List of surgical procedures
Here are further guidelines.
What are the most common surgical procedures in every state?
| Appendectomy | Breast biopsy | Carotid endarterectomy | Cataract surgery | Cesarean section | Cholecystectomy | Coronary artery bypass | Debridement of wound, burn, or infection | Dilation and curettage | Free skin graft | Hemorrhoidectomy | Hysterectomy | Hysteroscopy | Inguinal hernia repair | Low back pain surgery | Mastectomy | Partial (segmental) mastectomy | Total (or simple) mastectomy | Modified radical mastectomy | Radical mastectomy | Partial colectomy | Prostatectomy | Releasing of peritoneal adhesions | Tonsillectomy |
|
Appendectomy
An appendectomy is the surgical removal of the appendix, a small tube that branches off the large intestine, to treat acute appendicitis. Appendicitis is the acute inflammation of this tube due to infection. Breast biopsy A biopsy is a diagnostic test involving the removal of tissue or cells for examination under a microscope. This procedure is also used to remove abnormal breast tissue. A biopsy may be performed using a hollow needle to extract tissue (needle aspiration), or a lump may be partially or completely removed (lumpectomy) for examination and/or treatment. Carotid endarterectomy Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove blockage from carotid arteries, the arteries located in the neck that supply blood to the brain. Left untreated, a blocked carotid artery can lead to a stroke. Cataract surgery Cataracts cloud the normally clear lens of the eyes. Cataract surgery involves the removal of the cloudy contents with ultrasound waves. In some cases, the entire lens is removed. Cesarean section Cesarean section (also called a c-section) is the surgical delivery of a baby by an incision through the mother's abdomen and uterus. This procedure is performed when physicians determine it a safer alternative than a vaginal delivery for the mother, baby, or both. Cholecystectomy A cholecystectomy is surgery to remove the gallbladder (a pear-shaped sac near the right lobe of the liver that holds bile). A gallbladder may need to be removed if the organ is prone to troublesome gallstones, if it is infected, or becomes cancerous. Coronary artery bypass coronary artery bypass - Most commonly referred to as simply "bypass surgery," this surgery is often performed in people who have angina (chest pain) and coronary artery disease (where plaque has built up in the arteries). During the surgery, a bypass is created by grafting a piece of a vein above and below the blocked area of a coronary artery, enabling blood to flow around the obstruction. Veins are usually taken from the leg, but arteries from the chest may also be used to create a bypass graft. Anatomy of the heart following coronary artery bypass surgery 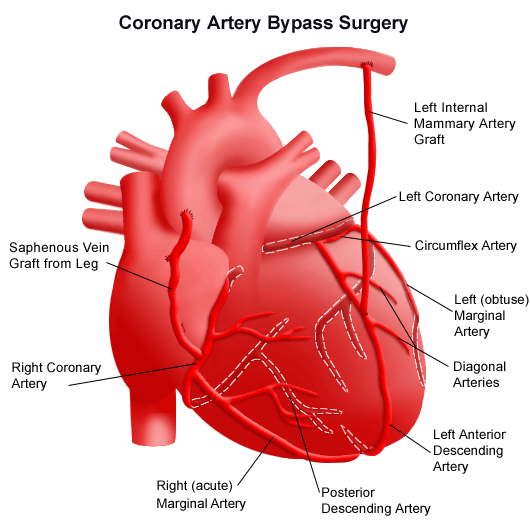 Debridement of wound, burn, or infection Debridement involves the surgical removal of foreign material and/or dead, damaged, or infected tissue from a wound or burn. By removing the diseased or dead tissue, healthy tissue is exposed to allow for more effective healing. Dilation and curettage (Also called D & C.) A D&C is a minor operation in which the cervix is dilated (expanded) so that the cervical canal and uterine lining can be scraped with a curette (spoon-shaped instrument). free skin graft A skin graft involves detaching healthy skin from one part of the body to repair areas of lost or damaged skin in another part of the body. Skin grafts are often performed as a result of burns, injury, or surgical removal of diseased skin. They are most often performed when the area is too large to be repaired by stitching or natural healing. Hemorrhoidectomy A hemorrhoidectomy is the surgical removal of hemorrhoids, distended veins in the lower rectum or anus. Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is the surgical removal of a woman's uterus. This may be performed either through an abdominal incision or vaginally. Hysteroscopy Hysteroscopy is a surgical procedure used to help diagnose and treat many uterine disorders. The hysteroscope (a viewing instrument inserted through the vagina for a visual examination of the canal of the cervix and the interior of the uterus) can transmit an image of the uterine canal and cavity to a television screen. Inguinal hernia repair Inguinal hernias are protrusions of part of the intestine into the muscles of the groin. Surgical repair pulls the intestine back to its original location. low back pain surgery Low back pain can have various causes, including abnormal development of the backbone, stress on the back, injury, or a physical disorder that affects the bones of the spine. Usually, surgery is not considered until other options have been exhausted, including rest, medication, and mild exercise. The type of surgery performed on the back depends on the diagnosis. Illustration of a partial mastectomy 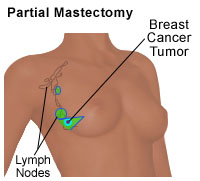
