List of English Irregular Verbs
A list of 212 common English irregular verbs, including their base form, past simple, past participle, 3rd person singular, and the present participle / gerund.
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle | 3rd Person Singular | Present Participle / Gerund |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abide | Abode/Abided | Abode/Abided/Abidden | Abides | Abiding |
| Alight | Alit/Alighted | Alit/Alighted | Alights | Alighting |
| Arise | Arose | Arisen | Arises | Arising |
| Awake | Awoke | Awoken | Awakes | Awaking |
| Be | Was/Were | Been | Is | Being |
| Bear | Bore | Born/Borne | Bears | Bearing |
| Beat | Beat | Beaten | Beats | Beating |
| Become | Became | Become | Becomes | Becoming |
| Begin | Began | Begun | Begins | Beginning |
| Behold | Beheld | Beheld | Beholds | Beholding |
| Bend | Bent | Bent | Bends | Bending |
| Bet | Bet | Bet | Bets | Betting |
| Bid | Bade | Bidden | Bids | Bidding |
| Bid | Bid | Bid | Bids | Bidding |
| Bind | Bound | Bound | Binds | Binding |
| Bite | Bit | Bitten | Bites | Biting |
| Bleed | Bled | Bled | Bleeds | Bleeding |
| Blow | Blew | Blown | Blows | Blowing |
| Break | Broke | Broken | Breaks | Breaking |
| Breed | Bred | Bred | Breeds | Breeding |
| Bring | Brought | Brought | Brings | Bringing |
| Broadcast | Broadcast/Broadcasted | Broadcast/Broadcasted | Broadcasts | Broadcasting |
| Build | Built | Built | Builds | Building |
| Burn | Burnt/Burned | Burnt/Burned | Burns | Burning |
| Burst | Burst | Burst | Bursts | Bursting |
| Bust | Bust | Bust | Busts | Busting |
| Buy | Bought | Bought | Buys | Buying |
| Cast | Cast | Cast | Casts | Casting |
| Catch | Caught | Caught | Catches | Catching |
| Choose | Chose | Chosen | Chooses | Choosing |
| Clap | Clapped/Clapt | Clapped/Clapt | Claps | Clapping |
| Cling | Clung | Clung | Clings | Clinging |
| Clothe | Clad/Clothed | Clad/Clothed | Clothes | Clothing |
| Come | Came | Come | Comes | Coming |
| Cost | Cost | Cost | Costs | Costing |
| Creep | Crept | Crept | Creeps | Creeping |
| Cut | Cut | Cut | Cuts | Cutting |
| Dare | Dared/Durst | Dared | Dares | Daring |
| Deal | Dealt | Dealt | Deals | Dealing |
| Dig | Dug | Dug | Digs | Digging |
| Dive | Dived/Dove | Dived | Dives | Diving |
| Do | Did | Done | Does | Doing |
| Draw | Drew | Drawn | Draws | Drawing |
| Dream | Dreamt/Dreamed | Dreamt/Dreamed | Dreams | Dreaming |
| Drink | Drank | Drunk | Drinks | Drinking |
| Drive | Drove | Driven | Drives | Driving |
| Dwell | Dwelt | Dwelt | Dwells | Dwelling |
| Eat | Ate | Eaten | Eats | Eating |
| Fall | Fell | Fallen | Falls | Falling |
| Feed | Fed | Fed | Feeds | Feeding |
| Feel | Felt | Felt | Feels | Feeling |
| Fight | Fought | Fought | Fights | Fighting |
| Find | Found | Found | Finds | Finding |
| Fit | Fit/Fitted | Fit/Fitted | Fits | Fitting |
| Flee | Fled | Fled | Flees | Fleeing |
| Fling | Flung | Flung | Flings | Flinging |
