Facilities Maintenance Engineer
Questions relevant to your profession.
http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/facilitiesmaintenanceengineer.html
|
What profession is been described in these guidelines? What are other names for this profession? What other professions should you differentiate from this profession? What abilities/skills should you have relevant to this profession? What is consultation? What type of consultation is required from this professional? What questions should be answered relevant to repairs? What need repairs in the building and is the facilities maintenance engineer able to fix the faults/problems? What are building blueprint? What are the features of building blueprints? Who maintains records of building blueprints in the state? How are building blueprints useful? What are other names for building blueprints? How do you make building blueprints? How do you read building blueprints? Who should know about building blueprints? What’s the difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker? What should you do if you need to take over duty from other individual? What facts did the previous worker hand over to you? What facts should have been transmitted to you? What resource has better products? What is operations management? What types of test are usually done on electric home appliances? Did the maintenance engineer test the electric appliance (electric stove) fault/problem with a scientific method? How did the maintenance engineer test the electric appliance (electric stove) fault/problem? How should the maintenance engineer have tested the electric appliance (electric stove) fault/problem by a scientific method? What are Watts? How is Electricity Measured? How much electricity do household items use? What are amps, watts, volts and ohms? How many watts does a house use? How many watts does a TV use? How many watts does a refrigerator use? What equipment does a maintenance engineer need to fix electric stove faults/problems? What are the types of maintenance engineer? What are other names for a facilities maintenance engineer? What should a facilities maintenance engineer know? What is the department affiliation in the state for this profession or occupation? How long does it take to get educated for this profession? What minimum equipment or resources are required for this profession? What other equipment or resources are required for this profession from time to time? What minimum knowledge is required for this profession? What maximum knowledge is required for this profession? What are the usual duties/tasks for the profession/occupation? What questions should you ask in this situation? What type of engineer is required for electric stove maintenance, repairs, and operations? Who is the supervisor for this position? Is there a difference between a facilities maintenance engineer and a facilities maintenance technician? What is the difference between facilities maintenance engineer and Facilities Maintenance Technician? What are you expected to know relevant to this profession? What are examples of emergencies relevant to this profession in the state? How should you do maintenance of a building? What best describes the building? Where are work orders for repairs or maintenance by residents submitted in the building? What questions should the facility maintenance engineer answer as soon as he or she receives work orders for repairs or maintenance? Does this work orders for repairs or maintenance need to be completed within 24 hours? Is the fault/problem within the building or outside the building? What work orders for repairs or maintenance need to be completed within 24 hours after they are received? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Annotation or definition. What profession is been described in these guidelines? Facilities Maintenance Engineer. What are other names for this profession? Building Service Engineer Building Maintenance Engineer What other professions should you differentiate from this profession?
Abilities. What abilities/skills should you have relevant to this profession? General abilities. Profession-specific abilities. General abilities. English language understanding, reading, writing, and speaking. Credibility. (You should never lie.) Politeness (speech, manners, behavior). Desire for public service. Consultation What is consultation? The process of getting advice from an expert or a professional person. What type of consultation is required from this professional? Building Maintenance & Repairs Repairs What questions should be answered relevant to repairs? Questions you need to answer. What type of product is it? What is the year of manufacture of this product? How long has this product been in use? What is the problem/fault with this product at this point? What was the date, time, location, and circumstances that this problem/fault occurred? What are the specifications of the product? What are the dimensions of the product? Where exactly is the problem/fault with this product at this point? How did you