Abductor Digiti Minimi (Foot)
Abductor Digiti Minimi (Hand)
Abductor Hallucis
Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Abductor Pollicis Longus
Adductor Brevis
Adductor Hallucis
Adductor Longus
Adductor Magnus
Adductor Pollicis
Alaeque Nasi
Anconeus
Articularis Cubiti
Articularis Genu
Aryepiglotticus
Aryjordanicus
Auricularis
Biceps Brachii
Biceps Femoris
Brachialis
Brachioradialis
Buccinator
Bulbospongiosus
Constrictor Of Pharynx - Inferior
Constrictor Of Pharynx - Middle
Constrictor Of Pharynx - Superior
Coracobrachialis
Corrugator Supercilii
Cremaster
Cricothyroid
Dartos
Deep Transverse Perinei
Deltoid
Depressor Anguli Oris
Depressor Labii Inferioris
Diaphragm
Digastric
Digastric (Anterior View)
Erector Spinae - Spinalis
Erector Spinae - Iliocostalis
Erector Spinae - Longissimus
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Extensor Digiti Minimi (Hand)
Extensor Digitorum (Hand)
Extensor Digitorum Brevis (Foot)
Extensor Digitorum Longus (Foot)
Extensor Hallucis Longus
Extensor Indicis
Extensor Pollicis Brevis
Extensor Pollicis Longus
External Oblique Abdominis
Flexor Carpi Radialis
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis (Foot)
Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis (Hand)
Flexor Digitorum Brevis
Flexor Digitorum Longus (Foot)
Flexor Digitorum Profundus
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Flexor Hallucis Brevis
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Flexor Pollicis Brevis
Flexor Pollicis Longus
Frontalis
Gastrocnemius
Gemellus Inferior
Gemellus Superior
Genioglossus
Geniohyoid
Gluteus Maximus
Gluteus Medius
Gluteus Minimus
Gracilis
Hyoglossus
Iliacus
Inferior Oblique
Inferior Rectus
Infraspinatus
Intercostals External
Intercostals Innermost
Intercostals Internal
Internal Oblique Abdominis
Interossei - Dorsal Of Hand
Interossei - Dorsal Of Foot
Interossei- Palmar Of Hand
Interossei - Plantar Of Foot
Interspinales
Intertransversarii
Intrinsic Muscles Of Tongue
Ishiocavernosus
Lateral Cricoarytenoid
Lateral Pterygoid
Lateral Rectus
Latissimus Dorsi
Levator Anguli Oris
Levator Ani - Coccygeus
Levator Ani - Iliococcygeus
Levator Ani - Pubococcygeus
Levator Ani - Puborectalis
Levator Ani - Pubovaginalis
Levator Labii Superioris
Levator Labii Superioris
Levator Palpebrae Superioris
Levator Scapulae
Levator Veli Palatini
Levatores Costarum
Longus Capitis
Longus Colli
Lumbricals Of Foot (4)
Lumbricals Of Hand
Masseter
Medial Pterygoid
Medial Rectus
Mentalis
M. Uvulae
Mylohyoid
Nasalis
Oblique Arytenoid
Obliquus Capitis Inferior
Obliquus Capitis Superior
Obturator Externus
Obturator Internus (A)
Obturator Internus (B)
Omohyoid
Opponens Digiti Minimi (Hand)
Opponens Pollicis
Orbicularis Oculi
Orbicularis Oris
Palatoglossus
Palatopharyngeus
Palmaris Brevis
Palmaris Longus
Pectineus
Pectoralis Major
Pectoralis Minor
Peroneus Brevis
Peroneus Longus
Peroneus Tertius
Piriformis (A)
Piriformis (B)
Plantaris
Platysma
Popliteus
Posterior Cricoarytenoid
Procerus
Pronator Quadratus
Pronator Teres
Psoas Major
Psoas Minor
Pyramidalis
Quadratus Femoris
Quadratus Lumborum
Quadratus Plantae
Rectus Abdominis
Rectus Capitus Anterior
Rectus Capitus Lateralis
Rectus Capitus Posterior Major
Rectus Capitus Posterior Minor
Rectus Femoris
Rhomboid Major
Rhomboid Minor
Risorius
Salpingopharyngeus
Sartorius
Scalenus Anterior
Scalenus Medius
Scalenus Minimus
Scalenus Posterior
Semimembranosus
Semitendinosus
Serratus Anterior
Serratus Posterior Inferior
Serratus Posterior Superior
Soleus
Sphincter Ani
Sphincter Urethrae
Splenius Capitis
Splenius Cervicis
Stapedius
Sternocleidomastoid
Sternohyoid
Sternothyroid
Styloglossus
Stylohyoid
Stylohyoid (Anterior View)
Stylopharyngeus
Subclavius
Subcostalis
Subscapularis
Superficial Transverse
Perinei
Superior Oblique
Superior Rectus
Supinator
Supraspinatus
Temporalis
Temporoparietalis
Tensor Fasciae Lata
Tensor Tympani
Tensor Veli Palatini
Teres Major
Teres Minor
Thyro-Arytenoid & Vocalis
Thyro-Epiglotticus
Thyrohyoid
Tibialis Anterior
Tibialis Posterior
Transverse Arytenoid
Transversospinalis - Multifidus
Transversospinalis - Rotatores
Transversospinalis - Semispinalis
Transversus Abdominis
Transversus Thoracis
Trapezius
Triceps
Vastus Intermedius
Vastus Lateralis
Vastus Medialis
Zygomaticus Major
Zygomaticus Minor
