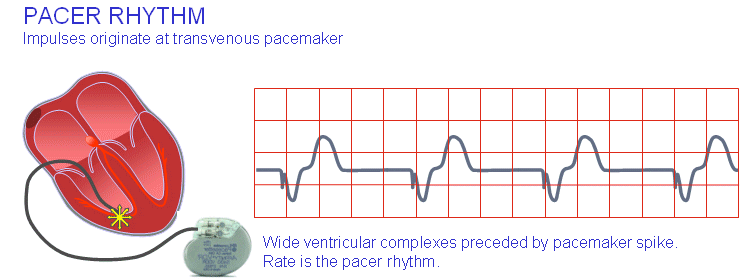
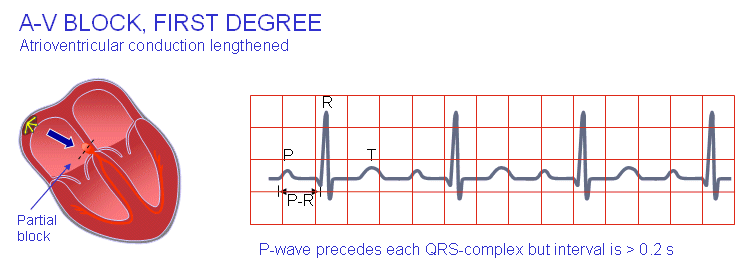
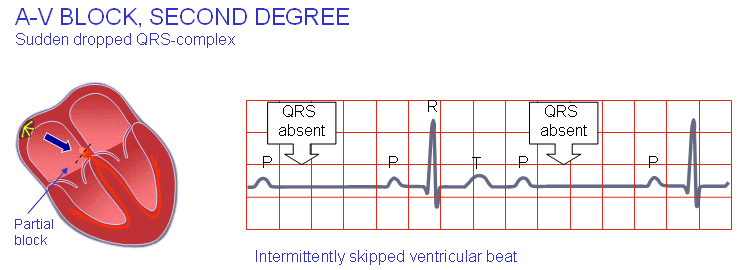
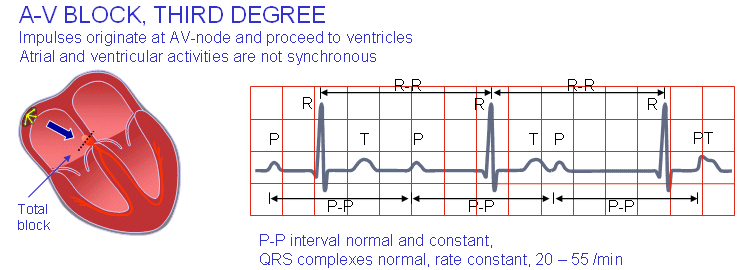
When was this resource last updated?
Last Updated: April 6, 2015
|
Internet Human Health Care Services Human Healthcare The King's University www.qureshiuniversity.com http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html Who has authored this resource? Doctor Asif Qureshi.  What is the title of this resource? Medical Diagnosis and Treatment Resource every physician on this planet must have. Resource every human healthcare professional on this Planet must have. Resource every state department of health on this planet must have. |
| For whom are these training programs meant in the state or outside the state around the world? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Allied health workers guidelines
The reference resource for medical doctors. The reference resource for human healthcare. What is included in the reference resource for medical doctors? What is included in the reference resource for health care? |
|
What is wrong with existing physicians around the world? Existing physicians around the world are not able to do proper health care assessment in various human healthcare settings. Existing physicians are not able to reach correct diagnoses and treatment in various human healthcare settings. How many types of human health care assessment are there? There are 18 types of human health care nonemergency assessment and 15 types of human health care, emergency assessment in various human healthcare settings. What is an assessment of a patient? Patient assessment is the term used to describe the process of identification of the condition, needs, abilities, and genuine preferences of a patient. Identify possible solutions and/or remedies. Prepare a plan. Who should ideally do an assessment of a patient? The physician should ideally do an assessment of the patient. There is only one best doctor on this planet.  His name: Dr. Asif Qureshi. His focus: The planet. Questions relevant to the patient. Here are further guidelines. PATIENT ASSESSMENT DEFINITIONS Emergency Medical Services. Here are further guidelines. Emergency medical room in a hospital Here are further guidelines. Primary care physician consultation New patient relevant to primary health care (nonemergency). Here are further guidelines. |
|
What are skills? A skill is the learned ability to carry out a task with pre-determined results often within a given amount of time, energy, or both. In other words the abilities that one possesses. Skills can often be divided into domain-general and domain-specific skills. For example, in the domain of work, some general skills would include time management, teamwork and leadership, self motivation and others, whereas domain-specific skills would be useful only for a certain job. Is there a difference between human organ system functions and abilities? Yes. What is the difference between human organ system functions and abilities? Human pulse, blood pressure, temperature, consciousness, and respiratory rate are signs of human organ system functions. These signs exist from birth onwards. These are signs of human organ system functions; they are not abilities. Abilities are learned gradually after birth. This example will make you understand. English language reading abilities. English language speaking abilities. English language understanding abilities. English language writing abilities. If an individual does not have English language reading, speaking, understanding, and writing abilities, that does not mean there is impairment of human organ system functions. These are all learned abilities. If an individual is educated properly, he or she will learn these abilities. What are the vital signs of human organ systems functions? Consciousness Pulse Blood pressure Respiratory rate Temperature Pain In some regions, consciousness and pain are not considered vital signs. What are the differences between abilities of a newborn and abilities of an 18-year-old human? A newborn does not have any learned abilities. A newborn has five findings: Breathing effort, Heart rate, Muscle tone, Response to smell or foot slap, Skin color. A doctor of medicine calls this Apgar scoring. Apgar scoring determines the health of a newborn. These findings are due to human organ systems’ functions. Sucking reflex, defecation, urination, and crawling are monitored later. A human learns more than 600 abilities from birth up to 18 years. What should you know about human organ systems’ functions? Human organ systems functions exist from birth. How is a human body organized? Cells are the basic unit of life. Tissues are clusters of cells that perform a similar function. Organs are made of tissues that perform one specific function. Organ systems are groups of organs that perform a specific purpose in the human body. The purpose of the 11 organ systems is for the human body to maintain homeostasis. Organs and Functions What are the human organs and their function? Adrenal glands - Fight or flight emergency explosive action and mental clarity. Appendix - No longer in direct use, theorized to help Immune system. Bladder - Temporally collects liquids from food waste. Brain - A neural network of interdependent systems to send signals to muscles. Epidermis - protect against pathogens, oxidant stress (UV light) and chemicals. Esophagus - Muscular tube through which food travels to the stomach. Eyes - Conversion of photons into a data stream for the optic nerve. Gall bladder - Fat conversion/digestion with high powered chemicals. Heart - Pump to move blood around the body. Kidney - Regulate acidity, blood pressure, salt/water balance, signal hormones. Large intestine - Absorb water and last remaining nutrients from waste. Liver - Filter out the blood of impurities and toxins. Lungs - Absorption of Oxygen and release of Carbon Dioxide. Mouth - Temporary storage area for food while it is evaluated and crushed. Ovaries - In Females, secrete estrogen, progesterone and create ovums. Pancreas - Break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in food. Parathyroid - Control the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones. Pleura - Lubricant and structure to convert muscle movements to inhale/exhale. Prostate gland - In Males, Assist in the preparation of semen. Rectum - About 12cm of temporary storage site for feces. Small intestine - Primary absorption of nutrients and minerals in food. Spine - Bendable support structure for