| Fly | Flew | Flown | Flies | Flying |
| Forbid | Forbade/Forbad | Forbidden | Forbids | Forbidding |
| Forecast | Forecast/Forecasted | Forecast/Forecasted | Forecasts | Forecasting |
| Foresee | Foresaw | Foreseen | Foresees | Foreseeing |
| Foretell | Foretold | Foretold | Foretells | Foretelling |
| Forget | Forgot | Forgotten | Forgets | Foregetting |
| Forgive | Forgave | Forgiven | Forgives | Forgiving |
| Forsake | Forsook | Forsaken | Forsakes | Forsaking |
| Freeze | Froze | Frozen | Freezes | Freezing |
| Frostbite | Frostbit | Frostbitten | Frostbites | Frostbiting |
| Get | Got | Got/Gotten | Gets | Getting |
| Give | Gave | Given | Gives | Giving |
| Go | Went | Gone/Been | Goes | Going |
| Grind | Ground | Ground | Grinds | Grinding |
| Grow | Grew | Grown | Grows | Growing |
| Handwrite | Handwrote | Handwritten | Handwrites | Handwriting |
| Hang | Hung/Hanged | Hung/Hanged | Hangs | Hanging |
| Have | Had | Had | Has | Having |
| Hear | Heard | Heard | Hears | Hearing |
| Hide | Hid | Hidden | Hides | Hiding |
| Hit | Hit | Hit | Hits | Hitting |
| Hold | Held | Held | Holds | Holding |
| Hurt | Hurt | Hurt | Hurts | Hurting |
| Inlay | Inlaid | Inlaid | Inlays | Inlaying |
| Input | Input/Inputted | Input/Inputted | Inputs | Inputting |
| Interlay | Interlaid | Interlaid | Interlays | Interlaying |
| Keep | Kept | Kept | Keeps | Keeping |
| Kneel | Knelt/Kneeled | Knelt/Kneeled | Kneels | Kneeling |
| Knit | Knit/Knitted | Knit/Knitted | Knits | Knitting |
| Know | Knew | Known | Knows | Knowing |
| Lay | Laid | Laid | Lays | laying |
| Lead | Led | Led | Leads | Leading |
| Lean | Leant/Leaned | Leant/Leaned | Leans | Leaning |
| Leap | Leapt/Leaped | Leapt/Leaped | Leaps | Leaping |
| Learn | Learnt/Learned | Learnt/Learned | Learns | Learning |
| Leave | Left | Left | Leaves | Leaving |
| Lend | Lent | Lent | Lends | Lending |
| Let | Let | Let | Lets | Letting |
| Lie | Lay | Lain | Lies | Lying |
| Light | Lit | Lit | Lights | Lighting |
| Lose | Lost | Lost | Loses | Losing |
| Make | Made | Made | Makes | Making |
| Mean | Meant | Meant | Means | Meaning |
| Meet | Met | Met | Meets | Meeting |
| Melt | Melted | Molten/Melted | Melts | Melting |
| Mislead | Misled | Misled | Misleads | Misleading |
| Mistake | Mistook | Mistaken | Mistakes | Mistaking |
| Misunderstand | Misunderstood | Misunderstood | Misunderstands | Misunderstanding |
| Miswed | Miswed/Miswedded | Miswed/Miswedded | Misweds | Miswedding |
| Mow | Mowed | Mown | Mows | Mowing |
| Overdraw | Overdrew | Overdrawn | Overdraws | Overdrawing |
| Overhear | Overheard | Overheard | Overhears | Overhearing |
| Overtake | Overtook | Overtaken | Overtakes | Overtaking |
| Pay | Paid | Paid | Pays | Paying |
| Preset | Preset | Preset | Presets | Presetting |
| Prove | Proved | Proven/Proved | Proves | Proving |
| Put | Put | Put | Puts | Putting |
| Quit | Quit | Quit | Quits | Quitting |
| Re-prove | Re-proved | Re-proven/Re-proved | Re-proves | Re-proving |