| Admissions | Contact Us | Examinations | Grants | Instructors | Lecture | Membership | Students login | Schools | Colleges | Universities | Professional Examinations | Recommendations | Research Grants | Search | Librarians | Forms | Booksellers | Continents/States/Districts | Contracts | Volunteer |
|
What is a medical college? A medical college is a resource that offers study resources to build skills of specific physicians. A medical college is a resource, such as www.qureshiuniversity.com/physicians.html, which offers study resources authored by Doctor Asif Qureshi leading to skills of the specific physician. If a specific physician can guide many specific aspiring, in training, and existing physicians, the person is a guide for specific physicians. At least 1000 academic projects carried out between 1999 and 2019 led to the establishment of the resources at www.qureshiuniversity.com/physicians.html. Who has authored these resources? This question is very important. Doctor Asif Qureshi has authored these resources. Global Medical College Allopathic
How do you conclude that a person does not need to complete a medical residency in the United States? Answer these questions. How many years of experience as a physician outside the United States do you have to have? I have seven years of hospital experience as a physician in the medical emergency room, a primary care physician, and a critical care physician. I have 15 years of research experience in Chicago, Illinois, United States. How many specific physicians can you guide at this point—for example, on October 23, 2019? I can guide 19 specific types of physicians. What is the proof of this claim? Take a look at this. https://qureshiuniversity.com/physicians.html After verifying such a person does not need to complete a medical residency in the United States, Doctor Asif Qureshi can guide 19 specific types of physicians on October 23, 2019. This has been verified. Other specific physicians cannot guide him. |
College of Medicine – Curriculum News
| Previous curriculum of specific physicians |
|
Doctor Asif Qureshi’s lecture to first-year medical students during first class. |
Previous curriculum of specific physicians
What was the previous first-year medical college curriculum?
Some medical colleges are still teaching a historical or outdated curriculum.
What was previously taught for 4 years in medical college?
In those days, there was no computer or Internet.
In those days, there was not such advanced research.
How many competent medical doctors do you need?
I can educate them within a short period of time.
Human anatomy
Questions you must be ready to answer.
Male reproductive system
Internal reproductive organs
External reproductive organs |
Endocrine glands
Circulatory system
| Cardiovascular system |
Lymphatic system
Integumentary system
Superficial anatomy
Surface Human Anatomy
|
Can you name the Human Surface Anatomy?
Arms Armpit Abdomen (stomach,belly,tummy) Arches of the foot Ankles Big toe Back Buttocks(Behind) Back of head Breast bone Belly button Back of knees Back center of shins Ball of foot Between spine and butt cheeks Butt cheeks Back of genitals Between pelvis and genitals Chest Calf Cheeks Chin Eyes Elbow Ears Forehead Fingers Finger nail Front of knees Front center of shins Feet Genitals Head Hands Hips Heels Index-finger Inner elbows Knuckles Knee Little-finger Legs Lower arms Lower sides around spine Mouth Middle-finger Nose Neck Nipple Navel, bellybuttom Outer elbows Palms Pelvis Ring-finger Shoulders Shoulder blade Sides of back Spine Side of shins(Right) Side of shins(Left) Throat Thumbs Thighs Toes Upper torso Under arms Upper arms Wrists Body Systems - Human Anatomy What is a human body system? A system of human body means a collective functional unit made by several organs in which the organs work in complete coordination with one another. Organs cannot work alone because their are certain needs of every organ that need to be fulfilled and the organ itself cannot fulfill those needs. So all organs of human body need the support of other organs to perform their functions and in this way an organ system is formed. Systems of the Human Body: Human body is made of ten different systems. All the systems require support and coordination of other systems to form a living and healthy human body.