upper body, protects wires from brain to lower body. Spleen - Secondary backup systems to regulate blood and immune system. Stomach - Dissolve and churn eaten foods with acids. Testes - In Males, create sperm containing the DNA code to build another human. Thyroid gland - Configuration for energy storage, dial in sensitivity to hormones. Tongue - Evaluate and reposition food in the mouth and push down esophagus. Uterus - Hold and supply nutrients to the ovum while it grows into a human. How many organ systems does the human body have? The human body has 11 organ systems. What are the organ systems of the human body? Take a look at this. Organ Systems of the Body Brain & central nervous system (nervous system) Circulatory System Digestive System Endocrine System Integumentary system Lymphatic (immune) system Muscular system Reproductive System Respiratory System Skeletal System Urinary system Is there a difference between human body functional capacity evaluation and fitness for duty? Yes. What is the difference between human body functional capacity evaluation and fitness for duty? Functional capacity evaluation measures 11 human organ system functions relevant to age. Fitness for duty measures general abilities and professional abilities relevant to a profession. Functional Capacity Evaluation measures 11 human organ system functions relevant to age. Here are further guidelines. Body Systems Quiz http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/Quizhumanbodtsystems.html http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/abilitiesworld.html Abilities/skills Various medical colleges start with anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, pediatrics, ear nose & throat, forensic medicine, ophthalmology, preventive and social medicine and end with medicine, surgery, obstetrics and gynecology. They must start directly with a medical condition. Each medical condition should be enumerated in at least 40 questions and answers with relevant anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, microbiology, pathology, pharmacology, and preventive concepts. What human anatomy should one know relevant to this medical condition? What human physiology should one know relevant to this medical condition? What human biochemistry should one know relevant to this medical condition? What human microbiology should one know relevant to this medical condition? If one needs these questions and answers, Qureshi University is willing to provide them. |
Academic degree for physician
|
How should you introduce yourself if you are a physician? I am Asif Qureshi. I have a Doctor of Medicine academic degree. I am a physician. I am a forensic psychiatrist. I can guide all medical specialties. If a person is a physician and interprets his or her academic degree with such terms as MB BCh, M.D, MBBS, MB BCh BAO, MBChB, MBBChir, BMBS, BMed, BM, MChDetc, this can create confusion. Doctor of Medicine is an academic degree for a physician. Being a physician is the profession. State department of health director is a professional rank. Medical superintendent of a hospital is a professional rank. Ideally, state department of health director should be a physician. Head of the state is a professional rank. Head of the United Continents of the world is a professional rank. Head of the United States of world is a professional rank. You may have gone for 4, 5, 6, or 8 years to medical college and be licensed to practice as a physician, but that does not mean you can reach a correct diagnosis of and treat complex human problems or complaints in the real world in various health care settings. A physician’s abilities can range from physician/general practice to the best among physicians, that is, a physician/forensic psychiatrist. Doctor Asif Qureshi is an example of forensic psychiatrist. A forensic psychiatrist can evaluate fitness for duty of all other physicians. A forensic psychiatrist can evaluate fitness for duty of all other professions in addition to physicians. What does the practice of medicine include? The practice of medicine includes the diagnosis, treatment, correction, advisement, or prescription for any human disease, ailment, injury, infirmity, deformity, pain, or other condition, physical or mental, real or imaginary. Remember, if you claim to be a physician, you have to diagnose and treat various complex human problems and complaints in various health care settings. |
Administrative Issues
|
What can be reasons for suspension from services of a medical doctor? This is usually applicable to a junior doctor. Absent from specific location of duty during duty hours. Negligence. A junior doctor usually remains at a specific location. A senior doctor supervises from a distance. What does a senior doctor do from a distance? Provides education to junior doctors. Monitors. Does research. Makes recommendations. What is the minimum affiliation a physician or medical specialist should have? Minimum collaboration with state department of health. What degrees do I need to hold to become a physician? Doctor of Medicine degree Many physicians may also hold other advanced degrees, such as: Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) Master's of Public Health (MPH) Doctor of Jurisprudence, or Law (JD) How many state departments of health are there in the world? There are at least 323 state departments of health around the world. How has the Internet changed the concept of medical education for physicians or medical specialists? There previously were demarcations like medical college in America and medical college outside America. Internet medical education has made it possible for someone in Asia to get educated from an American medical education resource to become a physician or a medical specialist. Is there a difference between a physician and a medical doctor? No. What are other names for a physician? Doctor Medical doctor Medical practitioner What is a physician assistant? In real-world practice, a physician may not get your medical history directly. A physician assistant or a nurse can get medical history before a real physician consultation. What do you have to do before a patient or individual from the public seeks individualized doctor consultation? Has this issue been explained at the public health level? Take a look at this. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/publichealthworld.html Has this issue been explained in patient education? Take a look at this. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/patienteducation.html If yes, you need to go through these facts. If no, you need to seek individualized doctor consultation. A doctor should first try to resolve health issues at the public health level or patient education. If the public health level or patient education does not resolve your issues, individualized doctor consultation is required. Doctor Consultation Here are further guidelines. |
