|
Steel What are three main shapes in which steel products can be manufactured? 1. Plate/Coil. 2. Pipe/Tube. 3. Stainless Steel. 4. Structure Steel. TIANJIN HONGTANGDA STEEL http://www.htdsteel.com/en/single/menu_33.htm?menuid=36 Sheets, plates, and bars. Here are further guidelines. What is steel? How is steel made? What is the difference between iron and steel? How many types of steel are there? How much steel is produced in a year? Is steel environmentally friendly and sustainable? Can steel be recycled? Who invented steel? Why does steel rust? What is steel? Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon containing less than 2% carbon and 1% manganese and small amounts of silicon, phosphorus, sulphur and oxygen. Steel is the world's most important engineering and construction material. It is used in every aspect of our lives; in cars and construction products, refrigerators and washing machines, cargo ships and surgical scalpels. How is steel made? Most steel is made via one of two basic routes: Integrated (blast furnace and basic oxygen furnace). Electric arc furnace (EAF). The integrated route uses raw materials (that is, iron ore, limestone and coke) and scrap to create steel. The EAF method uses scrap as its principal input. The EAF method is much easier and faster since it only requires scrap steel. Recycled steel is introduced into a furnace and re-melted along with some other additions to produce the end product. Steel can be produced by other methods such as open hearth. However, the amount of steel produced by these methods decreases every year. What is the difference between iron and steel? AIron is an element that when combined with carbon and other elements makes steel. How many types of steel are there? Steel is not a single product. There are more than 3,500 different grades of steel with many different physical, chemical, and environmental properties. Approximately 75% of modern steels have been developed in the last 20 years. If the Eiffel Tower were to be rebuilt today, the engineers would only need one-third of the steel. Modern cars are built with new steels that are stronger, but up to 25% lighter than in the past. How much steel is produced in a year? World crude steel production reached 1,414 million metric tons (mmt) in 2010. This is an increase of 15% compared to 2009 and is a new record for global crude steel production. Is steel environmentally friendly and sustainable? Steel is very friendly to the environment. It is completely recyclable, possesses great durability, and, compared to other materials, requires relatively low amounts of energy to produce. Innovative lightweight steel construction (such as in automobile and rail vehicle construction) help to save energy and resources. The steel industry has made immense efforts to limit environmental pollution in the last decades. Energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions have decreased to half of what they were in the 1960s. Dust emissions have been reduced by even more. Can steel be recycled? Yes, very easily. Steel's unique magnetic properties make it an easy material to recover from the waste stream so it can be recycled. The properties of steel remain unchanged no matter how many times the steel is recycled. The electric arc furnace (EAF) method of steel production can use recycled steel exclusively. Steel is the world's most recycled material. Who invented steel? It is not known who produced the first steel. Since 200 BC, many cultures have produced steel in one form or another. A British inventor, Henry Bessemer, is generally credited with the invention of the first technique to mass produce steel in the mid 1850s. Steel is still produced using technology based on the Bessemer Process of blowing air through molten pig iron to oxidise the material and separate impurities. Why does steel rust? Many elements and materials go through chemical reactions with other elements. When steel comes into contact with water and oxygen there is a chemical reaction and the steel begins to change to its original form - iron oxide. In most modern steel applications this problem is easily overcome by coating. Many different coating materials can be applied to steel. Paint is used to coat cars and enamel is used on refrigerators and other domestic appliances. In other cases, elements such as nickel and chromium are added to make stainless steel, which can help prevent rust. Steel Industry World 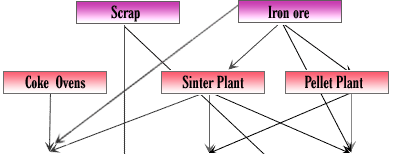
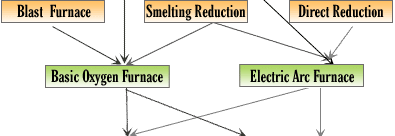
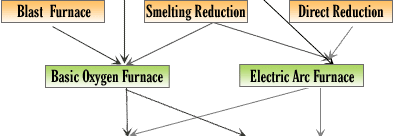
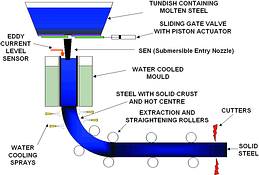 Steel Industry Furnace
Steel Industry Furnace
Steel is the most important engineering and construction material in the world. It is used in every aspect of our lives, from automotive manufacture to construction products, from Cars to refrigerators and washing machines and from cargo ships to the finest scalpel for hospital surgery. Defence, railways, construction, engineering, power, automotive, etc. Q) What's the difference between an alloy and an ore? An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of elements; at least one of the elements must be a metal. An ore is a naturally occuring mixture (usually heterogenous) that contains a particular metal (or a compound of that metal) in amounts that make extraction of the metal economically worthwhile. Q) Can you recycle steel? Q) How many different types of steel are available? Q) How much steel is produced in a year? Q) Is steel environmentally friendly and sustainable? Q) What is a finished product? Q) What is a flat steel product? Q) What is a long steel product? Q) What is a mini-mill? Q) What is a semi-finished product? Q) What is blast furnace iron (BFI)? Q) What is direct reduced iron (DRI)? Q) Where is steel produced? Q) Where are the galvanised plain and corrugated steel sheets, rods and wires produced? Q) What is TMT bar? Q) What is the difference between TMT, HYSD, TOR steel? Casting Superalloys Brazing |