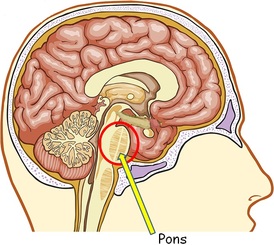
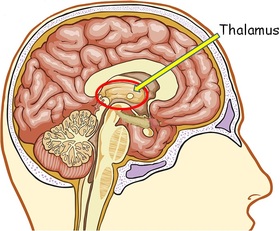
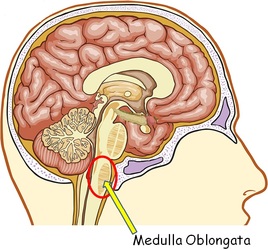
What are all the human body parts A-Z? Human Anatomy Index A Abdominal cavity, Abdominal wall, Acetabulum, Air cells, Ampulla, Anatomical snuff box, Angle, Antitragus, Anus, Aorta, Aperture, Aponeurosis, Appendages, Appendix, Arch, Arm, Artery, Atrium, Auricle, Axilla B Bladder, Body, Bone, Brain, Breast (mammary gland), Brim, Bronchus, Bulb, Bulla, Bursa C Calyx, Canal, Canaliculi, Cartilage, Cauda equina, Cavity, Cecum, Cerebellum, Cerebrum, Cervix, Chamber, Chiasm, Choanae, Chordae tendineae, Circle, Cisterna chyli, Clitoris, Cochlea, Colon, Columns, Commissure, Compartments, Concha, Condyle, Conus medullaris, Cord, Cornea, Corpora cavernosa, Corpus luteum, Crest, Crista, Crus D Dermatomes, Diaphragm, Diaphragma sellae, Dorsum sellae, Duct, Ductus, Duodenum E Ear, Eminence, Endocranium, Endometrium, Enlargements of spinal cord, Epicondyles, Epididymis, Epiglottis, Esophagus, Extensor expansion F Falx, Fascia, Fat, Fibers, Filum terminale, Fissure, Flexure, Fluid, Fold, Follicle, Foramen, Forearm, Fornix, Fossa, Fovea, Frenulum G Galea aponeurotica, Gallbladder, Ganglion, Gland, Granulation, Groove, Gubernaculum, Gutter H Hamulus, Hand, Haustra (sacculations), Heart, Helix, Hemispheres, Hiatus, Hymen I Ileum, Infundibulum, Infundibulum (pituitary stalk), Intersections, Iris J Jejunum, Joint, Junction K Kidney, Kidneys L Labia, Labrum, Laminectomy, Laryngopharynx, Larynx, Leg, Lens, Ligament, Ligamentum, Line, Linea, Lingula, Liver, Lobule, Lung, Lymph nodes M Malleolus, Margin, Meatus, Mediastinum, Medulla oblongata, Membrane, Meninges, Meniscus, Mesentery, Mesocolon, Mesometrium, Mesorchium, Mesosalpinx, Mesovarium, Midbrain, Mons pubis, Muscle, Muscles, Myometrium N Nasopharynx, Neck, Nerve, Nipple, Node, Nodule, Nose, Notch O Omentum, Ora serrata, Orbit, Orifice, Oropharynx, Os, Ovaries, Oviduct P Palate, Pancreas, Papilla, Parametrium, Parotid duct, Pelvis, Penis, Pericardium, Perimetrium, Perineum, Peritoneum, Pes anserinus superficialis, Peyer's patches, Pharynx, Plate, Pleura, Plicae circulares, Point, Erb's, Pons, Pouch, Process, Prominence, Promontory, Protuberance, Pterion, Pupil Q R Ramus, Raphe, Recess, Rectum, Region, Retina, Retinaculum, Ring, Rugae S Sac, Scalp, Sclera, Scrotum, Segment, Sella turcica, Seminal colliculus, Seminal vesicles, Septum, Sheath, Sinus, Space, Sphincter, Spinal cord, Spine, Spleen, Stomach, Sulcus, Superior epigastric artery, Suture, Symphysis T Taeniae coli, Teeth, Tegmen tympani, Tendon, Tentorium, Thigh, Thoracocentesis, Tongue, Tonsil, Torus tubarius, Trabeculae carneae, Trachea, Tract, Tragus, Triad, Triangle, Trigone, Trochlea, Trunk, Tube, Tubercle, Tuberosity, Tubule, Tunic, Tunica, Tunnel, carpal, Turbinate U Umbilicus, Ureter, Urethra, Uterus, Utricle V Vagina, Vallecula, Valve, Vein, Venous plexus, Ventricle, Vertebra, Vesicles, Vessels, Vestibule, Vinculae W Wing X Y Z Internal Parts 柊drenals 柊ppendix 稗ladder 稗rain 髭sophagus 髭yes 膝allbladder 菱eart 肘ntestines 必idney 畢iver 畢ung 桧varies 姫ancreas 姫arathyroids 姫ituitary 姫rostate 百pleen 百tomach 謬esticles 謬hymus 謬hyroid 俵terus 彪eins External Parts 菱ead 彦orehead 弼aw 匹heek 匹hin 髭ye 髭ar 逼ose 筆outh 謬eeth 謬ongue 謬hroat 逼eck 柊dam's apple 百houlders 柊rm 髭lbow 標rist 菱and 彦ingers 謬humb 百pine 匹hest 謬horax 稗reast 柊bdomen 膝roin 菱ip 稗uttocks 逼avel 姫enis 百crotum 匹litoris 彪ulva 畢eg 謬high 必nee 匹alf 菱eel 柊nkle 彦oot 謬oes Surface Anatomy and Surface Markings Surface Anatomy of the Head and Neck Surface Markings of Special Regions of the Head and Neck Surface Anatomy of the Back Surface Markings of the Back Surface Anatomy of the Thorax Surface Markings of the Thorax Surface Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Markings of the Abdomen Surface Anatomy of the Perineum Surface Markings of the Perineum Surface Anatomy of the Upper Extremity Surface Markings of the Upper Extremity Surface Anatomy of the Lower Extremity Surface Markings of the Lower Extremity Here are further guidelines. Largest Organs Of The Body Brain Thyroid Skin Lungs Heart Pancreas Liver Spleen Prostate Kidneys Stomach Bladder Organs Of The Body There are almost 78 organs in a human body which vary according to their sizes, functions or actions. An organ is a collection of millions of cells which group together to perform single functions in a human body. The cells in these body organs are highly specialized and formed for all the necessary actions for some specific time. Out of these 78 organs of a male or female body, skin is the largest or biggest organ with respect to its size and weight. The major organ in the body of human beings is the brain which is primarily responsible for performing all the functions and actions of a human body. Other top ten organs of the body are given in the following list with names and functions. Adrenal Glands Anus Appendix Bladder Bones Brain Bronchi Ears Esophagus Eyes Gall Bladder Genitals Heart Hypothalamus Kidneys Large Intestine Larynx (voice box) Liver Lungs Lymph Nodes Mouth Nose Pancreas Parathyroid Glands Pituitary Gland Prostate Rectum Salivary Glands Skeletal Muscles Skin Small Intestine Spinal Cord Spleen Stomach Thymus Gland Trachea Thyroid Ureters Urethra Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. Osteology Anatomy - levels of structural organization in the human body 1. chemical level; 2. cellular level; 3. tissue level; 4. organ level; 5. system; and 6. organismal