| Read | Read | Read | Reads | Reading |
| Rid | Rid/Ridded | Rid/Ridded | Rids | Ridding |
| Ride | Rode | Ridden | Rides | Riding |
| Ring | Rang | Rung | Rings | Ringing |
| Rise | Rose | Risen | Rises | Rising |
| Rive | Rived | Riven/Rived | Rives | Riving |
| Run | Ran | Run | Runs | Running |
| Saw | Sawed | Sawn/Sawed | Saws | Sawing |
| Say | Said | Said | Says | Saying |
| See | Saw | Seen | Sees | Seeing |
| Seek | Sought | Sought | Seeks | Seeking |
| Sell | Sold | Sold | Sells | Selling |
| Send | Sent | Sent | Sends | Sending |
| Set | Set | Set | Sets | Setting |
| Sew | Sewed | Sewn/Sewed | Sews | Sewing |
| Shake | Shook | Shaken | Shakes | Shaking |
| Shave | Shaved | Shaven/Shaved | Shaves | Shaving |
| Shear | Shore/Sheared | Shorn/Sheared | Shears | Shearing |
| Shed | Shed | Shed | Sheds | Shedding |
| Shine | Shone | Shone | Shines | Shining |
| Shoe | Shod | Shod | Shoes | Shoeing |
| Shoot | Shot | Shot | Shoots | Shooting |
| Show | Showed | Shown | Shows | Showing |
| Shrink | Shrank | Shrunk | Shrinks | Shrinking |
| Shut | Shut | Shut | Shuts | Shutting |
| Sing | Sang | Sung | Sings | Singing |
| Sink | Sank | Sunk | Sinks | Sinking |
| Sit | Sat | Sat | Sits | Sitting |
| Slay | Slew | Slain | Slays | Slaying |
| Sleep | Slept | Slept | Sleeps | Sleeping |
| Slide | Slid | Slid/Slidden | Slides | Sliding |
| Sling | Slung | Slung | Slings | Slinging |
| Slink | Slunk | Slunk | Slinks | Slinking |
| Slit | Slit | Slit | Slits | Slitting |
| Smell | Smelt/Smelled | Smelt/Smelled | Smells | Smelling |
| Sneak | Sneaked/Snuck | Sneaked/Snuck | Sneaks | Sneaking |
| Soothsay | Soothsaid | Soothsaid | Soothsays | Soothsaying |
| Sow | Sowed | Sown | Sows | Sowing |
| Speak | Spoke | Spoken | Speaks | Speaking |
| Speed | Sped/Speeded | Sped/Speeded | Speeds | Speeding |
| Spell | Spelt/Spelled | Spelt/Spelled | Spells | Spelling |
| Spend | Spent | Spent | Spends | Spending |
| Spill | Spilt/Spilled | Spilt/Spilled | Spills | Spilling |
| Spin | Span/Spun | Spun | Spins | Spinning |
| Spit | Spat/Spit | Spat/Spit | Spits | Spitting |
| Split | Split | Split | Splits | Splitting |
| Spoil | Spoilt/Spoiled | Spoilt/Spoiled | Spoils | Spoiling |
| Spread | Spread | Spread | Spreads | Spreading |
| Spring | Sprang | Sprung | Springs | Springing |
| Stand | Stood | Stood | Stands | Standing |
| Steal | Stole | Stolen | Steals | Stealing |
| Stick | Stuck | Stuck | Sticks | Sticking |
| Sting | Stung | Stung | Stings | Stinging |
| Stink | Stank | Stunk | Stinks | Stinking |
| Stride | Strode/Strided | Stridden | Strides | Striding |
| Strike | Struck | Struck/Stricken | Strikes | Striking |
| String | Strung | Strung | Strings | Stringing |
| Strip | Stript/Stripped | Stript/Stripped | Strips | Stripping |
| Strive | Strove | Striven | Strives | Striving |
| Sublet | Sublet | Sublet | Sublets | Subletting |
| Sunburn | Sunburned/Sunburnt | Sunburned/Sunburnt | Sunburns | Sunburning |
