How do you manufacture electrical equipment in the state?
Answer these questions.
What electrical equipment is required in the state that needs to be manufactured?
What electrical equipment in the alphabetical list of electric products needs to be manufactured relevant to a specific state?
What specification does the product need to have?
What raw materials with quantity are required to manufacture these products per year?
How many such products are required?
When are such products required?
What processes are available in the manufacture of this product?
What is the best process to manufacture this product?
How many electrical engineers have the ability to learn to manufacture these products within the state?
How many existing locations are there for the manufacture of such electrical products?
What is the profile of the electrical engineers in the state who will assist in the manufacture of these electrical products?
Who is the guide?
Asif Qureshi
What will happen once these questions are answered?
A specific electrical product to be manufactured will be identified with specifications, total number, and raw materials.
A separate section has to be created to manufacture specific electrical product with guidelines in the state. A team will manufacture this product.
How do you classify electrical equipment?
Assembly Automation and General Factory Machinery
Building electrical equipment.
What are examples of building electrical equipment?
-
Appliances
-
Building Wires
-
Circuit breakers and disconnects
-
Conduit and Wire
-
Electric switchboards
-
Electric motor
-
Electrical Box Covers
-
Electrical Fittings Products
-
Electrical Junction Boxes
-
Electricity meter
-
Electrical sockets
-
Electrical Switches
-
Junction box
-
Lampholders
-
Lamps
-
Power Inverter
Here are further guidelines.
http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/buildingelectricsystem.html
Appliance may refer to:
Home appliance, household machines, using electricity or some other energy input
Small appliances
Major appliances
In medicine and dentistry, custom-fitted appliances to an individual for the purpose of correction of a physical or dental problem such as:
A prosthesis
An orthotic appliance
dental braces
Computer appliance, a computing device with a specific function and limited configuration ability
Software appliance, software application combined with just enough operating system (JeOS)
Fire apparatus, a fire engine or fire truck in British English
In film, a term for latex pieces, such as false ears or other features, used by make-up artists
Appliance (band), a British musical group
|
Data center for guidelines.
Electricity generation plant equipment.
Most power plants make electricity with a machine called a generator.Generators have two important parts: the rotor (which rotates) and the stator (which remains stationary). Generators use the principle of electro-magnetic induction, which exploits the relation between magnetism and electricity. In large AC generators, an outer shell with powerful magnets rotates around a stationary "armature" which is wound with heavy wire. As they move, the magnets induce an electric current in the wire.
It is important to recognize that electricity is not mined or harvested, it must be manufactured. And since it's not easily stored in quantity, it must be manufactured at time of demand. Electricity is a form of energy, but not an energy source. Different generating plants harness different energy sources to make electric power. The two most common types are "Thermal Plants" and "Kinetic Plants".
Thermal Generating Plants
Kinetic Generating Plants
Here are further guidelines.
http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/electricitygenerationplantequipment.html
Here are further guidelines.
http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/electricalproducts.html
|
Heavy electrical equipment.
What is heavy electrical equipment?
Heavy electrical equipment is large, permanently installed machinery.
What are examples of heavy electrical equipment?
-
Automation and Control Systems
-
Boilers
-
Conveyor belt systems
-
Elevators
-
Escalators
-
Gas and Steam Turbines
-
Generators
-
Heat Exchangers
-
Hydraulic, steam, gas, and wind turbines
-
Large generators
-
Power electronics
-
Power grid equipment, such as transformers.
-
Pumps
-
Sensors
-
Switchgears
-
Transmission systems etc.
Here are further guidelines.
www.qureshiuniversity.com/electricalequipmentheavy.html
|
Major appliances.
What are examples of major appliances?
Refrigeration equipment
Freezer
Refrigerator
Water cooler
Stoves
Cooker, also known as range, stove, oven, cooking plate, or cooktop
Electric Stoves
Microwave oven
Washing equipment
Washing machine
Clothes dryer
Drying cabinet
Dishwasher
Miscellaneous
Air conditioner
Water heater
|
Microcontrollers.
What are examples of microcontrollers?