How will study of this subject help in diagnosis of human medical conditions, medical advice as per international standards and recent advances, as per preventive and curative concepts of medicine? \ Let's examine this question. Which splints and casts should be used for various injuries? What bones, muscles, arteries, veins, nerves, are associated with this injury or fracture? Which structures and movements are affected with this injury or fracture? What will happen if you don't immediately manage an injury or fracture? Where and when will you use a nail, screw, rod, plate in fixation of a fracture? This is an orthopedics question. To answer this question correctly. You have to know about human bones, muscles, arteries, veins, nerves and all related subjects. What are the most common fractures? How many total fracture cases were reported every year from last 20 years? What are the most common fractures reported at your hospital every year? How many reported fractures were operated? How many developed post operative deformities? Do you know anyone who developed post operative deformity? Did you developer any post operative deformity? Bones How many bones are in the human body? What is the longest bone in the human body? What is the smallest bone in the human body? What are the bones of upper limb? What are the bones of lower limb? What comes under axial skeleton? What muscles originate from each bone? What are the main foramen of base of skull? What structures pass through each foramen? How do bones form? How do bones grow? What types of cells form bone? What is the structure of bone? What materials make up bone? How do muscles attach to bones? What is the function of bone? What are the differences between a human skeleton and a chimpanzee skeleton? Why do teeth come in different shapes? How long does it take a bone to heal normally after a fracture? What is the difference between a splint and a cast? Which splints and casts should be used for various injuries? How each is applied? What should be proper position of the injured extremity? Why is this the proper position of the injured extremity? Muscles of upper limb What are the muscles that move the glenohumeral joint? What is axial skeleton? What are the muscles originating on axial skeleton? What are the muscles originating on scapula? What are the muscles that move the scapula? How can the deltoid muscle both extend and flex the arm? What are the arm muscles that move the elbow joint or forearm? What are the types of movement? What are the hand muscles? What is the origin, insertion, nerve supply and type of movement? What movements are associated with this muscle? How does exercise help build muscles? Cranial nerves How many total cranial nerves are there? What is the location of the nucleus of cranial nerves? What is the pathway from the nucleus to the nerve supply? How many spinal nerves are there? Blood What are the constituents of human blood? What is hematopoiesis? Where are hematopoietic stem cells located? What are the different types and functions of blood cells? Why and how does total cell count increase during infection? Science What is evolution? What is a fossil? Did your ancestors evolve from a single cell, monkey or Adam and eve? What is action potential? Can action potential be initiated remotely? How can action potential be initiated remotely? How are hormones synthesized in the human body? What are the types of hormones? How do hormones work? What is the effect of hormones on Growth and development, Metabolism - how your body gets energy from the foods you eat, sexual function, reproduction, mood? Treatment of esophageal reflux and acid peptic disease with exercise. Have you been diagnosed with esophageal reflux or acid peptic disease? Are you on antacids, h2 blockers? Are you on digene, omperazole, ranitidine, etc? Would you like to give it up? Would you like to have esophageal reflux and acid peptic disease cured with exercise? Here are the guidelines. Sit up right against a wall or back rest. Extend your legs. Keep a hard pillow of at least one foot height below your knees. Lift at least 20 lbs weight with your feet one foot above ground. 120 times. How long will it take? Not more than 5 minutes. Your will get relief within five minutes. You will feel nice throughout the day and night. You have to do it every day. This exercise has other advantages as well. When is the best time to do this exercise? As soon as you feel any discomfort of epigastrium or related symptoms. Now are the scientific questions. What is the mechanism involved? What happens to human biochemisty with exercise? What happens to stomach biochemistry and related organs with this exercise? How does this exercise help in esophageal reflux or acid peptic disease? How does this exercise help in stabilizing human stomach and related bio-chemistry? Is anyone interested in manufacturing Dr. Qureshi's weight training equipment for acid peptic disease? Glucometer What materials are required to manufacture this product? How does it work? How long can it last? What faults may arise? What errors may it give? How do you fix it? How is quality of results measured? What regular supplies are required for product to give results? What is required for maintenance? Is there any other similar product in the market? Is this product of better quality and less expensive? How much space is required to manufacture this product? How many people are required to manufacture this product? Is there an automated system to manufacture this product? Can this product be modified to give other results? Where should be the service station? How often should there be maintenance service? Where and Who is expected to use this product? How many people are expected to use this product? What will be the advantage of this product over other products? Gallstone diseases. Injuries due to gallstone surgeries. This is been reported commonly. How could this have been prevented? Medical Pre-travel medical consultation. You will have to answer these questions for this type of consultation. There are recommendations for vaccines. There is no guarantee these vaccines will be effective. Here are further guidelines. |
Anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry of human beings.