| Swear | Swore | Sworn | Swears | Swearing |
| Sweat | Sweat/Sweated | Sweat/Sweated | Sweats | Sweating |
| Sweep | Swept/Sweeped | Swept/Sweeped | Sweeps | Sweeping |
| Swell | Swelled | Swollen | Swells | Swelling |
| Swim | Swam | Swum | Swims | Swimming |
| Swing | Swung | Swung | Swings | Swinging |
| Take | Took | Taken | Takes | Taking |
| Teach | Taught | Taught | Teaches | Teaching |
| Tear | Tore | Torn | Tears | Tearing |
| Tell | Told | Told | Tells | Telling |
| Think | Thought | Thought | Thinks | Thinking |
| Thrive | Throve/Thrived | Thriven/Thrived | Thrives | Thriving |
| Throw | Threw | Thrown | Throws | Throwing |
| Thrust | Thrust | Thrust | Thrusts | Thrusting |
| Tread | Trod | Trodden | Treads | Treading |
| Undergo | Underwent | Undergone | Undergoes | Undergoing |
| Understand | Understood | Understood | Understands | Understanding |
| Undertake | Undertook | Undertaken | Undertakes | Undertaking |
| Upsell | Upsold | Upsold | Upsells | Upselling |
| Upset | Upset | Upset | Upsets | Upsetting |
| Vex | Vext/Vexed | Vext/Vexed | Vexes | Vexing |
| Wake | Woke | Woken | Wakes | Waking |
| Wear | Wore | Worn | Wears | Wearing |
| Weave | Wove | Woven | Weaves | Weaving |
| Wed | Wed/Wedded | Wed/Wedded | Weds | Wedding |
| Weep | Wept | Wept | Weeps | Weeping |
| Wend | Wended/Went | Wended/Went | Wends | Wending |
| Wet | Wet/Wetted | Wet/Wetted | Wets | Wetting |
| Win | Won | Won | Wins | Winning |
| Wind | Wound | Wound | Winds | Winding |
| Withdraw | Withdrew | Withdrawn | Withdraws | Withdrawing |
| Withhold | Withheld | Withheld | Withholds | Withholding |
| Withstand | Withstood | Withstood | Withstands | Withstanding |
| Wring | Wrung | Wrung | Wrings | Wringing |
| Write | Wrote | Written | Writes | Writing |
| Zinc | Zinced/Zincked | Zinced/Zincked | Zincs/Zincks | Zincking |
|
BASE FORM |
SIMPLE PAST |
PAST PARTICIPLE |
|
Accept |
Accepted |
Accepted |
|
Achieve |
Achieved |
Achieved |
|
Add |
Added |
Added |
|
Admire |
Admired |
Admirer |
|
Admit |
Admitted |
Admitted |
|
Adopt |
Adopted |
Adopted |
|
Advise |
Advised |
Advised |
|
Agree |
Agreed |
Agreed |
|
Allow |
Allowed |
Allowed |
|
Announce |
Announced |
Announced |
|
Appreciate |
Appreciated |
Appreciated |
|
Approve |
Approved |
Approved |
|
Argue |
Argued |
Argued |
|
Arrive |
Arrived |
Arrived |
|
Ask |
Asked |
Asked |
|
Assist |
Assisted |
Assisted |
|
Attack |
Attacked |
Attacked |
|
Bake |
Baked |
Baked |
|
Beg |
Begged |
Begged |
|
Behave |
Behaved |
Behaved |
|
Boil |
Boiled |
Boiled |
|
Borrow |
Borrowed |
Borrowed |
|
Brush |
Brushed |
Brushed |
|
Bury |
Buried |
Buried |
|
Call |
Called |
Called |
|
Challenge |
Challenged |
Challenged |
|
Change |
Changed |
Changed |
|
Chase |
Chased |
Chased |
|
Cheat |
Cheated |
Cheated |
|
Cheer |
Cheered |
Cheered |
|
Chew |
Chewed |
Chewed |
|
Clap |
Clapped |
Clapped |
|
Clean |
Cleaned |
Cleaned |
|
Collect |
Collected |
Collected |
|
Compare |