find out exactly the problem/fault with this product at this point? Can this product be repaired? How long will it take to repair the product? What type of repair does this product need? What need repairs in the building and is the facilities maintenance engineer able to fix the faults/problems? Major appliances: Refrigeration equipment, stoves, washing equipment, air conditioners, water heaters, computers, televisions, amplifiers, receivers, projectors). Small appliances: Television and wireless sets, microwave ovens, coffee makers, personal computers) Consumer electronics: Radio receivers, television sets, MP3 players, video recorders, DVD players, digital cameras, camcorders, personal computers, video game consoles, telephones, mobile phones. Building blueprints What are building blueprint? Design drawings that indicate the size of a building, the materials used in its construction, and the placement of its features. Drawings must be understood by others. Drawings must be accomplished with questions and answers. Building drawings should always be enclosed with questions and answers relevant to the building. What are the features of building blueprints? Plot map Floor plans Elevations Foundation plan Details Sections Interior elevations Who maintains records of building blueprints in the state? The state public records department maintains these facts. The resource that constructed the building also maintains these records. How are building blueprints useful? The facilities maintenance engineer needs building blueprints for repairs and maintenance. At the point of renovation, building blueprints are required. To build an addition to an existing building, blueprints are required. What are other names for building blueprints? Building drawings. Building house plan. Homes designs. House plans. How do you make building blueprints? How do you read building blueprints? Know the scale in which the blueprint is displayed. Understand the symbols used to represent the components of a building project. Who should know about building blueprints? Construction workers Architects/engineers Facilities maintenance engineers. Questions that should be answered relevant to a building. What is the plot/land map and location in the state? What are the dimensions of the plot/land? What is the plinth area of the building? What does the floor plan of the building look like? What are the east, west, north, and south views of the building? How many floors is the building? Facility Profile Sheet Here are further guidelines. Facilities Here are further guidelines. Building Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. At least 40 questions relevant to a building need to be answered. Building electric system What’s the difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker? Fuses and circuit breakers are both found in the electrical panel (or sub-panel) of a house. They both serve the purpose of cutting the flow of electricity when a circuit gets overloaded—a potentially dangerous situation. Circuit breakers will be found in most houses built after the 1960s or in older buildings that have had their electrical systems upgraded. Fuses have a thin strip of metal that literally blows when there’s too much electricity flowing through it. When this happens, the fuse needs to be taken out and replaced. Since the 1960s circuit breakers have been used instead of fuses. They are more convenient, as they just need to be flipped back on if they are tripped. Unlike a fuse, they don’t need to be replaced. Both circuit breakers and fuses are rated according to how much electricity can flow through them before they trip and shut down the circuit. A 15- or 20-amp fuse is typical for regular light fixtures and such. If the right fuse or circuit breaker isn’t used, it can cause a dangerous situation. Clearly, if a fuse or circuit breaker becomes problematic, an electrician should be called in to look at it. Building electric system Here are further guidelines. Duty handover What should you do if you need to take over duty from other individual? Duty takeover should be done while getting all the facts. What facts did the previous worker hand over to you? What facts should have been transmitted to you? Electrical Safety in the Workplace Fact Sheet Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected against physical, social, spiritual, economic, political, emotional, occupational, psychological, educational or other types or consequences of failure, damage, error, accidents, harm or any other event which could be considered non-desirable. How long have you been doing electrical repairs or troubleshooting? What electrical responsibilities do you know are within your training? What electrical responsibilities do you know are outside your training? What type of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is available to you when working on or near live electrical equipment? What action does your facility need to take to comply with the revised Electrical Standards? Why is it so important to work safely with or near