|
Annual health assessment. Here are further guidelines. |
| Health administration (State health care administrative issues) |
| Hospital administrators |
| Administrative Issues |
| Computer and Internet education for doctors |
| Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
Here are few suggestions for you. This is for those who are counseled to appear for any examination for postgraduation. Examination before postgraduation is futile exercise. Relevant questions must be answered. You must get profiled by your guide for abilities with recommendations. Any postgraduation cannot teach you more than what is elaborated at www.qureshiuniveristy.com/healthcareworld.html Because of the computer and Internet, a physician can enhance his/her further abilities at home or home office with computer and Internet and connect to www.qureshiuniveristy.com/healthcareworld.html You need to maintain all these guidelines separately for future review, including guidelines at www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html. All these useless and unreasonable examinations for further studies or postgraduate studies can be challenged in courts in the state. Is there any standard examination and justified examination for physicians that can get them a postgraduation training program for further studies? No. How should any physician go ahead with any postgraduation in a state? Questions you need to answer. What is the profile of your guide? In what state do you plan to offer professional services of a physician? Do you plan to be around Asif Qureshi? If you plan to be around Asif Qureshi, you must visit www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html every day. You must call every Sunday. You must call on other days if required. If required, email or call that you would like to speak with me and I will call or email from this side. No resource can guide you better than the guidelines at www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html resources. If others contend that there are better resources, they must display them publicly like those at www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html. What do I expect from you? You will maintain all communications and learning materials you get. You are first a physician, then a specialist and superspecialist. |
| Aging Research |
Annual health assessment.
|
Encourage everyone to have an annual health assessment from a competent medical doctor able to answer relevant questions via e-mail, telephone, fax, postal mail, or face-to-face and able to reach a correct diagnosis and treatment in various health care settings. Why do you need an annual health assessment? Most medical emergencies can be prevented with a proper annual health assessment and treatment by a competent medical doctor. Most medical disabilities can be prevented or cured with an annual health assessment by a competent medical doctor. Most medical conditions can be diagnosed and cured with a proper annual health assessment by a competent medical doctor. The quality of health can be enhanced with a proper annual health assessment and treatment by a competent medical doctor. Every state must assign 200 patients to a competent medical doctor able to answer relevant questions and reach a correct diagnosis and treatment for primary health care that includes an annual health assessment. Every medical doctor must update the state department of health with relevant findings. The state department of health must maintain medical records of patients. A medical doctor can prolong the life of a person at least up to 90 years with a good quality of life. A medical doctor cannot sustain a person beyond 90-95 years of life. |
| Questions for professional regulators in the state. |
| Questions for health care providers or medical doctors. |
| Questions for residents or patients. |
Anesthesiologist
| Anesthesiologist |
Antibiotics
| Antibiotics |
| Alphabetical listing of human diseases and medical conditions. |
| Alphabetical listing of Human medical emergencies. |
Alphabetical listing of human healthcare settings.
| Alphabetical listing of human healthcare settings. |
Alphabetical listing of human medical conditions details.
| Alphabetical listing of human medical conditions details. |
| Alphabetical listing of doctors’ abilities. |
Arterial Blood Gases
| Arterial Blood Gases |
| Blood Chemistry Panel |
| Chemical Composition of the Human Body |
| Children's health |
Complaint
Complaints against human healthcare provider
|
Is there a difference between a complaint and a problem? Yes. How should you evaluate a complaint or problem? Is it a complaint or a problem? Problem Is this about one or many problems? If this is a problem, what type of problem is this? What best describes the problem? This is one problem in one document. These are many problems in one document. This is from one individual on one document. This is from many individuals on one document. Complaint Is this one complaint or many complaints in one document? If this is a complaint, what type of complaint is this? What best describes the complaint? This is one complaint in one document. These are many complaints from one individual in one document. These are many complaints from many individuals in one document. This is a criminal complaint document. Many individuals are involved in this criminal complaint from the other side. This is a civil complaint document. This is a medical nonemergency. This is a medical emergency. This is a medical emergency medicolegal case. This is a medical nonemergency medicolegal case. If there is any other description, please describe. What essential department in the state has the duty to resolve this complaint or problem? Who has the duty to resolve this complaint or problem in the state or outside the state? Here are further guidelines. Complaint http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/complaint.html Problem http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/problem.html |
| Complaints against human healthcare provider |
|
What should you know about this medical specialty?
You are first a physician, than a specialist or super specialist. What are the most common human skin disorders?