Compared |
Compared |
|
Complain |
Complained |
Complained |
|
Confess |
Confessed |
Confessed |
|
Construct |
Constructed |
Constructed |
|
Control |
Controlled |
Controlled |
|
Copy |
Copied |
Copied |
|
Count |
Counted |
Counted |
|
Create |
Created |
Created |
|
Cry |
Cried |
Cried |
|
Cycle |
Cycled |
Cycled |
|
Damage |
Damaged |
Damaged |
|
Dance |
Danced |
Danced |
|
Deliver |
Delivered |
Delivered |
|
Destroy |
Destroyed |
Destroyed |
|
Divide |
Divided |
Divided |
|
Drag |
Dragged |
Dragged |
|
Earn |
Earned |
Earned |
|
Employ |
Employed |
Employed |
|
Encourage |
Encouraged |
Encouraged |
|
Enjoy |
Enjoyed |
Enjoyed |
|
Establish |
Established |
Established |
|
Estimate |
Estimated |
Estimated |
|
Exercise |
Exercised |
Exercised |
|
Expand |
Expanded |
Expanded |
|
Explain |
Explained |
Explained |
|
Fry |
Fried |
Fried |
|
Gather |
Gathered |
Gathered |
|
Greet |
Greeted |
Greeted |
|
Guess |
Guessed |
Guessed |
|
Harass |
Harassed |
Harassed |
|
Hate |
Hated |
Hated |
|
Help |
Helped |
Helped |
|
Hope |
Hoped |
Hoped |
|
Identify |
Identified |
Identified |
|
Interrupt |
Interrupted |
Interrupted |
|
Introduce |
Introduced |
Introduced |
|
Irritate |
Irritated |
Irritated |
|
Joke |
Joked |
Joked |
|
Jump |
Jumped |
Jumped |
|
Kick |
Kicked |
Kicked |
|
Kill |
Killed |
Killed |
|
Kiss |
Kissed |
Kissed |
|
Laugh |
Laughed |
Laughed |
|
Lie |
Lied |
Lied |
|
Like |
Liked |
Liked |
|
Listen |
Listened |
Listened |
|
Love |
Loved |
Loved |
|
Marry |
Married |
Married |
|
Measure |
Measured |
Measured |
|
Move |
Moved |
Moved |
|
Murder |
Murdered |
Murdered |
|
Need |
Needed |
Needed |
|
Obey |
Obeyed |
Obeyed |
|
Offend |
Offended |
Offended |
|
Offer |
Offered |
Offered |
|
Open |
Opened |
Opened |
|
Paint |
Painted |
Painted |
|
Park |
Parked |
Parked |
|
Phone |
Phoned |
Phoned |
|
Pick |
Picked |
Picked |
|
Play |
Played |
Played |
|
Pray |
Prayed |
Prayed |
|
|
Printed |
Printed |
|
Pull |
Pulled |
Puled |
|
Punch |
Punched |
Punched |
|
Punish |
Punished |
Punished |
|
Purchase |
Purchased |
Purchased |
|
Push |
Pushed |
Pushed |
|
Question |
Questioned |
Questioned |
|
Race |
Raced |
Raced |
|
Relax |
Relaxed |
Relaxed |
|
Remember |
Remembered |
Remembered |
|
Reply |
Replied |
Replied |
|
Retire |
Retired |
Retired |
|
Return |
Returned |
Returned |
|
Rub |
Rubbed |
Rubbed |
|
Scold |
Scolded |
Scolded |
|
Select |
Selected |
Selected |
|
Smoke |
Smoked |
Smoked |
|
Snore |
Snored |
Snored |
|
Stare |
Stared |
Stared |
|
Start |
Started |
Started |
|
Study |
Studied |
Studied |
|
Talk |
Talked |
Talked |
|
Thank |
Thanked |
Thanked |
|
Travel |
Travelled |
Travelled |
|
Trouble |
Troubled |
Troubled |
|
Type |
Typed |
Typed |
|
Use |
Used |
Used |
|
Visit |
Visited |
Visited |
|
Wait |
Waited |
Waited |
|
Walk |
Walked |
Walked |
|
Want |
Wanted |
Wanted |
|
Warn |
Warned |
Warned |
|
Wink |
Winked |
Winked |
|
Worry |
Worried |
Worried |
|
Yell |
Yelled |
Yelled |
|
What is verb conjugation?