total (or simple) mastectomy, in which the surgeon removes the entire breast, including the nipple, the areola (the colored, circular area around the nipple), and most of the overlying skin, and may also remove some of the lymph nodes under the arm, also called the axillary lymph glands. Illustration of a total mastectomy 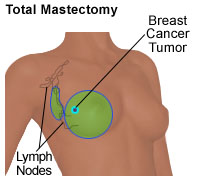
modified radical mastectomy, in which the surgeon removes the entire breast (including the nipple, the areola, and the overlying skin), some of the lymph nodes under the arm, and the lining over the chest muscles. In some cases, part of the chest wall muscles is also removed. Illustration of a modified radical mastectomy 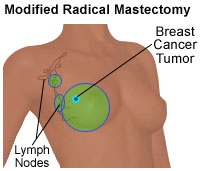
radical mastectomy, involves removal of the entire breast (including the nipple, the areola, and the overlying skin), the lymph nodes under the arm, and the chest muscles. Illustration of a radical mastectomy 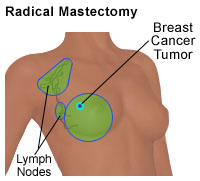
Partial colectomy A partial colectomy is the removal of part of the large intestine (colon) which may be performed to treat cancer of the colon or long-term ulcerative colitis. Prostatectomy The surgical removal of all or part of the prostate gland, the sex gland in men that surrounds the neck of the bladder and urethra - the tube that carries urine away from the bladder. A prostatectomy may be performed for an enlarged prostate, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or if the prostate gland is cancerous. Releasing of peritoneal adhesions The peritoneum is a two-layered membrane that lines the wall of the abdominal cavity and covers abdominal organs. Sometimes, organs begin to adhere to the peritoneum, requiring surgery to detach them. Tonsillectomy The surgical removal of one or both tonsils. Tonsils are located at the back of the mouth and help fight infections. |
|
Angioplasty and Stenting Carotid Endarterectomy Endoscopic Vein Surgery Endovascular Stent Graft Other surgical procedures performed by the Division of Vascular Surgery include: Ambulatory Phlebectomy Amputation Atherectomy Catheter Embolization Dialysis Access Interventional Cancer Treatments Interventional Stroke Treatments Liver Biopsy Portal Hypertension Surgery Sclerotherapy Surgical Aneurysm Repair Surgical Bypass Thrombolysis TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt) Uterine Fibroid Embolization Vascular Access Procedures Vasculight® Laser Therapy Vena Cava Filters Venous Thrombectomy Vein Stripping Minimally Invasive Treatment Options: Internal stents Catheter treatments |
|
What surgical skills should you know? What questions should be answered before, during, and after any surgical procedure? What surgical procedure has been recommended? Is this surgical procedure really required? Who recommended this surgical procedure? Is this individual professionally fit for the job? Here are further guidelines. Surgery |
|
Common operations Endoscopic (telescopic) procedures:
Resection and ablation (destruction) of the prostate with lasers or heat Removal of bladder tumours Treatment of bladder and kidney stones
Vasectomy Hydrocoele (water on the testis) Removal of the prostate, kidney or bladder for cancer Removal of kidney for stone or infection Diversion of urine into a stoma (ileal conduit or bag) Reconstruction of the bladder following it’s removal Reconstruction of the urethra (water passage) after damage (urethroplasty) Urology 24-Hour Urine Collection Twenty-four hour urine collection is performed by collecting a person's urine in a special container over a 24-hour period. The results of a 24- hour urine collection may provide information to help your physician make or confirm a diagnosis. Antegrade Pyelogram An antegrade pyelogram is a procedure that uses a combination of contrast dye and