ARM core processors (many vendors)
ARM Cortex-M cores are specifically targeted towards microcontroller applications
Atmel AVR (8-bit), AVR32 (32-bit), and AT91SAM (32-bit)
Cypress Semiconductor's M8C Core used in their PSoC (Programmable System-on-Chip)
Freescale ColdFire (32-bit) and S08 (8-bit)
Freescale 68HC11 (8-bit)
Intel 8051
Infineon: 8-bit XC800, 16-bit XE166, 32-bit XMC4000 (ARM based Cortex M4F), 32-bit TriCore and, 32-bit Aurix Tricore Bit microcontrollers[12]
MIPS
Microchip Technology PIC, (8-bit PIC16, PIC18, 16-bit dsPIC33 / PIC24), (32-bit PIC32)
NXP Semiconductors LPC1000, LPC2000, LPC3000, LPC4000 (32-bit), LPC900, LPC700 (8-bit)
Parallax Propeller
PowerPC ISE
Rabbit 2000 (8-bit)
Renesas Electronics: RL78 16-bit MCU; RX 32-bit MCU; SuperH; V850 32-bit MCU; H8; R8C 16-bit MCU
Silicon Laboratories Pipelined 8-bit 8051 Microcontrollers and mixed-signal ARM-based 32-bit microcontrollers
STMicroelectronics STM8 (8-bit), ST10 (16-bit) and STM32 (32-bit)
Texas Instruments TI MSP430 (16-bit) C2000 (32-bit)
Toshiba TLCS-870 (8-bit/16-bit).
|
Road electrical equipment.
What are examples of transmission electrical equipment (point of production/power generation to the point of demand/building)?
What are examples of road electrical equipment?
-
Road Lamps
-
Traffic Lights
-
Utility Poles
-
Wires
|
Power tools.
What are examples of power tools?
-
Air compressor
-
Alligator shear
-
Angle grinder
-
Bandsaw
-
Belt sander
-
Biscuit joiner
-
Brushcutter
-
Ceramic tile cutter
-
Chainsaw
-
Circular saw
-
Concrete saw
-
Cold saw
-
Crusher
-
Diamond blade
-
Diamond tools
-
Disc sander
-
Drill
-
Floor sander
-
Food Processor
-
Grinding machine
-
Heat gun
-
Hedgecutter
-
Impact wrench
-
Impact driver
-
Iron
-
Jackhammer
-
Jointer
-
Jigsaw
-
Knitting Machine
-
Lathe
-
Lawn Mower
-
Leafblower
-
Miter saw
-
Nail gun (electric and battery as well as powder actuated)
-
Needle scaler
-
Pneumatic torque wrench
-
Powder-actuated tools
-
Power wrench
-
Radial arm saw
-
Random orbital sander
-
Reciprocating saw
-
Rotary reciprocating saw
-
Rotary tool
-
Rotovator
-
Sabre saw
-
Sander
-
Scrollsaw
-
Sewing Machine
-
Steel cut off saw
-
Strimmer
-
Table saw
-
Thickness planer
-
Vacuum Cleaner
-
Wall chaser
-
Washing machine
-
Wood router
|
Portable electrical equipment (small appliances).
What are examples of portable electrical equipment (small appliances)?
-
Cooking, such as on a hot plate or with a slow cooker, microwave oven, rice cooker, bread machine, a tortilla/roti maker, or a sandwich toaster
-
Heating, such as an electric heater
-
Cooling, such as air conditioning
-
Lighting using light fixtures
-
Speaker-architectural, as in being of the infrastructure/structural type
-
Speaker-floorstanding, on-wall or in-wall varieties
-
Beverage-making, such as electric kettles, coffeemakers or iced tea-makers
-
MP3 Player - including but not limited to the Apple iPod
Computers - laptops, desktops, ultrabooks, etc.
|
Some consider small appliances to be electronic equipments.
Transmission electrical equipment (point of production/power generation to point of demand/building).
Vehicle electric equipment.
What are examples of vehicle electric equipment?
www.qureshiuniversity.com/vehicleelectricequipment.html.
What are examples of major electrical appliances and small electrical appliances?
http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/statedepartmentofelectricity.html
Who has the duty in the state to manufacture, repair, and replace various types of electrical equipment in the state?
Engineers who work for the state department of engineering.
Engineers who work for the state department of electricity or PDD (power development department).
Profiles of all engineers in the state are required.
Profiles of all engineers with ability to manufacture electrical equipments in the state are required.
What should happen if any product is not manufactured or repaired within the state?
Work order or needs should be forwarded to another state.
Issue directive to manufacture and repair such products within the state.
Electrical equipment manufacturing and repairs.
How should electrical equipment manufacturing and repair plants be established in the state?
Electrical equipment manufacturing plant in the state.
Electrical equipment repairs plant in the state.
What are existing locations of electrical equipment manufacture and repair plants in the state with name of the state?
How many more such manufacturing plants with specifications are required in the state?