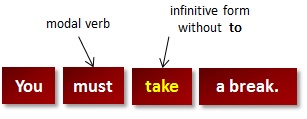
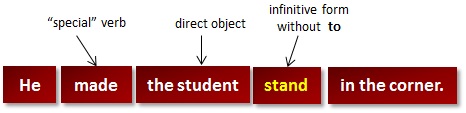
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (regular alteration according to rules of grammar). Conjugation may be affected by person, number, gender, tense, aspect, mood, voice, or other grammatical categories. Conjugated forms of a verb are called finite forms. In many languages there are also one or more forms that remain unchanged with all or most grammatical categories: the non-finite forms, such as the infinitive or the gerund. A table giving all the conjugated variants of a verb in a given language is called a conjugation table or a verb paradigm. English verb conjugation rules There are 3 categories of verbs: •Regular verbs •Irregular verbs •Modal verbs The Basic rules for regular and irregular verbs are: Present Simple: Affirmative: I, you, we, they + verb (Infinitive without “to”) He/she/it + verb (Infinitive without “to”) + “-s” Negative: I, you, we, they + do + not + verb (Infinitive without “to” He/she/it + does + not + verb (Infinitive without “to”) Interrogative: Do + I, you, we, they + verb (Infinitive without “to” Does + he/she/it + verb (Infinitive without “to”)? Past Simple: Affirmative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + verb (Past Participle) Negative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + did + not + verb (Infinitive without “to”) Interrogative: Did + I, you, he/she/it, we, they + verb (Infinitive without “to)? Present continuous: Affirmative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + be (Present Simple) + verb (Present Participle (verb+”-ing”)) Negative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + be (Present Simple) + not + verb (Present Participle) Interrogative: Be (Present Simple) + I, you, we, they + verb (Present Participle)? Past continuous: Affirmative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + be (Past Simple) + verb (Present Participle) Negative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + be (Past Simple) + not + verb (Present Participle) Interrogative: Be (Past Simple) + I, you, we, they + verb (Present Participle)? Present perfect: Affirmative: I, you, we, they + have + verb (Past Participle) He/she/it + has + verb (Past Participle) Negative: I, you, we, they + have + not + verb (Past Participle) He/she/it + has + not + verb (Past Participle) Interrogative: Have + I, you, we, they + verb (Past Participle)? Has+ he/she/it + verb (Past Participle)? Past perfect: Affirmative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + had + verb (Past Participle) Negative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + had + not + verb (Past Participle) Interrogative: Had + I, you, he/she/it, we, they + verb (Past Participle)? Present perfect continuous: Affirmative: I, you, we, they + have + been + verb (Present Participle) He/she/it + has + been + verb (Present Participle) Negative: I, you, we, they + have + not + been + verb (Present Participle) He/she/it + has + not + been + verb (Present Participle) Interrogative: Have + I, you, we, they + been + verb (Present Participle)? Has+ he/she/it + been + verb (Present Participle)? Past perfect continuous: Affirmative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + had + been + verb (Present Participle) Negative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + had+ not + been + verb (Present Participle) Interrogative: Had + I, you, he/she/it, we, they + been + verb (Present Participle)? Future: Affirmative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + will + verb (Infinitive without “to”) Negative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + will + not + verb (Infinitive without “to”) Interrogative: Will + I, you, he/she/it, we, they + verb (Infinitive without “to”)? Future Perfect: Affirmative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they +will + have + verb (Past Participle) Negative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they +will + not + have + verb (Past Participle) Interrogative: Will + I, you, he/she/it, we, they + have + verb (Past Participle)? Future continuous: Affirmative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + will + be + verb (Present Participle) Negative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + will + not + be + verb (Present Participle) Interrogative: Will + I, you, he/she/it, we, they + be + verb (Present Participle)? Future perfect continuous: Affirmative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + will + have + been + verb (Present Participle) Negative: I, you, he/she/it, we, they + will + not + have + been + verb (Present Participle) Interrogative: Will + I, you, he/she/it, we, they + have + been + verb (Present Participle)? Among the irregular verbs are the modal verbs. Modals are special verbs which behave very irregularly in English. For example they do not add "-s" in the third person in Present Simple tense. New irregular verbs are no longer being created in English so the list of irregular verbs to be learned is not getting any larger. |
|
What are verbs? What Is the Infinitive Form of a Verb? What Are Finite Verbs? What are non-finite verbs? What are adjectives? What is the subject of a sentence? What is verb tense? What are verbals? What are gerunds? What are participles? What are verbs? Definition of Verb (with Examples)Verbs are often described as doing words. A verb usually tells us what action is being performed. For example:
Verbs Expressing Physical Actions Verbs that express physical actions are the ones that spring to mind when most people think about verbs. Such verbs are easy to spot because the action can be easily envisaged. Here are some examples of verbs expressing physical actions:
Not all actions are physical. Some are mental. Here are some examples of verbs expressing mental actions:
The very act of being (i.e., just existing) is also an action. Below are some examples of verbs that express a state of being. The most common one (in fact, the most common verb of all) is the verb to be.
What Is the Infinitive Form of a Verb? (with Examples)
|