Classes of words or parts of speech Phrases Clauses Sentences Tenses |
Classes of words or parts of speech
|
How many are there? At least 9. How should you study classes of words or parts of speech in English language? Action verbs Auxiliary primary verbs be, am, are, is, was, were, be, been, being Auxiliary primary verbs: do, does, did Auxiliary primary verbs: have, had, has Auxiliary modal verbs: can, could, will, would Adjectives descriptive (20 categories, from age to touch) Adjectives demonstrative: this, that, these, those Adjective indefinite article: a, an Adjective definite article: the Adjective proper Adverbs of manner: quickly, kindly Adverbs of degree: very, rather Adverbs of frequency: often, sometimes Adverbs of time: now, today Adverbs of place: here, nowhere Determiners (at least 32 of them) Linking verbs Helping verbs Descriptive adjectives Demonstrative adjectives Common Nouns (at least 7 categories among a total of at least 15 categories of nouns) Proper Nouns Prepositions / Simple Prepositions Prepositions / Double Prepositions Prepositions / Compound Prepositions Prepositions / Phrasal Prepositions Prepositions / Participial Prepositions Prepositions / Disguised Prepositions Pronouns / Subject Pronouns: I, We, You, He, She, It, They Pronouns / Object Pronouns: Me, Us, You, Him, Her, It, Them Personal Pronouns Coordinating conjunctions Subordinating conjunctions Interrogative words or phrases (at least 52) Interjections
|
Relative Clause
What are the four types of clauses?
What is a clause?
A clause is a group of words containing a subject and verb. An independent clause is a simple sentence. It can stand on its own.
A phrase is a group of words without a subject-verb component, used as a single part of speech.
Types of Clauses
What are the different types of clauses?
A clause may be built around a finite verb or a non-finite verb.
If it is based on a finite verb, it is called a finite clause.
If it is based on a non-finite verb, it is called a non-finite clause.
Types of Finite Clauses
A finite clause may be independent or dependent.
Main or Independent Clause
Main (or independent) clause is a clause that expresses a complete thought and can stand as a sentence.
What are finite and non finite verbs?
Verbs which have the past or the present form are called FINITE verbs. Verbs in any other form (infinitive, -ing, or -ed) are called NONFINITE verbs. This means that verbs with tense are finite, and verbs without tense are nonfinite.
How many dependent clauses are there?
There are three basic dependent clauses.
Adverb clauses are also known as subordinate clauses.
Adjective clauses are also known as relative clauses.
What is a dependent clause?
A dependent clause has a subject and verb.
A dependent clause does not express a complete thought.
A dependent clause cannot be a sentence.
A dependent clause is dependent on an independent clause to form a complete complex sentence.
What does a dependent clause begin with?
A dependent clause begins with a subordinate conjunction or a relative pronoun.
Subordinating Conjunctions and Relative Pronouns Used with Subordinate Clauses
Adjective clauses.
What words begin an adjective clause in English language?
An adjective clause begins with a relative pronoun (that, who, whose, whom, which) or a subordinate conjunction (when and where).
What is the difference among an adverb clause, adjective clause, and noun clause?
An adverb clause, adjective clause, and noun clause are all dependent clauses.
A noun clause is a dependent clause that functions as a noun.
An adjective clause is a dependent clause that functions as an adjective.
Noun clauses are not written with commas.
Adjective clauses are sometimes set off by commas.
An adverb clause usually starts with a subordinating conjunction.
What is an adjective clause in English language?
Adjective clauses begin with words such as that, when, where, who, whom, whose, which, and why.
An adjective clause—also called an adjectival or relative clause—will meet three requirements: First, it will contain a subject and verb. Next, it will begin with a relative pronoun (who, whom, whose, that, or which) or a relative adverb (when, where, or why). Third requirement?
That / Relative pronoun
Who / Relative pronoun
Whom / Relative pronoun
Whose / Relative pronoun
Which / Relative pronoun
When / Relative adverb
Where / Relative adverb
Why / Relative adverb
Reducing Adjective Clauses to Phrases
An adjective clause that has a subject pronoun (which, that, or who) can also be shortened into an adjective phrase.