Acne

Skin Cancer

Lupus

Rubeola (Measles)

Hemangioma of Skin

Cold Sore

Psoriasis

Rosacea

Seborrheic Eczema» 
Hives

Vitiligo

Necrotizing Fasciitis
» 
Cutaneous Candidiasis
Carbuncle» 
Cellulitis» 
Hypohidrosis» Impetigo» Cutis Laxa

Decubitus Ulcer

Erysipelas

Diaper Rash
Dyshidrotic Eczema

Canker Sore
Herpes Stomatitis

Fungal Nail Infection

Ichthyosis Vulgaris
Dermatomyositis
» 
Molluscum Contagiosum» 
Ingrown Nails
Acrodermatitis
» Sebaceous Cyst

Seborrheic Keratosis
Pilonidal Sinus

Keloid
» 
Lichen Planus» 
Actinic Keratosis

Stasis Dermatitis and Leg Ulcers

Corns and Calluses» 
Eczema
Tinea Versicolor» Pemphigoid» Mouth Ulcers» 
Shingles
Warts» |
| What are the different types of counseling? |
| Crisis |
| Counseling Services |
Critical care unit record
Intensivist
|
Who is an intensivist? Intensivist: A physician who specializes in the care of critically ill patients, usually in an intensive care unit (ICU). An intensivist, also known as a critical care physician, is a medical doctor with special training and experience in treating critically ill patients. Intensivists are physicians who direct and provide medical care in a hospital's intensive care unit (ICU), working with the attending physician of record and other staff such as critical care nurses, pharmacists, respiratory therapists, nutritionists, rehabilitation services, social workers, case managers and especially spiritual care - as well as physician specialists How are intensivists different than other specialists, such as cardiologists, who treat critically ill patients? Intensivists provide a comprehensive approach to caring for ICU patients rather than focusing on specific body systems, such as cardiologists or pulmonologists. In many instances, they have the primary responsibility for the patient rather than acting as a consultant, as many specialists do. Depending on the intensivist program, critical care physicians provide round-the-clock ICU care rather than being on call off-site or spending most of their time seeing office patients, in surgery or treating patients in other parts of the hospital. How is an intensivist-led ICU different than a traditional ICU? In a traditional approach, primary care physicians have the chief responsibility for treating their critically ill patients. They often bring in specialists as needed, such as a nephrologist if the patient has a kidney problem or pulmonologist if the patient is placed on a ventilator. There are some clear drawbacks to this approach. For one, primary care doctors have little experience with critically ill patients, who are often suffering from multi-system problems or diseases. These doctors might average a handful of such patients a year. They also cannot devote large amounts of their time to monitoring and managing ICU patients since they may have other hospital patients as well as many patients to see throughout the day at their offices. As a result, care is generally fragmented and poorly coordinated. Intensivists, on the other hand, spend their time each day in the ICU treating the critically ill. They are trained and experienced in dealing with the complex issues of the sickest patients as well as treating, or when possible, averting complications that often arise quickly. Hospitalist What is a Hospitalist? A Hospitalist is a physician that is trained to specifically treat and be responsible for patients in the hospital. These doctors practice in the hospital 24 hours a day, seven days a week to provide immediate and ongoing care without delay. What about my Primary Care Physician? The Hospitalist will coordinate your care with your primary care physician. By working together, the hospitalist will have a full understanding of your current health and medical history. The Hospitalist will examine you and coordinate all other exams, tests, and treatments while you are in the hospital. Upon discharge from the hospital your medical care will transition back to your primary care physician. What is a Pediatric Hospitalist? Pediatric hospitalists are pediatricians who work in hospitals providing care for children ages 0-18. Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/criticalcareworld.html |
Critical Care unit
Critical care unit record
|
What should be included in the critical care unit record for the patient? What is the profile of the patient? Name: Date of birth: Address: Family: Emergency contact person: What is the location of the critical care unit? _______________________________________________ For example: Critical care unit, SKIMS, Soura, Srinagar, Kashmir, Asia. What brings the patient to the critical care unit? _______________________________________________ What is the day, date, time of arrival to a critical care unit? _______________________________________________ For example: Tuesday, November 25, 2014, 12:10 pm What is the profile of the physician supervisor of the critical care unit? _______________________________________________ Who brought the patient to the critical care unit? _______________________________________________ What is the health status of the patient on the day, date, and time of arrival to the critical care unit? _______________________________________________ Who are the physician, nurse, social worker, and technologists to look after the patient? _______________________________________________ Who are among supervising physician, nurse, social worker, and technologist to look after the patient? _______________________________________________ What is the diagnosis for this patient? _______________________________________________ What is the treatment plan for this patient? _______________________________________________ How often will there be a follow-up from a physician? _______________________________________________ Does the critical care unit have a computer with www.qureshiuniversity.com connected to the Internet? _______________________________________________ If you have any issue, email admin@qureshiuniversity.com or call 7735616102 Chicago, Illinois, North America, and you will get answers within 24 hours. |
|
What is the most common condition relevant to endocrinology? Diabetes type 2. Here are guidelines for patients older than 18 years. When was your last blood sugar test done? A year ago. What were the values of your last blood sugar? Normal. How often should you get your blood sugar checked if you are more than 18 years old and have not been diagnosed with diabetes? If yearly blood sugar is normal, a check of blood sugar every two years is reasonable. Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/endocrinologyworld.html |
|