X-rays to diagnose obstructions and other problems in the upper urinary tract. Circumcision Circumcision is the surgical removal of the foreskin that covers the tip of the penis. Computed Tomography (CT or CAT) Scan of the Kidney CT/CAT scans are more detailed than standard x-rays and are often used to assess the kidneys for injuries, abnormalities, or disease. Cryotherapy for Prostate Conditions Cystography A cystography is a procedure that uses a combination of contrast dyes and X-rays to find the source of problems in, or assess injuries to the bladder. Cystometry Cystometry may be recommended to evaluate problems related to the muscle function of the bladder and urethra. Cystoscopy for Women Cytoscopy is a procedure in which a long, lighted scope is used to examine the urinary tract, bladder, urethra, and openings to the ureters and is used when problems with the urinary tract are suspected. Intravenous Pyelogram An intravenous pyelogram is a procedure that uses a combination of contrast dyes and X-rays to look for obstructions in the blood flow of the kidneys or poor kidney function. Kidney Biopsy A kidney biopsy is a procedure in which tissue samples are removed with a special needle to determine if cancer or other abnormal cells are present, or to determine how well the kidney is working. Kidney Scan A kidney scan uses nuclear radiology to assess the function and structure of the kidneys, as well as blood flow to the kidney tissue. Kidney Transplantation Procedure A kidney transplant is a surgical procedure performed to replace a diseased kidney with a healthy kidney from another person. Kidney Ultrasound An ultrasound of the kidney uses An ultrasound of the kidney is a procedure in which sound wave technology is used to assess the size, shape, and location of the kidneys in order to detect injuries, abnormalities or disease. Kidney, Ureter, and Bladder X-ray A KUB x-ray may be the first diagnostic procedure used to assess the urinary system; to find the cause of abdominal pain, such as masses, perforations, or obstruction; or to evaluate the urinary tract before other diagnostic procedures are performed. Lithotripsy Lithotripsy treats certain kidney stones with ultrasonic energy, or shock waves, once they are located with fluoroscopy or ultrasound. Prostate Biopsy A prostate biopsy is a procedure in which tissue samples are removed with a special needle to determine if cancer or other abnormal cells are present. Prostate/Rectal Sonogram A sonogram uses ultrasound technology to allow quick visualization of the prostate and related structures from outside the body. It may be used to examine the prostate gland for evidence of cancer. Radical Prostatectomy A prostatectomy is a surgical procedure for the partial or complete removal of the prostate. It may be performed to treat prostatic cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Renal Angiogram A renal angiogram, also called an arteriogram, is an x-ray image of the blood vessels of the kidneys. Renal Venogram A renal venogram is a procedure in which contrast dye is combined with X-rays to examine the veins that carry blow away from the kidneys. It is often nused in conjunction with fluoroscopy. Retrograde Cystography Retrograde cystography is a procedure in which contrast dye is combined with X-rays to examine a bladder after abdominal trauma, or to find other bladder conditions such as tumors, blood clots, or diverticula. Retrograde Pyelogram A retrograde pyelogram is a type of x-ray that uses dye to highlight the bladder, ureters, and renal pelvis, and is usually performed during a procedure called cystoscopy. Robotic Prostatectomy Your prostate can be removed several ways. One way is for the surgeon to make several smaller cuts and removing the prostate using a tiny camera and surgical tools. This is called a laparoscopic prostatectomy. When a surgeon uses a robot during the procedure, it's known as a robotic prostatectomy. Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) A transurethral resection of the prostate is a surgical procedure that uses a tiny instrument to remove portions of the prostate gland through the penis, requiring no external incision. Uroflowmetry Uroflowmetry is a quick, simple diagnostic screening test that is commonly performed to determine if there is obstruction to normal urine outflow. Vasectomy Vasectomy is surgical procedure you may choose if you are a man and you do not want to father any more children. The word "vasectomy" comes from the two tubes called the "vas deferens" that are cut during the operation. |