|
What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy is the study of the structure and relationship between body parts. Physiology is the study of the function of body parts and the body as a whole. Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. There are several branches of anatomy, including the following: Histology: The study of the microscopic structure of organs, tissues, and cells. Embryology: Also known as developmental anatomy, the study of embryo development from a single-celled zygote to a fully formed fetus. Gross anatomy: No, not 'disgusting' anatomy. This branch of anatomy has a large scale focus on organs and body structures as a whole. Zootomy: The anatomical study of animals. Phytotomy: The anatomical study of plants. Human anatomy: Also known as anthropotomy, the anatomical study of the human body. Comparative anatomy: The comparative study of the anatomy of different organisms. Anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry of human beings. Anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry of human beings.
Human body
List of the Cranial Nerves 1.I Olfactory (Smell) 2.II Optic (Sight) 3.III Oculomotor (Moves eyelid and eyeball and adjusts the pupil and lens of the eye) 4.IV Trochlear (Moves eyeballs) 5.V Trigeminal (Facial muscles incl. chewing; Facial sensations) 6.VI Abducens (Moves eyeballs) 7.VII Facial (Taste, tears, saliva, facial expressions) 8.VIII Vestibulocochlear (Auditory) 9.IX Glossopharyngeal (Swallowing, saliva, taste) 10.X Vagus (Control of PNS e.g. smooth muscles of GI tract) 11.XI Accessory (Moving head & shoulders, swallowing) 12.XII Hypoglossal (Tongue muscles - speech & swallowing)
|
Muscular System Anatomy
|
There are three types of muscle tissue: Visceral, cardiac, and skeletal.
Alphabetical list of Human Muscles |
|
Q: What is the most important duty and responsibility of a medical doctor? A: A medical doctor should be able to reach to correct diagnosis. Q: What's the second most important duty and responsibility of a medical doctor? A: It is to form a workable, current management plan that meets international standards and recent medical advances. It is appropriate to form a current management plan as per the known preventive and curative concepts of medicine. In case a diagnosis is wrong, international standards and recent advances and preventive and curative measures can often be ineffective. Q: Who is a surgeon? A: A surgeon is a medical doctor with additional training in specific medical procedures. Getting the title of surgeon does not mean he or she is a competent medical doctor. Not all surgeons can perform all medical procedures. Not all medical doctors can perform all medical procedures. Making an eight-inch incision and closing in three layers does not prove you are a surgeon or a medical doctor. Doing a burr hole and closing does not prove you are a surgeon. This is a medical or surgical procedure that can be taught in a few weeks. Doing medical or surgical procedures does not prove you are a competent medical doctor. The ability to reach to a correct diagnosis and provide treatment is a requirement of all medical doctors while maintaining good character and good behavior. Q: How long will it take you to become a medical doctor? A: It takes many resources, efforts, and years to educate a medical doctor to learn skills and knowledge to reach to correct diagnosis and treatment. It takes a few additional weeks to months to learn additional medical or surgical procedures. There are medical colleges that educate medical students for five years with an additional two years considered as specialization - and after completion, the students still cannot reach a correct diagnosis and treatment. Qureshi University College of Medicine has designed and developed courses in question-and-answer format in such a way that you can become a medical doctor in less than five years. Q: What will enhance your early completion? A: You should have the desire to learn to reach to correct diagnosis and treatment of human medical conditions. You should have 24/7 Internet resources. You should have regular discussion with others about medical conditions. You should associate with people who are good charactered and well behaved, and know how to reach a correct diagnosis and treatment. During your practice, these are common questions you should typically expect to receive from your seniors, juniors, colleagues, auditors, investigators, lawyers, patients, and others. After evaluating a case and examining the details, what's your diagnosis? How did you reach this diagnosis? What's your management plan for this particular case? What are the international standards and recent advances that you should know and understand? What is medical malpractice? Do you understand the concept clearly? The list of questions goes on and on and is indeed long. In today's globalized world, every case is subject to open discussions, scrutiny and review. Don't be an embarrassment to the hospital you are working for, your medical College/School, or the administration that may be funding your hospital, medical College/School or practice. Don't be swayed directly, indirectly, overtly, or covertly by any administrative directives or instructions into dishonesty or unethical practices. Physicians are members of a global community. Created by interlocking economies, a global language, the informatics revolution and rapid globalization, all aspects of human existence including science, public health, the environment, law, security, religion and Medicine. Q: What kind of global medical college does this world require? A: Global Medical College Allopathic Who says medical education hasn't changed? International standards are emerging across international boundaries. Evaluation permits the critical question to be asked and answered: have the goals and objectives of new curriculum been met? State Medical Council Association of Global Medical Colleges (Coming Soon) Association of American Medical Colleges (World wide alert. Association of American Medical Colleges is declared as a racist, harmful organization) What are your duties and responsibilities? How would this question have been answered in 1950?