What does a forensic psychiatrist do? A forensic psychiatrist’s expertise is required on more than 111 issues. What is the most important duty of a forensic psychiatrist? Fitness for duty evaluation is one of the duties of a forensic psychiatrist. How many forensic psychiatrists are there around the world? A forensic psychiatrist is a rare entity around the world. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/forensicpsychiatrist.html |
Forensic Pathologist
|
What is a forensic pathologist?
Forensic pathologists, or medical examiners, are specially trained physicians who examine the bodies of people who died suddenly, unexpectedly, or violently. The forensic pathologist acts as the case coordinator for the medical and forensic scientific assessment of a given death, How does the forensic pathologist use the history, external physical examination, autopsy and laboratory studies to determine the cause and manner of death? The history is the beginning of the investigation and is of utmost importance in making the determination of cause of death. Where do forensic pathologists work? State department of health. Forensic psychiatrist and forensic pathologist difference. What is the difference between a forensic psychiatrist and forensic pathologist? A forensic psychiatrist has more abilities and knowledge than a forensic pathologist. What are other names for forensic pathologist? Coroner Medical Examiner Origin of term medical examiner is from Scotland. It later was introduced into various American states. Origin of word coroner is from England. It later was introduced into various American states. Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/forensicmedicineinternational.html |
Identify Unidentified Dead Individual.
|
Identify Unidentified Dead Individual. Criminal Death Investigation. Here are further guidelines.
|
Medical Emergency
Patient assessment
Emergency medical room in a hospital
|
How should an emergency medical room in a hospital be set up/organized in a state?
How many patients does an emergency medical room get every 24 hours? How can genuine medical emergencies in a medical emergency room be separated from nonemergency medical cases? Does this patient need to be seen by a physician in a medical emergency room or the patient screening area? Where is the patient now? Who gets a medical record with a medical record number? What is a medical record number? What does a medical record of a patient for inpatient care contain? What cases go to a medical emergency room and what cases go to room to screen medical emergencies? Who guides medical emergency room physicians from a distance and who remains at the location in a medical emergency room? How many physicians are required for a medical emergency room? What does the roster for a medical emergency room for physicians, nurses, paramedics, emergency room administrator (assistant medical superindentent) look like? What is the profile of junior physicians on duty at medical emergency room SMHS hospital Srinagar, Kashmir Asia? What type of problems and complaints are evaluated in a medical emergency room? What types of cases are diagnosed and treated in a medical emergency room? How should you go ahead in the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions in a medical emergency room? What is an Emergency medicine specialists? What is a medical emergency? What are the types of patient assessment? What will happen if this medical condition is left without treatment? What should be displayed on an emergency medical record? What problems, complaints, incidents, and issues need on-the-spot diagnosis and treatment? In what emergency medical category do you fit the condition of the patient you are diagnosing and treating on this date and time? In what type of setting does this patient need treatment? How do you do a quick assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of a conscious patient? How do you do a quick assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of an unconscious patient? What are examples of emergency relevant to an individual? What are various symptoms, signs, statements, questions, issues, and histories that should raise suspicion of a medical emergency? How should patients be categorized around the world, including in America, in case of a medical emergency? Is there a difference between emergency and non-emergency medical diagnosis? What is the difference between non-emergency and emergency medical diagnosis? What is the role of www.qureshiuniversity.com/medicalemergencyworld.html in a medical emergency? How has Internet human healthcare changed the way hospitals work around the world? Why you must specifically mention the state relevant to medical superintendent in the state and hospital administration in the state? What should hospital administration, including medical superintendent, in the state recommend? What should you know about hospitals in the state? What should a hospital in the state display on the Internet? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
How should an emergency medical room in a hospital be set up/organized in a state? A medical emergency room in a state has to be open 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Emergency room beds and screening locations for patients should be separate. There should be at least four separate rooms in case the patient needs extra care. Email, fax, and telephone number of emergency medical room should be displayed publicly. The telephone preferably should be connected to an answering machine with regular monitoring. How many patients does an emergency medical room get every 24 hours? An emergency room in a hospital received 300 patients in 24 hours. Out of the 300 patients, few had genuine medical emergencies. How can genuine medical emergencies in a medical emergency room be separated from nonemergency medical cases? A screening location in the emergency room should diagnose and treat nonemergency cases. Questions you need to answer in this situation. Does this patient need to be seen by a physician in a medical emergency room or the patient screening area? Where is the patient now? Who gets a medical record with a medical record number? This is usually for inpatient care. Outpatient care also gets a separate record. What is a medical record number? This is the number on a patient’s medical record. MRD numbers for medical emergency room patient and screening patient are different. What does a medical record of a patient for inpatient care contain? Assessment and plan Chief complaint History of the present illness Medical encounters Medical history Other information Physical examination Prescriptions and Orders Progress notes Test results What cases go to a medical emergency room and what cases go to room to screen medical emergencies? If the patient is in front of you talking normally, after walking in the location, this patient goes to room to screen medical emergencies. Here is an example. Acute