Subdisciplines of plastic surgery may include:
|
Aesthetic Surgery Aesthetic surgery is an essential component of plastic surgery and includes facial and body aesthetic surgery. Plastic surgeons use cosmetic surgical principles in all reconstructive surgical procedures as well as isolated operations to improve overall appearance. Burn Surgery Burn surgery generally takes place in two phases. Acute burn surgery is the treatment immediately after a burn. Reconstructive burn surgery takes place after the burn wounds have healed. Craniofacial Surgery Craniofacial surgery is divided into pediatric and adult craniofacial surgery. Pediatric craniofacial surgery mostly revolves around the treatment of congenital anomalies of the craniofacial skeleton and soft tissues, such as cleft lip and palate, craniosynostosis, and pediatric fractures. Adult craniofacial surgery deals mostly with fractures and secondary surgeries (such as orbital reconstruction) along with orthognathic surgery. Craniofacial surgery is an important part of all plastic surgery training programs, further training and subspecialisation is obtained via a craniofacial fellowship. Hand Surgery Hand surgery is concerned with acute injuries and chronic diseases of the hand and wrist, correction of congenital malformations of the upper extremities, and peripheral nerve problems (such as brachial plexus injuries or carpal tunnel syndrome). Hand surgery is an important part of training in plastic surgery, as well as microsurgery, which is necessary to replant an amputated extremity. The Hand surgery field is also practiced by orthopedic surgeons and general surgeons (see Hand surgeon). Scar tissue formation after surgery can be problematic on the delicate hand, causing loss of dexterity and digit function if severe enough. Microsurgery Microsurgery is generally concerned with the reconstruction of missing tissues by transferring a piece of tissue to the reconstruction site and reconnecting blood vessels. Popular subspecialty areas are breast reconstruction, head and neck reconstruction, hand surgery/replantation, and brachial plexus surgery. Pediatric Plastic Surgery Children often face medical issues very different from the experiences of an adult patient. Many birth defects or syndromes present at birth are best treated in childhood, and pediatric plastic surgeons specialize in treating these conditions in children. Conditions commonly treated by pediatric plastic surgeons include craniofacial anomalies, cleft lip and palate and congenital hand deformities. Techniques and procedures In plastic surgery, the transfer of skin tissue (skin grafting) is a very common procedure. Skin grafts can be taken from the recipient or donors: Autografts are taken from the recipient. If absent or deficient of natural tissue, alternatives can be cultured sheets of epithelial cells in vitro or synthetic compounds, such as integra, which consists of silicone and bovine tendon collagen with glycosaminoglycans. Allografts are taken from a donor of the same species. Xenografts are taken from a donor of a different species. Usually, good results are expected from plastic surgery that emphasizes careful planning of incisions so that they fall in the line of natural skin folds or lines, appropriate choice of wound closure, use of best available suture materials, and early removal of exposed sutures so that the wound is held closed by buried sutures. | <.tr>
| Abdominoplasty ("tummy tuck"): reshaping and firming of the abdomen |
| Blepharoplasty ("eyelid surgery"): reshaping of the eyelids or the application of permanent eyeliner, including Asian blepharoplasty |
| Bodytite |
| Brachioplasty ("Arm lift"): reducing excess skin and fat between the underarm and the elbow[23] |
| Breast Augmentation |
| Breast uplift |
| Brow lift |
| Buccal fat pad |
| Buttock augmentation ("butt implant"): enhancement of the buttocks using silicone implants or fat grafting ("Brazilian butt lift") and transfer from other areas of the body |
| Buttock lift: lifting, and tightening of the buttocks by excision of redundant skin |
| Cheek implants |
| Cheek augmentation ("cheek implant"): implants to the cheek |