There were no central processing units. There was no World Wide Web. Q: What other duties and responsibilities can a medical doctor have? A: This ranges from being a medical hospital director/administrator or Director of Health, Researcher, Principal Medical College, member of the Governing Council, Administrative secretary health, to being head of the regional administration, an entrepreneur, a global leader, Governor, Senator, Judge, Minister, Foreign minister/Secretary, a head of state, or an administrator of an international organization with a global perspective and manifesto. A global leader, Governor, Senator, Judge, Minister, Foreign minister/Secretary, a head of state, or an administrator of an international organization with a global perspective and manifesto. What do I have to do? Medical college, Real world case management experience, plus, Take a look at this. Political science Law Economics Police Training International Business Computer Science Mass Communication Engineering Psychology Military Science Industry specific One of the medical doctors mentions that our primary duty as clinicians is to treat the ailing. Will you do symptomatic treatment? Will you do empirical treatment? Will you reach a scientific correct diagnosis and then treat the patient? Correct diagnosis is essential. Without correct diagnosis, treatment can be harmful or ineffective. It's better to see one patient per day and reach a correct diagnosis and treatment than to see dozens of patients per day and give wrong diagnoses with wrong treatments. Diagnosis audit, treatment audit, conduct audit, procurement audit, vicarious liability: incompetence is been taken seriously worldwide. How do you update your skills and knowledge? How do you impart skills and knowledge to others? Teaching, research, continuing education. Q: What should be the focus of treatment? A: Use of drugs and surgical procedures aren't the only treatment options. Counseling can help. Physical rehabilitation can cure. Start with counseling and physical rehabilitation; after that, drug use or surgical option. How do you reach a correct diagnosis? How do you treat cases according to international standards and recent advances, and to the preventive and curative aspects of medicine? Here are important guidelines for admission to Medical College International. What is the difference between allopathic medicine and homeopathic medicine? What subjects do they study? What questions do they address? What problems do they solve? What cases do they diagnose? What cases do they manage? What international standards, recent advances, preventive and curative concepts of medicine do they follow? Is cardiology allopathic medicine or homeopathic medicine? Is internal medicine allopathic medicine or homeopathic medicine? Is gastroenterology allopathic medicine or homeopathic medicine? Is emergency medicine allopathic medicine or homeopathic medicine? A medical doctor often adds titles after his/her name, i.e., MBBS, MD, DM, FRCP (Edin.), FACP (USA), Master of the American College of Physicians, Director Digestive Diseases Center. This doctor doesn't know what is good human character or good human behavior. On February 17, 2010, he gives an unintelligible presentation on Morbidity and Mortality without knowing the difference between Morbidity, Mortality and medical malpractice. Do these titles have any value if the person listing them isn't able to answer correctly? Q: What is the proof of your