electricity? What do I need to know about electricity? What kinds of injuries result from electrical currents? What should I do if I think I am too close to overhead power lines? What are some general safety tips for working with or near electricity? What are some tips for working with power tools? What are some tips for working with power cords? What is a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)? When and how do I test the Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)? What is a sample checklist for basic electrical safety? What resource has better products? http://betterchefimpress.com/pages/contact-us/ Who has the duty to manufacture various products in the state? The state department of engineering. Who has the duty to distribute various manufactured products in the state? The state department of human services. In various regions, this department is known by food and supplies, consumer affairs public distribution system, or some other name. What materials must every state department of engineering manufacture within the state? Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/statedepartmentofengineering.html Department affiliation What is the department affiliation in the state for this profession or occupation? State department of engineering Education How long does it take to get educated for this profession? In olden days, this used to take 5-7 years. With Internet education, an individual can become a Facilities Maintenance Engineer in less than 5 years. The desire to learn and a desire for public service is prerequisite for a Facilities Maintenance Engineer. Emergencies Emergency Maintenance How to deal with emergencies relevant to this profession What are examples of emergencies relevant to this profession in the state? http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/emergencymaintenance.html Education Knowledge What minimum knowledge is required for this profession? What maximum knowledge is required for this profession? Advanced Boiler Operations Advanced Projects Basic Refrigeration Boiler Operations and Certification Building Maintenance and Repair Methods Communications Computer Applications Computers Electrical Service Engineering Drawings Fundamentals of Electricity Grounds Keeping Human Relations HVAC Systems Introduction to Blueprint Reading Introduction to Building Maintenance Introduction to Hydraulics/Pneumatics Introduction to Remodeling Machine Components Mathematics Mechanical and Machine Maintenance Safety Principles Safety Principles Tools and Equipment Tools and Equipment Welding Basics Work-based Learning Maintenance Fundamentals Courses Hand Tools Industrial Safety and Health Making Measurements Mathematics in the Plant Metals in the Plant Nonmetals in the Plant Portable Power Tools Reading Blueprints Reading Schematics and Symbols Troubleshooting Skills Electrical Systems Courses AC Control Equipment Basic Electricity and Electronics Batteries and DC Circuits Electrical Measuring Instruments Electrical Safety and Protection Electrical Safety in the Workplace Electrical Troubleshooting Single-Phase Motors Three-Phase Systems Transformers and AC Circuits Mechanical Systems Courses Basic Mechanics Basic Pneumatics Bearings Lubricants and Lubrication Piping Systems Pneumatic Troubleshooting Power Transmission Equipment Pumps Air-Conditioning & Refrigeration Systems Courses Air-Handling Systems Compressors Condensers and Cooling Towers Control Systems Evaporators and Metering Devices Piping Refrigerants & Refrigerant Oils The Refrigeration Cycle Building & Grounds Maintenance Courses Constructing the Building Shell Finishing the Building Interior Flat Roof Maintenance Introduction to Carpentry Landscaping Maintenance Locks and Key Systems Plumbing Systems Maintenance Structural Painting Custodial Maintenance Courses Carpet and Upholstery Care Cleaning Chemicals Floors and Floor Care Equipment Maintaining Floors and Other Surfaces Rest Room Care Electronics Courses Amplifiers Digital Logic Systems Oscillators Power Supplies Semiconductors Energy Conservation Courses Electrical Energy Conservation Energy Conservation Basics Energy Losses in Buildings Heating/Cooling System Efficiency Mechanical Energy Conservation Industrial Hazard Control Course Chemical Hazards: OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard Machine Shop Practices Courses Machine Shop Practice Material Handling Systems Course Bulk-Handling Conveyors Mechanical Maintenance Applications Courses Mechanical Drive Maintenance Mechanical and Fluid Drive Systems Bearing and Shaft Seal Maintenance Pump Installation and Maintenance Maintenance Pipefitting Tubing & Hose System Maintenance Valve Maintenance/Piping System Protection Microprocessors Courses How Computers Function-Technician Level Input/Output Devices I Input/Output Devices II Introduction to Computers Maintaining/Troubleshooting Computer Systems Power Plant Operations Courses Generating Steam in the Power Plant How Power Plants Work Using Steam in the Power Plant Process Control Instrumentation Courses