| Chemical peel: minimizing the appearance of acne, chicken pox, and other scars as well as wrinkles (depending on concentration and type of agent used, except for deep furrows), solar lentigines (age spots, freckles), and photodamage in general. Chemical peels commonly involve carbolic acid (Phenol), trichloroacetic acid (TCA), glycolic acid (AHA), or salicylic acid (BHA) as the active agent. |
| Chin remodelling |
| Cryolipolysis: refers to a medical device used to destroy fat cells. Its principle relies on controlled cooling for non-invasive local reduction of fat deposits to reshape body contours.[21] In September 2010, the Food and Drug Administration approved the non surgical Zeltiq device for the purpose of selective fat reduction for “cryolipolysis”.[22] |
| Cryoneuromodulation: Treatment of superficial and subcutaneous tissue structures using gaseous nitrous oxide, including temporary wrinkle reduction, temporary pain reduction, treatment of dermatologic conditions, and focal cryo-treatment of tissue |
| Dermal fillers |
| Face lift |
| Fat transfer |
| Fillers injections: collagen, fat, and other tissue filler injections, such as hyaluronic acid |
| Gynecomastia |
| Genioplasty ("chin implant"): augmentation of the chin with an implant, usually silicone, by sliding genioplasty of the jawbone or by suture of the soft tissue |
| Keloid removal - The keloid forms when the body fails to stop producing new tissue during healing. This leads to an overabundance of fibrous protein and collagen. |
| Laser Skin Rejuvenation or Resurfacing:The lessening of depth in pores of the face |
| Labiaplasty: surgical reduction and reshaping of the labia |
| Liposuction ("suction lipectomy"): removal of fat deposits by traditional suction technique or ultrasonic energy to aid fat removal |
| Lip enhancement: surgical improvement of lips' fullness through enlargement |
| Mammoplasty: Breast augmentations ("breast implant" or "boob job"): augmentation of the breasts by means of fat grafting, saline, or silicone gel prosthetics, which was initially performed to women with micromastia |
| Reduction mammoplasty ("breast reduction"): removal of skin and glandular tissue, which is done to reduce back and shoulder pain in women with gigantomastia and/or for psychological benefit men with gynecomastia |
| Mastopexy ("breast lift"): Lifting or reshaping of breasts to make them less saggy, often after weight loss (after a pregnancy, for example). It involves removal of breast skin as opposed to glandular tissue |
| Neck lift |
| Otoplasty ("ear surgery"/"ear pinning"): reshaping of the ear, most often done by pinning the protruding ear closer to the head. |
| Orthognathic Surgery: manipulation of the facial bones through controlled fracturing |
| Phalloplasty ("penile liposuction") : construction (or reconstruction) of a penis or, sometimes, artificial modification of the penis by surgery, often for cosmetic purposes |
| Rhinoplasty ("nose job"): reshaping of the nose |
Rhytidectomy ("face lift"): removal of wrinkles and signs of aging from the face
Browplasty ("brow lift" or "forehead lift"): elevates eyebrows, smooths forehead skin Midface lift ("cheek lift"): tightening of the cheeks |
| Thigh lift |
| Vaser |
| Wrinkle treatment |

|
Questions to be answered before the surgery. Questions to be answered in postoperative notes. Questions to be answered in follow-up consultations. If the expected procedure or surgery is likely to harm the patient, do not go ahead with surgery. If all the questions are not answered, do not go ahead with surgery. |
|
| |
|
Question 2
What is the name of the individual who needs doctor consultation? | |
|
Question 3
What is the date of birth of the individual who needs doctor consultation? | |
|
Question 4
Address What is your mailing address? | |
|
Question 5
What was your mailing address from birth until now? | |
|
Question 6
Where is the patient now? | |
|
Question 7
Where do you live now? How long have you lived at this address? | |
|
Question 8
How long do you plan to live at this address? | |
|
Question 9
What is your contact information including current mailing address, telephone, e-mail, and any other details, and person to contact in case of emergency? | |
|
Questions to be answered before the surgery. Question 10 Who will do the expected procedure? | |
|
Question 11
What is the expected procedure? | |
|