bronchial asthma, diabetic hyperosmolar coma, acute angina, open wound and similar diagnoses go to medical emergency room. Flu, sprain, aches and pains, insomnia, etc., go to room to screen medical emergencies with diagnosis and treatment without admission to a medical emergency room. Screening next to medical emergency room is like managing an outpatient department (OPD) to limit patient load on emergency room physicians to those with a genuine medical emergency. Who guides medical emergency room physicians from a distance and who remains at the location in a medical emergency room? Senior physician guides from a distance. www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html A junior physician works in the medical emergency room. Sometimes distance is like professor of forensic psychiatry Asif Qureshi is in Chicago, Illinois, North America, on November 17, 2014, with the guidelines displayed at www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html Junior physicians are in the medical emergency room SMHS hospital Srinagar, Kashmir, Asia. These junior physicians were nominated: Dr. Tazim, Dr. Manzoor Ahmed, Dr. Parvez Ahmad, Dr. Shahida. How many physicians are required for a medical emergency room? There should be at least 17 physicians with the publicly displayed profile. Emergency contact details should be in the medical emergency room in a hospital with rotation eight hours duty. What does the roster for a medical emergency room for physicians, nurses, paramedics, emergency room administrator (assistant medical superindentent) look like?
Total profile of Physicians/Nurses/Paramedics/Medical superintendent. What is the profile of junior physicians on duty at medical emergency room SMHS hospital Srinagar, Kashmir Asia? Your email, contact information, profile is required. What type of problems and complaints are evaluated in a medical emergency room? What types of cases are diagnosed and treated in a medical emergency room? How should you go ahead in the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions in a medical emergency room? http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html What is an Emergency medicine specialists? Emergency Physicians must have the skills of many specialists—the ability to resuscitate a patient (critical care medicine), manage a difficult airway (anesthesia), suture a complex laceration (plastic surgery), reduce (set) a fractured bone or dislocated joint (orthopedic surgery), treat a heart attack (cardiology), work-up a pregnant patient with vaginal bleeding (Obstetrics and Gynecology), stop a bad nosebleed (ENT), place a chest tube (cardiothoracic surgery), and to conduct and interpret x-rays and ultrasounds (radiology). What is a medical emergency? If a human being has any problem, symptom, complaint, or situation listed below, it is a medical emergency. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/medicalemergency.html What best describes the problem, symptom, complaint, or situation in the list? _________________________ What type of assessment does this patient need? _________________________ What are the types of patient assessment? What will happen if this medical condition is left without treatment? _________________________ The individual can die. The individual can have a disability. The individual can have severe pain. The individual can have irreparable harm. Does this situation need a doctor? _________________________ What should be displayed on an emergency medical record? Details of the patient. Details of the diagnosing and treating medical doctor. Details of the patient. What should be your first question in case a patient is referred to you? Patient 60-second assessment by call center/Internet/telemedicine. Where is the patient now? _________________________ How old is the patient? _________________________ What is the gender of the patient? _________________________ Who is reporting this emergency? _________________________ What are the sources of medical history? _________________________ Patient. Family. Patient not responding to medical history questions. Community member. Police officer. Referral from medical doctor. Other. How much time has elapsed from the start of the emergency until now? _________________________ Does one individual or many individuals have medical emergencies at this location? _________________________ How many individuals have medical emergencies at this location? _________________________
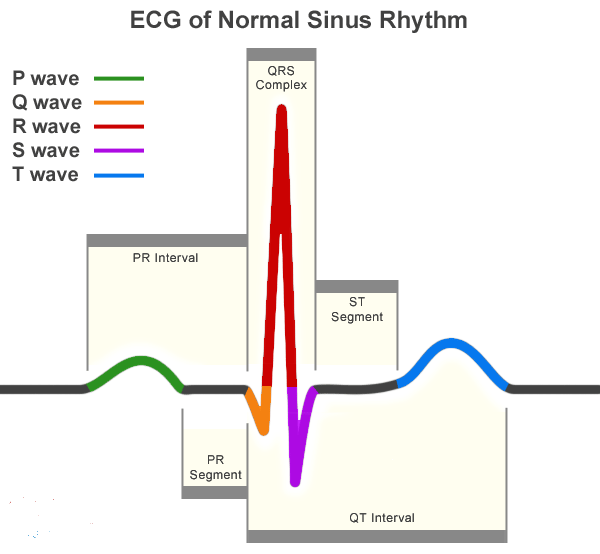
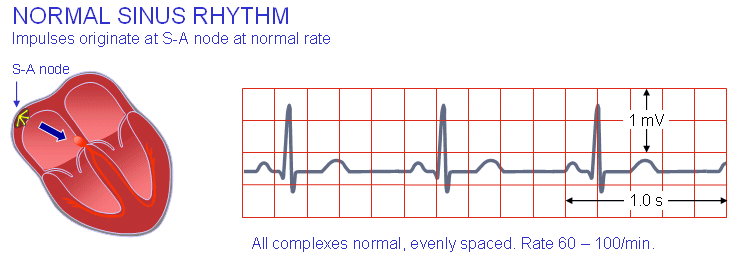
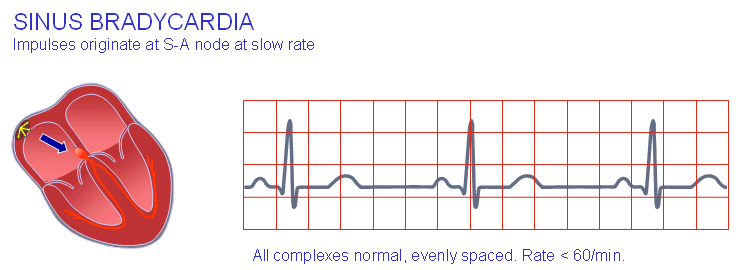
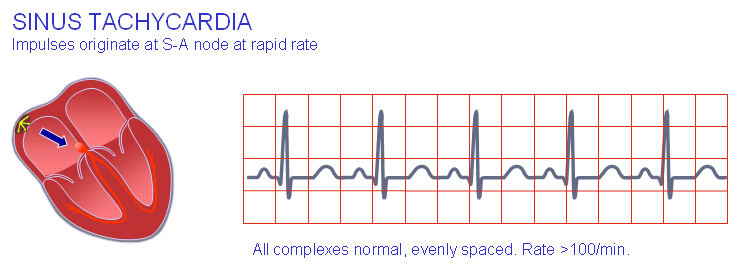
If it is a multiple causality incident, the guidelines are different. Check vital signs, mobility, and survival needs. Consciousness of a human being has to be included in vital signs. Vital Signs Consciousness, pulse, blood pressure, respiratory rate, temperature. Consciousness is extremely essential in reaching a correct diagnosis and treatment. What are the vital signs on the date and time of diagnosis and treatment?
How do you categorize the condition of the patient? _________________________ Undetermined Good Fair Serious Critical Is this an emergency? _________________________ What is the category of this emergency? _________________________ Is this a medical emergency? _________________________ In what type of setting does this patient need treatment? _________________________ Here are various examples. Who has the duty to manage this emergency? _________________________ What best describes this human emergency? _________________________
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patient assessment | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Patient 60-second on-the-spot diagnosis and treatment. What problems, complaints, incidents, and issues need on-the-spot diagnosis and treatment?
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Are you the person reporting a medical emergency for yourself? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emergency | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| How do you do a quick assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of an unconscious patient? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Are all vital signs normal? Can the person move relevant to age? Has the person been provided with survival resources? Does the person or caregiver complaint of anything? Are these justified complaints? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emergency Diagnosis and Treatment |
Hospital labs errors or variable test reports.
|
What should physicians know about errors or variable test reports from hospital laboratories?
Verified findings of hospital laboratory errors or variable test reports. Do not reach a diagnosis based only on hospital lab reports. Consider all medical history, clinical presentation, and follow up findings before reaching diagnoses of patients. |