| Galvanizing |
|
Q) How does steel become stainless? A: Adding 10 to 30 percent chromium to steel creates stainless steel, which is very resistant to rust. Q) Do you manufacture aeronautical grade of alloys? Q) What is iron ore? Q) Have you ever wondered how people refine iron and steel? You probably have heard of iron ore, but how is it that you extract a metal from a rock? Q) How Do We Mine Iron Ore? To make iron, you start with iron ore. Iron ore is simply rock that happens to contain a high concentration of iron. Common iron ores include: Hematite - Fe2O3 - 70 percent iron Magnetite - Fe3O4 - 72 percent iron Limonite - Fe2O3 + H2O - 50 percent to 66 percent iron Siderite - FeCO3 - 48 percent iron If you had to pick a few technologies that have had a tremendous effect on modern society, the refining of iron and steel would have to be somewhere near the top of the list. Iron and steel show up in a huge array of modern products. Cars, tractors, bridges, trains (and their rails), tools, skyscrapers, guns, ships -- even the common steel can -- all depend on iron and steel to make them strong and inexpensive. Basic shapes such as plates, sheets, strips, rods, bars, and tubing. This industry also uses blast furnaces and coke ovens. Occupational Safety and Health Administration What OSHA standards apply? What are some examples of hazards and possible solutions in this industry? How can I develop and implement a safety and health program? What additional information is available? What are the duties and responsibilities of this job? What are the skills and knowledge required for this job? Managing Director Executive Director (F&A) Executive Director (Projects) Executive Director (P&A) Executive Director (MM) Executive Director (Works) GM (CRM & Technology) GM (Projects) GM (Services) GM (C&IT) Addl Director (M&HS) GM (Traffic) GM (Electrical) GM (Refractories) GM (Coke Ovens) GM (OHP) GM (Quality) GM (HRD) GM (RGBS) GM (PPC & SC) GM (Mechanical) GM (Vig) & ACVO GM (HRCF) GM (Projects) GM (Shops & Foundries) GM (MARKETING) GM (I & A) GM (SMS-I) GM (P&A) GM (Projects-Modrn Elect) GM (CSR) GM (TS) GM (BF) GM (Safety) GM (Utilities) GM (Projects) GM (HSM) GM (Projects) Addl Director (M&HS) GM (SP) GM (CRM) GM (SMS-II & CCS) GM (MM) Sr Manager (PR) & Chief of Communications Steel Mill Maintenance Steel Mill Operator Steel Mill Schedule Steel Mill Supervisor Steel Plate Fabrication Steel Mill Welders Steel Plant Casting Steel Plant Foremen Plant Manager Mechanical Engineer Plant Maintenance Electrical Maintenance Specialist Structural Iron and Steel Workers Structural Metal Fabricators and Fitters Plant Cafeteria Q) Would you like to add anything? Q) Do you have an answer? Q) Do you have a better answer? Q) Does anyone have a better answer? Q) Does anyone else have an answer better than the answers I already have, we have? Q) Would you like to add anything? Q) Can you make me wiser? How? Q) Can you make us wiser? How? Q) Do you have any recommendations? |
| Safety and health |
| Economics |
| Climate change |
| Sustainability |
| Life cycle thinking |
| Automotive steel |
| Technology |
| Construction |
| Raw materials |
| Packaging |
| Stainless steel |
|
Q) What's the difference between an alloy and an ore?
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of elements; at least one of the elements must be a metal. An ore is a naturally occuring mixture (usually heterogenous) that contains a particular metal (or a compound of that metal) in amounts that make extraction of the metal economically worthwhile. Q) Can you recycle steel? Q) How many different types of steel are available? Q) How much steel is produced in a year? Q) Is steel environmentally friendly and sustainable? Q) What is a finished product? Q) What is a flat steel product? Q) What is a long steel product? Q) What is a mini-mill? Q) What is a semi-finished product? Q) What is blast furnace iron (BFI)? Q) What is direct reduced iron (DRI)? Q) Where is steel produced? Q) Who invented steel? Q) Why does steel rust? Q) Where are the galvanised plain and corrugated steel sheets, rods and wires produced? Q) What is TMT bar? Q) What is the difference between TMT, HYSD, TOR steel? Casting Superalloys Brazing |
| Galvanizing |
|
Q) How does steel become stainless? A: Adding 10 to 30 percent chromium to steel creates stainless steel, which is very resistant to rust. Q) Do you manufacture aeronautical grade of alloys? Q) What is iron ore? Q) Have you ever wondered how people refine iron and steel? You probably have heard of iron ore, but how is it that you extract a metal from a rock? Q) How Do We Mine Iron Ore? To make iron, you start with iron ore. Iron ore is simply rock that happens to contain a high concentration of iron. Common iron ores include: Hematite - Fe2O3 - 70 percent iron Magnetite - Fe3O4 - 72 percent iron Limonite - Fe2O3 + H2O - 50 percent to 66 percent iron Siderite - FeCO3 - 48 percent iron If you had to pick a few technologies that have had a tremendous effect on modern society, the refining of iron and steel would have to be somewhere near the top of the list. Iron and steel show up in a huge array of modern products. Cars, tractors, bridges, trains (and their rails), tools, skyscrapers, guns, ships -- even the common steel can -- all depend on iron and steel to make them strong and inexpensive. Basic shapes such as plates, sheets, strips, rods, bars, and tubing. This industry also uses blast furnaces and coke ovens. History of Steelmaking |