competence? A: You should be able to answer questions correctly. The same should be displayed publicly. Q: Can an English teacher guide a medical doctor in diagnosis and treatment? A: No. Q: Can a social worker guide a medical doctor to reach to a correct diagnosis and treatment? A: No. Q: Can a medical doctor guide a medical doctor? A: Yes, a competent medical doctor can guide a medical doctor. A medical doctor fraudulently and maliciously selected medical doctors for post-graduation and became director of a hospital. A female medical doctor had sex with one political cult and became principal of a medical college. That is not proof of competence. That is criminal wrongdoing. How should you guide others? Here are further guidelines. |
|
Are humans superior to animals and plants? Is there a difference between anthropology and human health care? What is biology? What is life? When did life begin on Planet earth? What is the population of humans on the planet earth? What needs to be modified in scientific classification of living things? How should you elaborate humans in the scientific classification of living things? What is health? What is human health care? | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Are humans superior to animals and plants? Yes. Is there a difference between anthropology and human health care? Yes. What is biology? Biology is the science concerned with the study of life. What is life? When did life begin on Planet earth? Here are further guidelines. Health What is health? Health is the level of functional or metabolic efficiency of a living organism. What is human health care? Human health care is the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in humans. What is the population of humans on the planet earth? By 2013, the global human population was estimated to be around 7 billion. Scientific classification What needs to be modified in scientific classification of living things? Humans have to be categorized separately. Homo or homo sapiens should not be connected to humans. Homo has various different meanings, thus confusing others. How should you elaborate humans in the scientific classification of living things? Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Class Mammalia Order Primates Family Hominidae Genus Intellectual (renamed after research of Asif Qureshi. Do not write Homo) Species sapiens You can also elaborate in alphabetical order Class Mammalia Domain Eukarya Family Hominidae Genus Intellectual (renamed after research of Asif Qureshi, Do not write Homo) Kingdom Animalia Order Primates Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Species sapiens | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
What is health? What is human health care? Here are further guidelines. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Human Body Anatomy Systems 11 Systems of the Human Body
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 100 Very Cool Facts About The Human Body | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| effects of aging on the human body | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Human Body Systems 100 trillion cells 206 bones 600 muscles 22 internal organs |
Bones
|
