|
Are humans superior to animals and plants? Is there a difference between anthropology and human health care? What is biology? What is life? When did life begin on Planet earth? What is the population of humans on the planet earth? What needs to be modified in scientific classification of living things? How should you elaborate humans in the scientific classification of living things? What is health? What is human health care? | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Are humans superior to animals and plants? Yes. Is there a difference between anthropology and human health care? Yes. What is biology? Biology is the science concerned with the study of life. What is life? When did life begin on Planet earth? Here are further guidelines. Health What is health? Health is the level of functional or metabolic efficiency of a living organism. What is human health care? Human health care is the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in humans. What is the population of humans on the planet earth? By 2013, the global human population was estimated to be around 7 billion. Scientific classification What needs to be modified in scientific classification of living things? Humans have to be categorized separately. Homo or homo sapiens should not be connected to humans. Homo has various different meanings, thus confusing others. How should you elaborate humans in the scientific classification of living things? Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Class Mammalia Order Primates Family Hominidae Genus Intellectual (renamed after research of Asif Qureshi. Do not write Homo) Species sapiens You can also elaborate in alphabetical order Class Mammalia Domain Eukarya Family Hominidae Genus Intellectual (renamed after research of Asif Qureshi, Do not write Homo) Kingdom Animalia Order Primates Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Species sapiens | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
What is health? What is human health care? Here are further guidelines. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Human Body Anatomy Systems 11 Systems of the Human Body
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 100 Very Cool Facts About The Human Body | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| effects of aging on the human body | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Human Body Systems 100 trillion cells 206 bones 600 muscles 22 internal organs | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Head Anatomy Neck Anatomy Shoulder Anatomy Back Anatomy Chest Anatomy Abdominal Anatomy Hip Anatomy Upper Leg Anatomy Knee Anatomy Lower Leg Anatomy Ankle Anatomy Foot Anatomy Upper Arm Anatomy Elbow Anatomy Forearm Anatomy Wrist Anatomy Hand Anatomy Skin Anatomy Internal Organ Anatomy |
| Internal Organs Anatomy |
Brain 
|
Colon 
|
Gall bladder 
|
Heart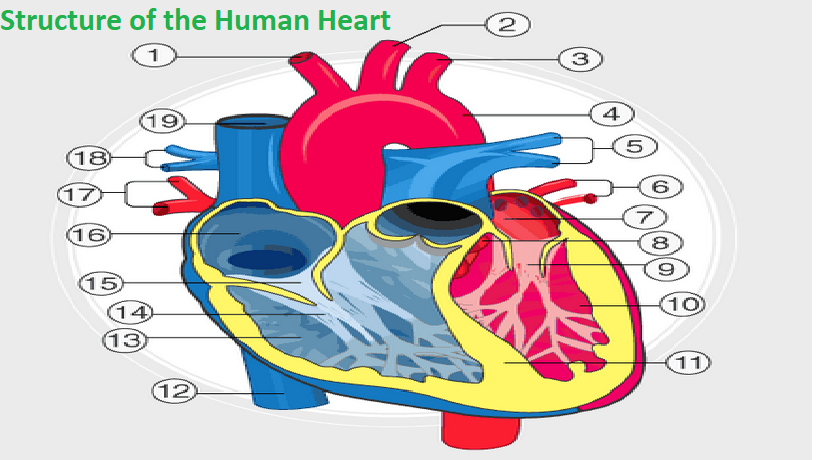
|
Kidneys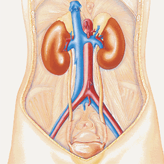
|
Large intestine 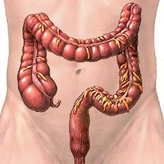
|
Lungs 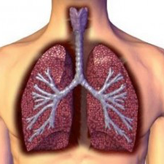
|
Liver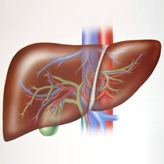
|
Pancreas 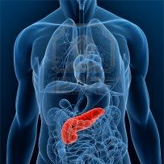
|
Small intestine 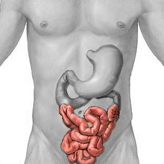
|
Spleen 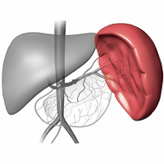
|
Stomach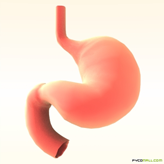
|
|
Adrenal Glands Appendix Bladder Brain Esophagus Gallbladder Heart Intestines Kidney Liver Lungs Ovaries Pancreas Parathyroid gland Pituitary gland Prostate gland Spleen Stomach Testicles Thymus gland Thyroid gland Uterus |