Question 12
What is the expected date, time, and location of surgery? | |
|
Question 13
What is the diagnosis of the patient? | |
|
Question 14
Who verified the diagnosis of the patient? | |
|
Question 15
What is the profile of the patient’s primary care physician? | |
|
Question 16
How will this procedure help or enhance the life of the patient? | |
|
Question 17
Is the surgery really required? | |
|
Question 18
If surgery is really indicated, these questions must be answered. Why do you recommend this operation? | |
|
Question 19
What operation are you recommending? | |
|
Question 20
Is there more than one way to do this operation? | |
|
Question 21
Are there alternative to surgery? | |
|
Question 22
What are the details of the operation? | |
|
Question 23
What are the advantages of this operation? | |
|
Question 24
What are the risks of having this operation? | |
|
Question 25
What will happen if this operation is not done? | |
|
Question 26
Who can give a second opinion? | |
|
Question 27
What kind of anesthesia is required? | |
|
Question 28
How long is the operation? | |
|
Question 29
How long will it take to recover from the operation? | |
|
Question 30
How much experience has the doctor had in diagnosing and treating such cases? | |
|
Question 31
How much experience does the doctor have in this specific operation? | |
|
Question 32
Has this type of operation been discussed publicly? | |
|
Question 33
At what hospital will the operation be done? | |
|
Question 34
How long will the doctor be available in the hospital? | |
|
Question 35
Has the surgeon marked the site where he or she will operate with all the preoperative, operative, and postoperative guidelines? | |
|
Question 36
What is the gender of the patient? What best describes the patient?: | |
|
Question 37
What best describes the surgery? Cardiothoracic surgery Eye surgery General surgery Neurosurgery OB/GYN surgery Oral and maxillofacial surgery Orthopedic surgery Otolaryngology Pediatric surgery Plastic surgery Urology | |
|
Question 38
Is this emergency surgery, urgent surgery, or elective surgery? What are examples of emergency surgery, urgent surgery, and elective surgery? Emergency surgery www.qureshiuniversity.com/emergencysurgery.html Urgent surgery href://www.qureshiuniversity.com/urgentsurgery.html Elective surgery href://www.qureshiuniversity.com/electivesurgery.html | |
|
Question 39
Questions to be answered in postoperative notes. | |
|
Question 40
Questions to be answered in follow-up consultations. How did the patient improve or was helped by the specific procedure or surgery? | |
|
Question 41
In general, how is your physical and mental health? | |
| I have read and agree to the Terms & Conditions. | |
|
These are basic questions. There are many more. | |
| Surgery: Is it really indicated? |
|
A statement mentions that the surgery department lacks equipments and infrastructure. What type of equipment do you need? If you audit existing surgeries, you will discover that most of them are not required, and there has been wrong clinical diagnosis. A diagnosis of appendicitis: on operation, no findings of appendicitis. A diagnosis of cholecystitis or cholelithiasis: on operation, no findings of cholecystitis or cholelithiasis. A medical doctor is required to make correct clinical diagnoses. A surgeon is basically a medical doctor. They ask for number of unwanted investigations but after that they still cannot reach a correct diagnosis and treatment. |
|
Q: Who is a surgeon? A: A surgeon is a medical doctor with additional training in specific medical procedures. Getting the title of surgeon does not mean he or she is a competent medical doctor. Not all surgeons can perform all medical procedures. Not all medical doctors can perform all medical procedures. Making an eight-inch incision and closing in three layers does not prove you are a surgeon or a medical doctor. Doing a burr hole and closing does not prove you are a surgeon. This is a medical or surgical procedure that can be taught in a few weeks. Doing medical or surgical procedures does not prove you are a competent medical doctor. The ability to reach to a correct diagnosis and provide treatment is a requirement of all medical doctors while maintaining good character and good behavior. |
| Surgical Skills |
| What type of suggestions should a medical doctor (MD) forward to improve training programs in health care and medical education? |