Flow Measurement Foundations of Measurement Instrumentation Pressure Measurement Programmable Logic Controllers Course Programmable Logic Controllers Rigging & Equipment Installation Courses Equipment Installation Industrial Rigging Water/Wastewater Treatment Courses Introduction to Water Technology Wastewater Treatment Processes Welding Courses Blueprint Reading for Welders Oxyfuel Operations Welding Principles Tasks What are the usual duties/tasks for the profession/occupation? This depends on the setting of work. Maintains heat and air conditioning systems through the building automation system; cleans condenser coils; performs preventive maintenance as needed following a preventative maintenance schedule; adjusts and replaces belts; checks flame detection devices, climate controls, boiler readings, water temps, water usage; works with engineers in the annual tear-down inspection and cleaning of boilers; replaces light bulbs; performs maintenance on exit lights, emergency lighting, and related equipment; runs generators on the weekly test procedure and records the results; repairs and maintains security systems; performs periodic maintenance on air compressors, fans, pumps, and outdoor equipment, including changing oil, belts and filters; maintains maintenance records; maintains piping and drain systems in good working order; cleans and snakes drains; maintains drain cleaning equipment; repairs and replaces plumbing fixtures, flushometers, faucets, leaking pipes, and drains; moves office furniture and equipment; raises and lowers work surfaces, flipper doors, and cabinets; repairs office furniture, including drawers and slides, hang bulletin board and pictures; performs carpentry, plastering, painting, wallpaper repairs, ceiling tile replacement, carpet repair and removal; maintains and operates _______ parking ramp; operates snow blowers, lawn mowers, leaf blowers, weed whips, and related tools and equipment; maintains walkways, including snow removal, spreading salt, trimming trees, and shrubs, and landscape maintenance; repairs and replaces irrigation sprinkler heads and performance of annual fall maintenance of this equipment; keeps doors and door hardware in good working order, including hinges, door closers, and door handles; maintains lock and key security and lock systems to include building security. Maintenance, repair, and operations Maintenance What are the types of maintenance? Preventive maintenance Operational maintenance Corrective maintenance Reliability centered maintenance What is operations management? Operations management is an area of management concerned with overseeing, designing, and controlling the process of production and redesigning operations in the production of goods or services. Tools & Technology Equipment/resources (tools & technology). What minimum equipment or resources are required for this profession? Computer with Internet. USB flash equipment. Telephone/fax. Equipment and resources will also depend on work setting. What other equipment or resources are required for this profession from time to time? Tools used in this occupation: Counters — Electronics counters Light absorption meters — Wave meters Multimeters Signal generators — Function generators Wattmeters Hammers, hoists, saws, drills, and wrenches Drain or pipe cleaning equipment — Drain augers; Drain cleaning cables; Hand spinners; Power drain cleaners Pipe or tube cutter — Pipe cutters; Power pipe cutters; Ratcheting polyvinyl chloride PVC cutters; Tubing cutters Power drills — Cordless power drills; Direct tap machines; Hammer drills; Hand drills Power saws — Circular saws; Radial arm saws; Reciprocating saws; Tile saws Pullers — Bearing pullers; Chain pullers; Comealongs; Tub drain removers Technology used in this occupation: Electronic mail software — Microsoft Outlook Facilities management software — Computerized maintenance management system CMMS software Industrial control software — Digital Direct Control DDC Energy Management software Spreadsheet software — Microsoft Excel Word processing software — Microsoft Word What types of test are usually done on electric home appliances? 1. Continuity 2. Voltage 3. Amperage Did the maintenance engineer test the electric appliance (electric stove) fault/problem with a scientific method? No. How did the maintenance engineer test the electric appliance (electric stove) fault/problem? He did not utilize any equipment to test 1. Continuity 2. Voltage 3. Amperage How should the maintenance engineer have tested the electric appliance (electric stove) fault/problem by a scientific method? He should have tested for continuity, voltage, and amperage of the electric appliance (electric stove). What are Watts? A Watt is a unit describing the instantanious power that an appliance is drawing at any one moment. 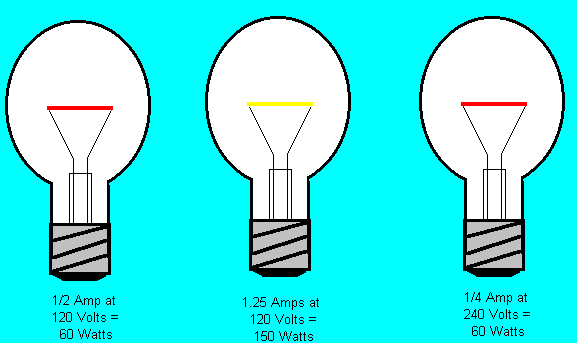