You can shorten an adjective clause in two ways:
1.Omit the subject pronoun and verb.
2.Omit the subject pronoun and change the verb so it ends in -ing.
•Adjective Clause: The girl who is leading the parade is my best friend.
•Adjective Phrase: The girl leading the parade is my best friend.
She's the person who is helping us.
She's the person helping us.
who is helping us. / Adjective clause
helping us / Adjective phrase
Can you find the problem that is making the noise?
Can you find the problem making the noise?
that is making the noise / Adjective clauses
making the noise / Adjective phrase
Adverb clauses
What are the words that begin an adverb clause in English language?
An adverb clause in English language begins with a subordinating conjunction.
After, although, because, and if are examples of subordinating conjunctions. An adverb clause contains a subject and a predicate.

Noun clauses
What is a noun clause in English language?
A noun clause is a dependent clause that acts as a noun.
A noun clause usually begins with a relative pronoun.
The structure of the noun clause: relative pronouns or subordinating conjunctions.
Noun clauses can act as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, predicate nominatives, or objects of a preposition.
What are complex sentences starting with a noun clause?
Because something was wrong, I will be investigating this case.
Whoever broke the window, I will be investigating this case.
Can you name various subordinating conjunctions?
How many subordinating conjunctions are there in English language?
There are more than 62.
What are examples of subordinating conjunctions that begin complex declarative sentences in English language?
- After
- Although
- As
- As far as
- As if
- As long as
- As much as
- As soon ss
- As though
- Because
- Before
- By the time
- Even
- Even if
- Even though
- Every time
- How
- If
- If only
- If … then
- If … when
- In case
- In order that
- In that
- Inasmuch
- Inasmuch as
- Insofar as
- Just as
- Lest
- No matter how
- Now
- Now since
- Now that
- Now when
- Once
- Provided
- Provided that
- Rather than
- Rather that
- Since
- So that
- Supposing
- Than
- That
- The first time
- Though
- Till
- Unless
- Until
- When
- Whenever
- Where
- Where if
- Whereas
- Wherever
- Whether
- Whether or not
- Which
- While
- Who
- Whoever
- Why
What are examples of relative pronouns?
- That
- Whoever
- How
- What
- Whatever
- Whatsoever
- When
- Where
- Whether
- Which
- Whichever
- Whichsoever
- Who
- Whom
- Whomever
- Whomsoever
- Whose
- Whosesoever
- Whosoever
- Why
What words start a noun clause in English language?
Noun clauses usually start with relative pronouns.
What are examples of complex declarative sentences beginning with subordinating conjunctions in English language?
After lunch, I will be investigating this case.
After we finish the discussion, I will investigate this case.
After completing this lesson, I will be investigating this case.
After (subordinator) they (subject) finish (verb) studying, I will be investigating this case.
Although the gallery has closed for the day, I will be investigating this case.
As you know, I will be investigating this case.
As soon as the alarm goes off, I will be investigating this case.
As far as I know, I will be investigating this case.
As if harmed, I will be investigating this case.
As long as I know, I will be investigating this case.
As much as I know, I will be investigating this case.
As soon as possible, I will be investigating this case.
As though [need object of “as thoughâ€], I will be investigating this case.
Because she lied on her application, I will investigate this case.
Because she was lying, I will be investigating this case.
Before she lies, I will be investigating this case.
Before I go to bed, I will be investigating this case.
Before I see the house, I will be investigating this case.
Before we arrive at school, I will be investigating this case.
Before you leave for school, I will be investigating this case.
By the time you sleep, I will be investigating this case. Even if you win a million dollars, it doesn’t mean you’ll be happy.
Even though I’d heard the song before, I didn’t know who sang it.
Ever since I met her, I haven’t been able to think about anything else.
Every time there is complaint, I will investigate this case.
If you find out, please let us know.
If you find out, I will investigate this case.
If you want to speak to me, then learn English.
If only harmed, I will be investigating this case.
If harmed, then I will be investigating this case.
If harmed, when will I be investigating this case?
In case you are harmed, I will be investigating this case.