| What do you have to do in case you need to be a surgeon? |
| What questions should a medical doctor or surgeon ask an anesthetist? |
|
What are the different types of surgery? What are the surgical specialties? |
Neurosurgery
Q: What is a neurosurgeon? Q: Who sees a neurosurgeon? Q: What might neurological care involve? Q: What areas of care are available? Q: Who is a neurosurgeon? Q: What does neuroscience care involve? Q: Where is the neuroscience patient cared for? Q: What medical conditions require brain surgery? Q: What risks are associated with brain surgery? Q: How is brain surgery done? Q: What are other names for brain surgery? Here are further guidelines. |
Cardiothoracic surgery
Q: What is an MCh in cardiovascular and thoracic surgery? Q: How many MCh's in cardiovascular and thoracic surgery are required in the state? Q: What skills and knowledge are needed for an MCh in cardiovascular and thoracic surgery? Q: What are the duties and responsibilities of a person with an MCh in cardiovascular and thoracic surgery? Q: What equipment does cardiovascular and thoracic surgery need? Q: What other resources does cardiovascular and thoracic surgery need? Here are further guidelines. |
| Oral and maxillofacial surgery |
| Otolayrngology |
| Eye Surgery |
| OB/GYN Surgery |
| Paediatric surgery |
| Plastic Surgery |
| Orthopaedic surgery |
| Urology |
General surgery
Do all cases of cholecystitis or gallstones need surgery? Dr. Qureshi's technique Q: What are the advantages of laparoscopy? A: It is less invasive, cost effective, results in fewer infections, and shorter hospital stay. Also, early return to work, minimal postoperative complications, and cosmetic advantages, too. Can appendicitis be managed with endoscopic/Laparoscopy removal without general anesthesia? Q: What does the surgeon use to close the wound? Q: What is the difference between sutures, staples and Steri-Strips? Q: Do all sutures dissolve? Q: Is it painful to have sutures and staples removed? Q: How is the wound bandaged? Q: How should I care for my wound? Q: Is it normal for the wound to itch? Q: How do I take care of my wound at home? Q: When can I take a shower? Q: Does it take a long time for the wound to heal? Do you have a question? Can you make me wiser? How? Can you make us wiser? How? Would you like to add anything? Who among you has done laparoscopic surgery? How many surgeries have you done so far? What was the diagnosis? What were the indications? What were the results? Were there any post- procedure complications? What were these complications? What is been done to prevent these complications? Who is the manufacturer of the equipment? What is the material of the existing equipment? What is been done to enhance the efficiency of a laparoscopy? What is been done to train others? Who has the responsibility to fund this research and development? |
|
Surgical Skills
Do you know various surgical skills? What are various surgical skills? What is a surgical technique? A systematic surgical procedure by which a medical condition is treated. What questions should you answer in case you introduce new surgical technique? Is this a new surgical technique or already listed in surgical skills practiced by others on human beings? New Surgical Technique Is there any specific name for this new surgical technique? What is the name of this new surgical technique? Have you discussed with other doctors the benefits, complications, and harms due to this new surgical technique? For what type of patients is diagnosis and treatment with this new surgical technique useful? How is this surgical technique going to improve the condition of the patient? How is this surgical technique performed, from beginning to end? For what medical condition is this surgical technique the only option of treatment? What issues is this medical condition causing the patient? What complications can occur due to this surgical technique? Why was there a need to elaborate on these facts? On September 12, 2013, Department of Surgical Gastroenterology SKIMS started sophisticated pancreatic surgery, pancreaticoduodenectomy with portal venous resection and later reconstruction. A team of surgeons headed by Prof. Omar Javed Shah was the first of its kind in Kashmir. The above questions were not answered in the academic deliberations. |