A Watt is a measure of electric power that depends on amps and volts. The bulb in the middle makes the most light because it uses more watts than the other two. But notice that the bulb on the right is using the same amount of power as the bulb on the left, even though it's using only half of the current. Watts = Volts x Amps How is Electricity Measured? Understanding Watts, Megawatts, Kilowatt-hours, and More Watts are a measurement of power, describing the rate at which electricity is being used at a specific moment. For example, a 15-watt LED light bulb draws 15 watts of electricity at any moment when turned on. Watt-hours are a measurement of energy, describing the total amount of electricity used over time. Watt-hours are a combination of how fast the electricity is used (watts) and the length of time it is used (hours). For example, a 15-watt light bulb, which draws 15 watts at any one moment, uses 15 watt-hours of electricity in the course of one hour. Kilowatts and kilowatt-hours are useful for measuring amounts of electricity used by large appliances and by households. Kilowatt-hours are what show up on your electricity bill, describing how much electricity you have used. One kilowatt (kW) equals 1,000 watts, and one kilowatt-hour (kWh) is one hour of using electricity at a rate of 1,000 watts. New, energy-efficient refrigerators use about 300-400 kilowatt-hours per year. The typical American home uses about 7,200 kilowatt-hours of electricity each year. Megawatts are used to measure the output of a power plant or the amount of electricity required by an entire city. One megawatt (MW) = 1,000 kilowatts = 1,000,000 watts. For example, a typical coal plant is about 600 MW in size. Gigawatts measure the capacity of large power plants or of many plants. One gigawatt (GW) = 1,000 megawatts = 1 billion watts. In 2012, the total capacity of U.S. electricity generating plants was approximately 1,100 GW. How much electricity do household items use?
ELECTRICITY & ELECTRONICS UNITS Volt (V) Ampere (A) Ohm (O) Watt (W) Farad (F) Decibel (dB) dB-milliwatt (dBm) dB-watt (dBW) Kilowatt (kW) Kilowatt-hour (kWh) Power consumption of some electrical components How many watts does a house use? How many watts does a TV use? How many watts does a refrigerator use?
Materials / Systems Concrete Masonry Metals Wood / Plastic / Composites Thermal & Moisture Protection Doors / Windows / Openings Finishes Specialties Equipment Vertical Circulation Fire Suppression Plumbing HVAC Electrical Site & Landscape Metals Structural Steel Shapes Cold Formed Metal Framing Metal Thickness (Gauge) Stainless Steel Grades Metal Coatings Galvanic Action Structural Steel Shapes
What equipment does a maintenance engineer need to fix electric stove faults/problems? What are the types of maintenance engineer? Aircraft maintenance engineer (mechanical) Facilities maintenance engineer Plant maintenance engineer Television maintenance engineer Other What are other names for a facilities maintenance engineer? Building services engineer. Building maintenance engineer. What should a facilities maintenance engineer know? Take a look at this. www.qureshiuniversity.com/facilitiesmaintenanceengineer.html What type of engineer is required for electric stove maintenance, repairs, and operations? A facilities maintenance engineer Who is the supervisor for this position? Facilities director Facilities supervisor Is there a difference between a facilities maintenance engineer and a facilities maintenance technician? Yes. What is the difference between facilities maintenance engineer and Facilities Maintenance Technician? Take a look at this. www.qureshiuniversity.com/facilitiesmaintenancetechnician.html Take a look at this. www.qureshiuniversity.com/facilitiesmaintenanceengineer.html What are you expected to know relevant to this profession? How should you do maintenance of a building? What best describes the building? A facility with 160 or more units. A house for a family. If other, specify. Where are work orders for repairs or maintenance by residents submitted in the building? Work orders for repairs or maintenance are submitted to the desk clerk in the building. The facility maintenance engineer picks up work orders for repairs or maintenance from the desk clerk in the building. In some cases, a house work order for repairs or maintenances is submitted to a facilities maintenance engineer office within walking distance, also called a state department of engineering maintenance office. What questions should the facility maintenance engineer answer as soon as he or she receives work orders for repairs or maintenance? Does this work orders for repairs or maintenance need to be completed within 24 hours? Is the fault/problem within the building or outside the building? What work orders for repairs or maintenance need to be completed within 24 hours after they are received? If the fault/problem is outside the building, the work order for repairs or maintenance goes to the state department of engineering local office. Priority goes to work orders for repairs or maintenance that need to be completed within 24 hours after being received. Let me know if you would like to add, delete, or modify anything. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||