar system and exerts a tremendous gravitational pull on planets and other bodies. 3.Our solar system formed about 4.6 billion years ago. 4.The four planets closest to the Sun - Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars - are called the terrestrial planets because they have solid, rocky surfaces. 5.Two of the outer planets beyond the orbit of Mars - Jupiter and Saturn - are known as gas giants; the more distant Uranus and Neptune are called ice giants. 6.Most of the known dwarf planets exist in an icy zone beyond Neptune called the Kuiper Belt, which is also the point of origin for many comets. 7.Many objects in our solar system have atmospheres, including planets, some dwarf planets and even a couple moons. 8.Our solar system is located in the Orion Arm of the Milky Way Galaxy. There are most likely billions of other solar systems in our galaxy. And there are billions of galaxies in the universe. 8.We measure distances in our solar system by Astronomical Units (AU). One AU is equal to the distance between the sun and the Earth, which is about 150 million km (93 million miles). It is our Sun and everything that travels around it. Our solar system is elliptical in shape. That means it is shaped like an egg. The Sun is in the center of the solar system. Our solar system is always in motion. Eight known planets and their moons, along with comets, asteroids, and other space objects orbit the Sun. The Sun is the biggest object in our solar system. It contains more than 99% of the solar system's mass. Astronomers think the solar system is more than 4 billion years old. Astronomers are now finding new objects far, far from the Sun which they call dwarf planets. Pluto, which was once called a planet, is now called a dwarf planet. The Solar System 1.What two elements is the universe made primarily of? Carbon and nitrogen Hydrogen and helium Iron and nickel Silicon and oxygen 2.What is the correct order of the planets in the Solar System, starting closest to the Sun? Mars, Mercury, Earth, Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto Mercury, Mars, Earth, Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto Mercury, Mars, Venus, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Pluto Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto 3.What is thought to be the age of the nine planets relative to each other? The inner planets formed together first and then the outer planets formed together later The outer planets formed together first and then the inner planets formed together later They all formed at roughly the same time They formed sequentially from Pluto inward with the one nearest the sun formed last They formed sequentially from the sun outward with Pluto formed last 4.Why does the moon have more craters than the earth? Craters develop much better on smaller planetary bodies The moon captured most asteroids before they could strike the earth The moon has a stronger gravitational attraction than the earth The moon has little tectonics or weathering to obliterate craters The moon is much older than the earth 5.What elements are the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn primarily composed of? Argon and krypton Hydrogen and helium Nitrogen and carbon dioxide Nitrogen and methane Nitrogen and oxygen 6.Where did the heavy elements that make up the bulk of the earth originate? In a supernova In meteorites In the Big Bang In the earth itself In the sun 7.What are the lunar maria made of? Basalt Breccia Granite Salt Water 8.Which planet is closest in size to the earth? Mars Mercury Neptune Uranus Venus 9.Which planet besides the earth has evidence of erosion by running water? Mars Mercury Neptune Uranus Venus 10.Which planet has a runaway greenhouse effect? Mars Mercury Neptune Uranus Venus 11.Which planet has virtually no atmosphere? Mars Mercury Neptune Uranus Venus 12.What is the largest planet in the solar system? Earth Jupiter Mars Neptune Saturn 13.Which of the following planets is not a gas giant? Jupiter Neptune Pluto Saturn Uranus 14.Which planet has the most extensive ring structure? Jupiter Neptune Pluto Saturn Uranus 15.What is Io? A comet A moon of Jupiter A protoplanet An asteroid The nearest star 16.What speed is needed for a gas molecule to escape from a planet? Escape velocity Orbital speed Solar wind speed Speed of light Speed of sound 17.What are comets mostly made of? Ammonia Hydrogen Ice Iron Rock 18.What is the glowing head of a comet called? Coma Crater Head Maria Nova |
| The Solar System |
| The Sun |
| Mercury |
| Venus |
| Earth |
| The Moon |
| Mars |
| Asteroids |
| Jupiter |
| Saturn |
| Uranus |
| Neptune |
| Pluto |
| Comets |
| Plate Tectonics |
|
Purpose: To explain the seasons of the year and the phases of the moon. Students often have many misconceptions about Earth's motion in space, the phases of the moon, and the causes of seasonal changes.
1. What causes night and day? 2. What causes the seasons? 3. Why are the seasons in the Southern Hemisphere opposite to those in the Northern Hemisphere? 4. Why are the days longer in the summer than in winter? 5. What causes the apparent changes in the sun’s position during the year? 6. Why does the moon go through phases? 7. Why does the moon rise a little later each day? 8. What causes the tides? 9. What causes lunar eclipses? 10. What causes solar eclipses? 11. What causes the difference between a sidereal day and a solar day? 12. What causes the difference between the sidereal period and the synodic period? 13. What is space? 14. Where does space begin? 15. How big is the universe? 16. Will the universe ever end? 17. Why does the moon shine? 18. How many stars can you see at night? 19. Why do some stars twinkle? 20. What would happen to the planets if the Sun suddenly wasn't there? 21. What is the moon's mass and density? Also how was it named, and what's it's gravity? 22. Is it possible for the new planet that we discovered, outside of Pluto's orbit, to be part of a space ripple sending a new galaxy to collide with ours? 23. How did the universe begin? 24. What color is each planet? 25. Is the Moon moving away from the Earth? 26. How far is each planet from Earth? 27. How do you measure the distance between Earth and the Sun? 28. How many stars are there in our Galaxy (Milky Way)? 29. What is the largest star? 30. Do all objects in the universe exert force on all other objects? 31. Do the orbits of any of our planets change, or do the planets always follow the same paths? 32. Are the planets in our solar system likely to be destroyed when the sun finally burns out, and will they be destroyed by a nuclear explosion or just drift off without the sun's gravitational pull? |
|
Discussion Questions
What are longitude and latitude? What is latitude and longitude used for? 1.The measure of how far north or south a place is from the equator is Latitude Longitude Prime Meridian 2. The measure of how far east or west of the Prime Meridian a place is located is Latitude Longitude Equator 3.The latitude line at 0 degrees latitude is The equator The Prime Meridian The Tropic of Cancer 4. The line at 0 degrees longitude is The equator The Prime Meridian The Tropic of Capricorn 5. How far a location is from the equator effects The time zone the place is in The climate of the area When it is day and when it is night 6. The longitude of a place or how far it is from the Prime Meridian effects The time zone a place is in How much rainfall a place receives The climate of the area 7. The closer to the equator a place is The colder it is The hotter it is 8. Latitude and longitude are measured in Degrees Pounds Acres |