Hospital ward patient in the state.
|
How should a physician speak to the hospital ward patient? This should be documented in the hospital ward medical record. What brings you to the hospital? How are you feeling now? What complaints or problems did you have that led to hospital ward admission? What complaint(s) or problems(s) do you have now? Do you know your diagnosis? What is your diagnosis? How did the physician reach this diagnosis? Who has diagnosed you? What complaint(s) did you have that made you a hospitalized patient? What date and time were you diagnosed? Are you satisfied with your diagnosis? What treatment are you on? Are you improving with the existing treatment? What are the findings from the physical examination of the patient? Do you know when you will be discharged from hospital ward? Has the state provided all survival needs for the patient at home? Who has verified these findings? What is the advice for the patient on discharge from the hospital ward? |
A–Z alphabetical listing of human health emergency symptoms and signs.
Medical emergencies.
| Common Medical Emergencies |
| Dispatching for an emergency |
| Emergency Diagnosis and Treatment |
| Emergency Diagnosis Code |
|
Emergency medical record Emergency Department record |
| Emergency medical responder |
| Emergency medical record |
| Emergency Medicine |
| Health Care |
| List of medical emergencies |
| Medico legal cases |
| Patient assessment |
| Surgical Emergencies |
| Symptoms & Signs A-Z List |
| State Offices and Agencies of Emergency Management |
| What are various symptoms, signs, statements, questions, issues, and histories that should raise suspicion of a medical emergency? |
|
How are most patients categorized in American triage locations up to February 12, 2012?
Immediately life threatening Urgent, but not immediately life threatening Less urgent How should patients be categorized around the world, including in America, in case of a medical emergency? Undetermined, Good, Fair, Serious, Critical. Fair, serious, or critical will always get a medical diagnosis that needs emergency treatment. This can be only done by an emergency medical doctor able to reach the correct diagnosis and provide treatment. Is there a difference between emergency and non-emergency medical diagnosis? Yes, there is. What is the difference between non-emergency and emergency medical diagnosis? This example will make you understand. Diabetes is a non-emergency medical diagnosis. Diabetes with hyperosmolar coma or diabetic ketoacidosis is an emergency medical diagnosis. What is the role of www.qureshiuniversity.com/medicalemergencyworld.html in a medical emergency? Guide the following: Doctor in a medical emergency. Emergency responder in a medical emergency. Emergency call center in a medical emergency. Watcher, relative, or acquaintance of the victim in a medical emergency. Victim himself or herself in a medical emergency. Guide the state department of health worldwide. |
| When Is It Really an Emergency? |
|
What types of patients get admitted to emergency room (ER), operating Room (OR), intensive care unit (ICU), and hospital wards and need Internet health care or outpatient (OPD) health care?
Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/medicalemergencyworld.html |
Hospitals around the world and Internet human healthcare.
|
How has Internet human healthcare changed the way hospitals work around the world?
If a physician at any location needs further consultations or reference, www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html has all guidelines in question-and-answer format in the English language. This gets researched and updated every day. Before the existence of Internet human healthcare, a junior physician had to consult a senior physician or head of the department relevant to patient care. With the existence of Internet human healthcare, a junior physician at any location on this planet can – with a few clicks at this resource: www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html – get guidance in question-and-answer format in the English language. Some still think this is a website. This is far more than a website with highly effective intellectual property resource. |
Hospital administration in the state
Medical superintendent in the state
|
Why you must specifically mention the state relevant to medical superintendent in the state and hospital administration in the state?
All these services are relevant to essential departments and administration in the state. What is the professional rank of an individual physician who takes care of administration of a hospital in the state? A physician with professional rank of medical superintendent. What are other names of medical superintendent of a hospital in the state? Chief physician Medical superintendent What is a medical superintendent? A medical superintendent is a physician who supervises the 24-hour operations of healthcare facilities, such as hospitals and nursing homes. This includes human resources needs, products and services resources needs, as well as patient care. What should hospital administration, including medical superintendent, in the state recommend? All medical conditions have to be diagnosed and treated at one hospital in a specific area in the state. You cannot have separate hospitals for internal medicine and surgery, maternity, chest conditions, psychiatry, orthopedics, or similar subspecialties. Remind physicians to serve in primary health care and Internet healthcare. What should you know about hospitals in the state? Hospitals in the state are state government-run hospitals. Many departments in the state have duty relevant to hospitals. This resource – www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html – has guidelines for all hospitals in states around the world. Questions medical superintendent of a hospital needs to answer. What is the profile of all physicians in the hospital? Are all physicians in the hospital competent? Can a physician answer relevant questions? What is the profile of all workers in the hospital? Does the hospital have required products and services? What is the requirement of the hospital relevant to human resources, starting with physicians? What is the requirement of the hospital relevant to products and services? How can patient care be improved further? Hospital Profile What should be specifications of a hospital in a state? http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/healthcareworld.html What should a hospital in the state display on the Internet? Area relevant to hospital: What is the plinth area of hospital buildings and the land area of the hospital? Building specifications: What should be included in building specifications? Continent and state location: For example: Kashmir, Asia. Number of patient beds: How many patient beds are there in the hospital? Number of beds for on-duty physicians: How many physicians’ on-duty beds are there? Number of Physicians: What is the profile of the physicians in the hospital? Number of Nurses: What is the profile of the nurses in the hospital? Number of paramedics: What is the profile of paramedics in the hospital? Profile of medical superintendent: What is the profile of the medical superintendent of the hospital? |