In order that you are not harmed, I will be investigating this case.
In that you were harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Inasmuch as you were harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Insofar as you were harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Just as he was harmed, I started investigating this case.
Lest harmed, I will be investigating this case.
No matter how harmful, I will be investigating this case.
Now healthy, I will be investigating this case.
It’s been three years now since I was harmed, so I will be investigating this case.
Now that he is harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Now when someone is harmed, I investigate the case.
Once this harm is known, I will investigate the case.
Provided no one is harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Provided that no one is harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Rather than be harmed, I will be investigating this case.
It isn’t that I will be harmed, but rather that I will be investigating this case.
Since harmed, I have been investigating this case.
So that no one is harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Supposing that someone might be harmed, I will be investigating this case.
So sure am I about potential harm that I will be investigating this case.
So that I’m sure, I will be investigating this case.
Since you are coming over anyway, I will be investigating this case.
Though he harmed me, I will still be investigating this case.
Than this harmed, I will be investigating this case.
That no one is harmed, I will be investigating this case.
The first time someone is harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Though harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Till you understand who was harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Unless you’re willing to understand who was harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Until spring arrives, I will be investigating this case.
Unless this harms me, I will be investigating this case.
Until I understand this harm, I will be investigating this case.
Whenever he is harmed, I will investigate the case.
Where this harm occurs, I will investigate the case.
Where if this has been harmful, I will be investigating this case.
Whereas this has been harmful, I will be investigating this case.
Wherever harm occurs, I will be investigating the case.
Whether he has been harmed or not, I will be investigating this case.
Which issues has harmed, I will be investigating this case.
While this has been harmful, I will still be investigating this case.
To determine who may have been harmed, I will be investigating this case.
Whoever harmed him, I will investigate the case to find you.
To understand why he was harmed, I will be investigating this case.
When Amy wrote an amazing paragraph, she earned an A+ in the course.
When I read the story, I will investigate the case.
When we’re done, let’s get some ice cream.
When you get home, call me.
Whether or not you agree, I will be investigating this case.
While I’m there, I will be investigating this case.
While we are on the way, I will be investigating this case.
Wherever harm occurs, I will investigate the case.
Relative pronouns.
To determine that harms have occurred, I will be investigating this case.
Whoever is harmed, I will be investigating this case.
To know who may have been harmed, I will be investigating this case.
To whom this may concern, I will be investigating this case.
To help whomever he harmed, I will be investigating this case.
To know which location may have been harmed, I will be investigating this case.
To know whichever harms occurred, I will be investigating this case.
Subordinating Conjunctions
|