Each plant has further subdivisions relevant to each type of equipment.
Here are further guidelines.
http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/statedepartmentofelectricity.html
|
Telecommunications equipment
Electrical engineers manufacture telecommunications equipment.
Telecommunications equipment is considered one of the categories of electrical equipment.
Can a telephone exchange, data center, or answering machine work without electrical supply?
No.
What are examples of telecommunications equipment?
Here are various examples.
www.qureshiuniversity.com/telecommunicationsequipment.html
Telecommunications equipment can be broadly broken down into the following categories:
Public switching equipment
Analogue switches
Digital switches
Transmission equipment
Transmission lines
Optical fiber
Base transceiver stations
Multiplexers
Local loops
Communications satellites
Customer premises equipment
Private switches
Local area networks
Modems
Mobile phones
Landline telephones
Answering machines
Teleprinters
Fax machines
Pagers
Routers
A data center is required for telecommunications services in the state or outside the state.
Here are further guidelines.
|
Transformers
What is a Transformer?
What are typical applications for
transformers?
How are transformers classified?
How are power transformers used?
Here are further guidelines.
|
Wire
A wire is a single, usually cylindrical, flexible strand or rod of metal. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads or electricity and telecommunications signals. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Wire gauges come in various standard sizes, as expressed in terms of a gauge number. The term wire is also used more loosely to refer to a bundle of such strands, as in 'multistranded wire', which is more correctly termed a wire rope in mechanics, or a cable in electricity.
What is raw material?
Basic substance in its natural, modified, or semi-processed state, used as an input to a production process for subsequent modification or transformation into a finished good.
Vast quantities of aluminium, copper, nickel and steel wire are employed for telephone and data cables, and as conductors in electric power transmission, and heating. It is in no less demand for fencing, and much is consumed in the construction of suspension bridges, and cages, etc.
Not all metals and metallic alloys possess the physical properties necessary to make useful wire. The metals must in the first place be ductile and strong in tension, the quality on which the utility of wire principally depends. The metals suitable for wire, possessing almost equal ductility, are platinum, silver, iron, copper, aluminium and gold; and it is only from these and certain of their alloys with other metals, principally brass and bronze, that wire is prepared.
By careful treatment extremely thin wire can be produced. Special purpose wire is however made from other metals (e.g. tungsten wire for light bulb and vacuum tube filaments, because of its high melting temperature). Copper wires are also plated with other metals, such as tin, nickel, and silver to handle different temperatures, provide lubrication, provide easier stripping of rubber from copper.
Production
Wire is often reduced to the desired diameter and properties by repeated drawing through progressively smaller dies, or traditionally holes in draw plates. After a number of passes the wire may be annealed to facilitate more drawing or, if it is a finished product, to maximise ductility and conductivity.
Finishing, jacketing, and insulating
Electrical wires are usually covered with insulating materials, such as plastic, rubber-like polymers, or varnish. Insulating and jacketing of wires and cables is nowadays done by passing them through an extruder.
Two or more wires may be wrapped concentrically, separated by insulation, to form coaxial cable.
What is Wire Rope?
Wire rope consists of one or more numbers of strands, laid spirally around one core of steel or fibre core. Generally, most widely used ropes are of six strands.
Wire rope consists of three basic components, while few in numbers, these vary in both complexity and configuration, which allow the production of rope for specific purposes or with specific characteristics.
The three basic components of a standard wire rope design are:
Wires (that form the strands)
The core
Multi-wire strand: laid helically around a core
The wire, for rope, is made from several materials such as steel, iron, and/or stainless steel. High Carbon steel is the most widely used material, available in a variety of grades, each of which has the properties related to the basic curve for steel wire rope. Wire rope manufacturers select a wire type which is most appropriate for the specific purpose of the finished product.
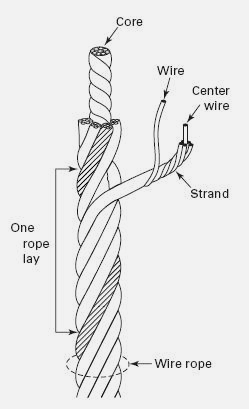
Wire rope nomenclature also defines the following:
Rope Description
Length
Size (diameter)
Preformed (pref) or non-preformed (non-pref)
Direction and type of lay
Finish
Grade of rope
Type of core
Types of Wire rope
What is AWG (American Wire Gage)?
What Does Wire Gage Have to Do with a Wire's Electrical Properties?
Here are further guidelines.
Wire
|
|