Health care and hospital administration.
Guidance for Hospital Administration, Hospital Faculty
Medical superintendent
What services does the medical superintendent of a hospital have to supervise in the state?
Hospital heating system in winter.
|
What should you know about the hospital heating system in winter in the state? The hospital heating system in winter in the state is like any building heating system in winter. When should the central heating system in hospitals start every year in a cold climate? The central heating system in hospitals in cold climate should start on November 15 every year . What complaints are there relevant to this service in the state? 1. Service started after November 15 of the year. 3. From November 15 onwards, this service runs only for some hours. 3.Temperature range in room is not between 10-18 degrees centigrade. 4.Resources in the state are not enough relevant to his service. To keep the desired room temperature, the building should be insulated with insulated doors and windows, with proper ventilation. What should be the range of room temperature in the building throughout the year? Room temperature should be maintained in the range of 10-18 degree centigrade. From November 15 onwards, a central heating system is needed. In summer, air conditioners or coolers are needed. Blowers and room heaters are not sufficient. |
Nephrologist
|
What is a Nephrologist? The definition of a nephrologist is a doctor who has had special training in kidney diseases. A nephrologist is a physician who studies and deals with nephrology. Nephrology is the adult and pediatric study of the kidneys and its diseases. The nephrologist deals with the diagnosis and management of kidney disease. The kidneys are vital for maintaining normal fluid and electrolyte balance in the body. Doctors use laboratory values to interpret your medical condition. With respect to kidney disease, the BUN and the creatinine help your nephrologist (as well as your internist and family physician) determine if your kidneys are working correctly. These two tests are commonly ordered for many reasons and are invaluable tools to help your doctor assess your condition. Let’s define what BUN (pronounced by spelling out the letters “B”, “U”, and “N”) and creatinine mean from a simple country nephrologist’s perspective. Creatinine is a molecule made by the muscles in your body. Creatinine is produced at a constant rate. Creatinine, for the purposes of this discussion, is cleared (or removed) from the kidney filters unchanged by the rest of the body’s metabolism. If the kidneys are having trouble getting rid of the creatinine, the molecules accumulate in the body and the laboratory number increases. Let’s say a normal creatinine is 1. Patients require kidney dialysis when the value becomes 4-5 and they complain of symptoms consistent with needing dialysis. In other words, the kidney filters are messed up and you now need an alternative method to remove toxins and water from your body — this method of removal we call kidney dialysis. To be more specific with respect to the function of the kidneys and take into account the differences among human beings, we use an equation called creatinine clearance to calculate how well a person’s kidneys are working. Creatinine is a component of the calculation. Why do we go through all this trouble to serve you? Creatinine can be an inaccurate marker of kidney function in certain circumstances. For example, men have more muscle mass than women on average and therefore produce more creatinine. This fact must be taken into account when determining if the level of creatinine is high or low. If men have more muscle mass, their creatinine should be higher at baseline because more muscle means more creatinine around. In addition, that’s why the lab differentiates whether a person is African American or not when giving results for the creatinine clearance or GFR (glomerular filtration rate) to determine a patient’s kidney renal function. BUN or blood urea nitrogen is a term to describe the breakdown products of protein in your body. This value is affected by many things including: ¦blood loss through the gastrointestinal tract ¦the use of steroids for patients with COPD and emphysema ¦the level of hydration in the body ¦in patients receiving intravenous nutrition in the hospital who are prescribed too much protein. Kidney doctors via consultation help other physicians including critical care doctors and hospitalists prescribe TPN (total parenteral nutrition) for the patients they serve if the patient is suffering from complex electrolyte disorders. A high BUN suggests toxins are not removed from the body. A low BUN suggests malnutrition. Because BUN is given to us in terms of concentration, we also use this laboratory value to determine a patient’s volume status. If the value is high we consider a patient might be dehydrated, for example. Therefore, we look at BUN with respect to the other laboratory values to make meaning of the term. For example, the BUN can be low when a patient is not eating. In other words, when a patient does not eat enough, there may not be enough protein in the body to convert to BUN, resulting in a low value. In this setting, there is a risk for malnutrition. That’s why the renal panel or kidney panel includes a patient’s albumin, which is a better marker of nutritional status. In conclusion, we nephrologists look at the removal of creatinine from the body when making decisions regarding kidney dialysis instead of the clearance of BUN from the body. BUN is used to help us make an assessment of the condition of the kidneys but the creatinine is better because the BUN is affected by so many things. So if the creatinine clearance is low (suggesting the need for dialysis) and the BUN is low (at first glance suggesting the patient is not in need of dialysis because there too few toxins in the body to make dialysis worth it), patients may still need kidney dialysis to not only remove fluid from the body but also clear toxins not represented by the BUN. Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/nephrologyworld.html |
Palliative Care Services
Pain and Palliative Care Services