What is a Subordinating Conjunction? Subordinating conjunctions are essential parts of complex sentences with include at least two clauses, with one of the clauses being main (independent) and the other being subordinate (dependent). Subordinating conjunctions are parts of speech that join dependent clauses to independent clauses. Sometimes referred to as subordinators or subordinate conjunctions, these important words and phrases may also introduce adverb clauses. Subordinating Conjunction Exercises The following exercises will help you gain greater understanding about how subordinating conjunctions work. Choose the best answer to complete each sentence. 1._________ the basement flooded, we spent all day cleaning up. 1.After 2.Although 3.Before 4.Even if Answer: 1. After the basement flooded, we spent all day cleaning up. 2.I don’t want to go to the movies ÂÂÂ_____________ I hate the smell of popcorn. 1.Although 2.Because 3.Whenever 4.So that Answer: 2. I don’t want to go to the movies because I hate the smell of popcorn. 3.I paid Larry, ___________ garden design work is top-notch. 1.Whenever 2.Whose 3.After 4.If Answer: 2. I paid Larry, whose garden design work is top-notch. 4.___________ spring arrives, we have to be prepared for more snow. 1.Because 2.Until 3.Although 4.Now that Answer: 2. Until spring arrives, we have to be prepared for more snow. 5._____________ the alarm goes off, I hit the snooze button. 1.As soon as 2.Because 3.Before 4.Now that Answer: As soon as the alarm goes off, I hit the snooze button. Subordinating Conjunctions List 
There are many subordinating conjunctions. This list contains 25 of those most commonly used. After Although As As soon as Because Before By the time Even if Even though Every time If In case Now that Once Since So that Than The first time Unless Until When Whenever Whether or not While Why |
Phrase Examples
|
Adjective phrase
What Is an Adjective Phrase? An adjective phrase is a group of words used collectively to describe a noun or pronoun in a sentence. The big white hen ran away. big white / Adjective Phrase Adjective phrases: position When an adjective is used with a noun, the usual order in English is adjective + noun: a yellow balloon Not: a balloon yellow Adjectives can go before the noun (attributive) or after linking verbs such as be, become, seem (predicative): What a beautiful flower! (attributive) This bridge looks unsafe. (predicative) Adverb phrase Time goes very quickly. very quickly. An adverb phrase can modify a verb, an adjective, another adverb, or even an entire sentence or main clause. As show below, it can appear in a number of different positions in a sentence. 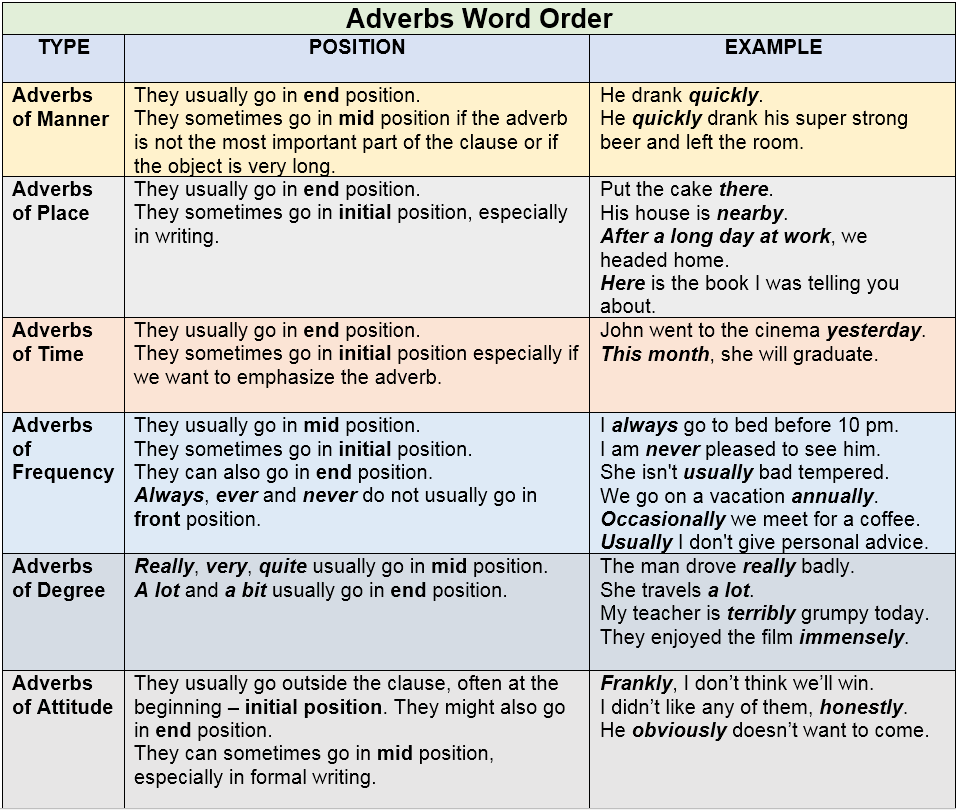
Noun phrase What is a noun phrase? Noun Phrase-a noun and any words in the sentence that modify it; words that can modify nouns include articles (a, an, the); adjectives; participles; and possessive pronouns 1. A noun phrase can be a subject: 2. A noun phrase can be a direct object: 3. A noun phrase can be the object of a preposition: 4. A noun phrase can be an indirect object: What are examples of noun phrases in English language? Examples of Noun Phrases: Examples of noun phrase as subject : The yellow house is for ____.The glistening snow covered the field. Examples of noun phrase as direct object: I want a skate board. Should we buy the yellow house? Examples of noun phrase as object of preposition: Jeff rode on a skate board. Karen lives in the yellow house. Example of noun phrase as indirect object: Lisa gave the little girl a candy. Verb PhrasesA verb phrase consists of a verb and all its modifiers. The brilliant Doctor Asif Qureshi will be investigating this case.The is the determiner. Brilliant is the descriptive adjective. Doctor Asif Qureshi = proper noun will be investigating = verb phrase This case = object Here are examples:
She was upset when it didn't boil. You have been sleeping for a long time. You might enjoy a massage. He was eager to eat dinner. Gerund PhrasesA gerund phrase is simply a noun phrase that starts with a gerund. Examples include:
Infinitive PhrasesAn infinitive phrase is a noun phrase that begins with an infinitive. Here are some examples:
Appositive PhrasesAn appositive phrase restates a noun and consists of one or more words. Examples are:
Participial PhrasesA participial phrase begins with a past or present participle. Examples are:
|
Prepositional Phrases
|
A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and can act as a noun, an adjective or an adverb. What is a Prepositional Phrase?Prepositions are words which begin prepositional phrases. A prepositional phrase is a group of words containing a preposition, a noun or pronoun object of the preposition, and any modifiers of the object. A preposition sits in front of (is “pre-positioned†before) its object. Every prepositional phrase is a series of words made up of a preposition and its object. The object may be a noun, pronoun, gerund or clause. Adjective and Adverb Prepositional Phrases There are two kinds of prepositional phrases: adjective phrases and adverb phrases. An adjective phrase modifies a noun or pronoun. It always comes immediately after the noun or pronoun it modifies: Joe is the student with the highest grade. ("with the highest grade" modifies "student.") An adverb phrase modifies a verb, adjective, or adverb. It is used to tell when, where, how, or to what extent about the word it modifies: Megan put her bird in its cage. ("in its cage" modifies the verb "put.") Examples are:
I'll arrive sometime ___ 8 and 9 am. between in next to on Correct! between The shops here are open ___ 9am until 5pm.v from for on at Correct! from They should be ready to go ___ 20 minutes. in on by to Correct! in She wants to stay ___ home tonight. of to at in Correct! of Did you watch the football ___ TV last night? on by in to Correct! on Do you always come to work ___ bike? on in of by Correct! by I read the news ___ the newspaper. on by to in Correct! in I'll be in the office ___ 5pm. until for on since Correct! until You must have this report finished ___ Monday. at by since while Correct! by I haven't had a call from him ___ last Wednesday. on since in for Correct! since |
Absolute Phrases
|
An absolute phrase has a subject, but not an acting verb, so it cannot stand alone as a complete sentence. It modifies the whole sentence, not just a noun. Examples are:
These are examples of all of the eight different kinds of phrases. Interrogative PhrasePosition of Interrogative Phrases in Content QuestionsContent questions are questions that contain an interrogative phrase, like the elements in boldface in the English examples in (1). (1) a. Who did you see? b. Which book do you want to buy? c. When are you going to ________? What day is it today? What = Question word Day = Noun Question word + Noun Interrogative Phrase |
Can you name various interrogative parts of questions?
How many interrogative parts of a question are there in English language?
There are more than 45.
There are more than 45 interrogative parts of a question in English language.
What are the various interrogative parts of a question in English language?
|
|
What is an English grammatical tense? An English grammatical tense is a sentence with tense that points to the past, present, or future time. Tenses are applicable to declarative sentences and questions. How many English grammatical tenses are there? At least 16. If you include conditionals with could or would, there are more. |
You can change future continuous tense to one of the 11 other tenses in English language.
|
Who investigates this case? Present simple tense Who investigated this case? Past simple tense Who will investigate this case? Future simple tense Who is investigating this case? Present continuous tense Who was investigating this case? Past continuous tense Who will be investigating this case? Future continuous tense Who has investigated this case? Present perfect tense Who had investigated this case? Past perfect tense Who will have investigated this case? Future perfect tense Who has been investigating this case? Present perfect continuous tense Who had been investigating this case? Past perfect continuous tense Who will have been investigating this case? Future perfect continuous tense |