How many human body bones are there in one matured human being? (206) What are the names of human body bones? Axial Skeleton (80) Appendicular Skeleton (126) Axial skeleton It consists of the following 80 bones. Skull: 22 bones Hyoid: 1 bone Vertebrae: 32 bones Ribs: 24 bones Sternum: 1 bone Attached to the axial skeleton is the appendicular skeleton, which consists of 126 bones. v Pectoral girdle: 4 bones .(Scapula and clavicle) Arms and forearms: 6 bones .(Humerus and radius) Wrists and hands: 54 bones .(Carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges)v Bony Pelvis: 2 bones .(Os coxae) Thighs and legs: 8 bones .(Femur, patella, tibia, and fibula) Ankles and feet: 52 bones .(Tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges) Axial Skeleton (80) Appendicular Skeleton (126) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) Torso (52) Appendicular Skeleton (126) Upper Extremity (32 x 2 = 64) Lower Extremity (31 x 2 = 62)
|
| Human Body (206) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Axial Skeleton (80) | Appendicular Skeleton (126) | ||
| Skull (28) | Torso (52) | Upper Extremity (32 x 2 = 64) | Lower Extremity (31 x 2 = 62) |
Paired Bones (11 x 2 = 22)
|
Paired Bones (12 x 2 = 24)
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
What is the longest bone in the human body?
What is the smallest bone in the human body? What are the bones of upper limb? What are the bones of lower limb? What comes under axial skeleton? What muscles originate from each bone? What are the main foramen of base of skull? What structures pass through each foramen? How do bones form? How do bones grow? What types of cells form bone? What is the structure of bone? What materials make up bone? How do muscles attach to bones? What is the function of bone? What are the differences between a human skeleton and a chimpanzee skeleton? Why do teeth come in different shapes? How long does it take a bone to heal normally after a fracture? What is the difference between a splint and a cast? Which splints and casts should be used for various injuries? How each is applied? What should be proper position of the injured extremity? Why is this the proper position of the injured extremity? |
|
How many human anatomy categories are there? 19 What should you know about human anatomy by category? Head Anatomy Neck Anatomy Shoulder Anatomy Back Anatomy Chest Anatomy Abdominal Anatomy Hip Anatomy Upper Leg Anatomy Knee Anatomy Lower Leg Anatomy Ankle Anatomy Foot Anatomy Upper Arm Anatomy Elbow Anatomy Forearm Anatomy Wrist Anatomy Hand Anatomy Skin Anatomy Internal Organ Anatomy |
| Internal Organs Anatomy |
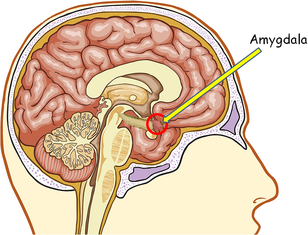
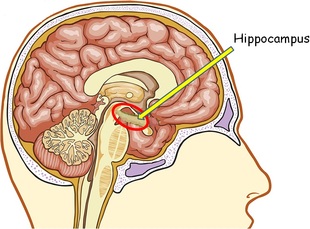
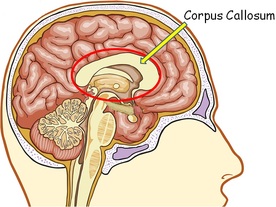
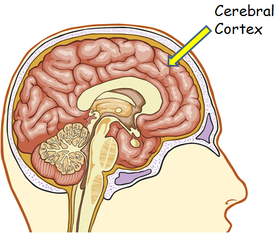
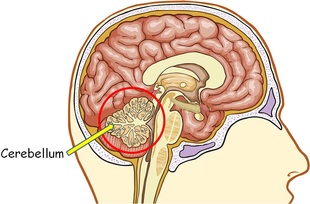
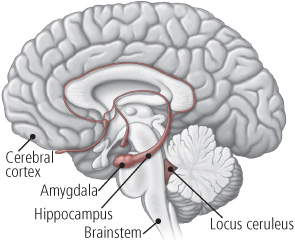
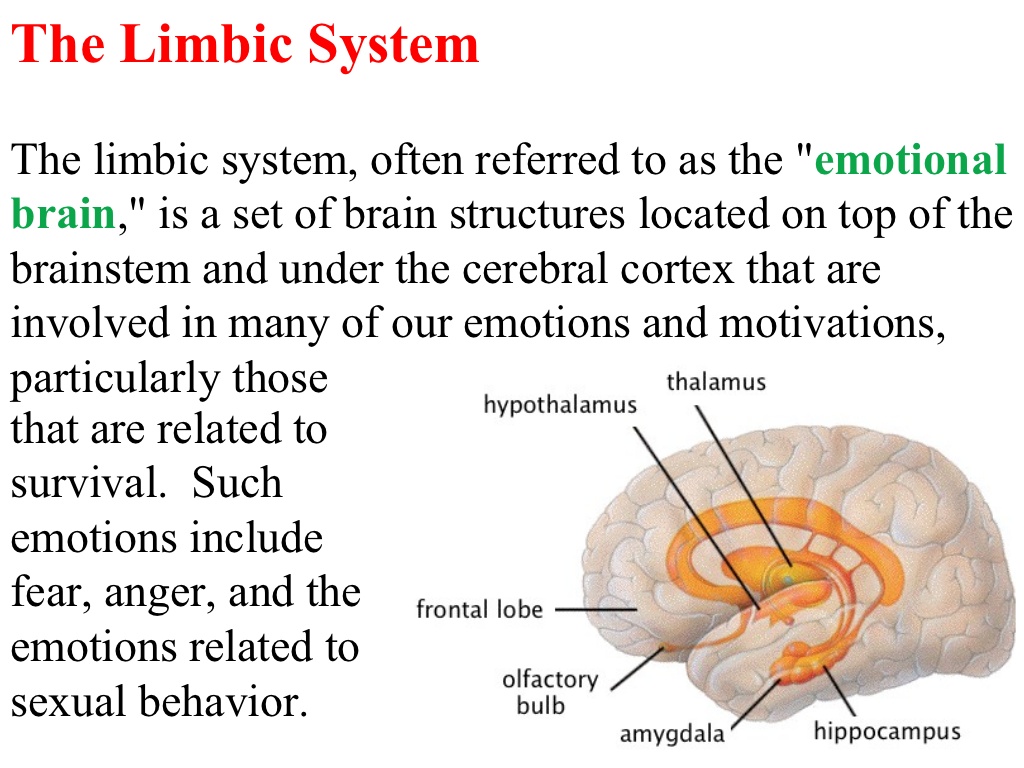
Brain 
|
Colon 
|
Gall bladder 
|
Heart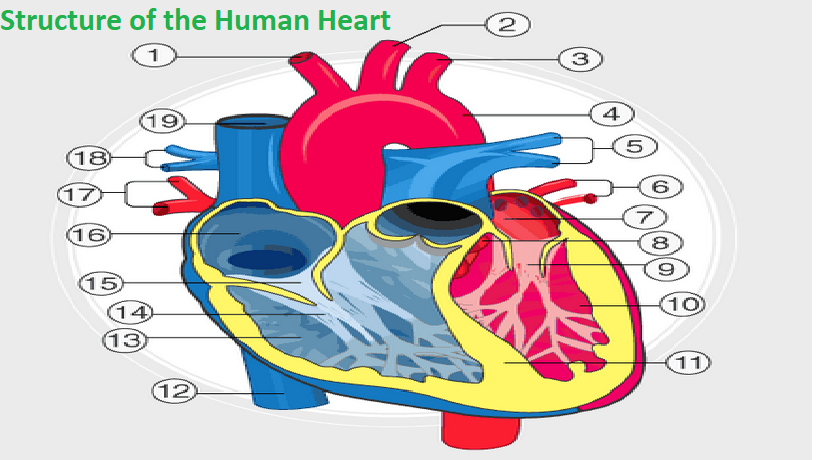
|
Kidneys
|
Large intestine 
|
Lungs 
|
Liver
|
Pancreas 
|
Small intestine 
|
Spleen 
|
Stomach
|
|
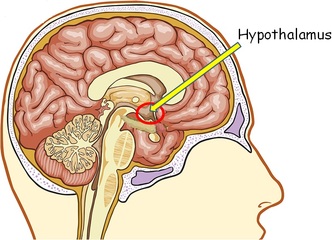
Adrenal Glands Appendix Bladder Brain Esophagus Gallbladder Heart Intestines Kidney Liver Lungs Ovaries Pancreas Parathyroid gland Pituitary gland Prostate gland Spleen Stomach Testicles Thymus gland Thyroid gland Uterus |
| Human Health Care Settings |
| Human Body Quiz |
| What is human anatomy? |
| Internet Human Health Care Services |
| People |
| Role of Minerals in the Body |
| Types of human deformities |
Human biochemistry
| What reference ranges of human blood tests does your biochemistry laboratory follow? |
| Medical biochemistry |
| What is the difference between basic metabolic panel, comprehensive metabolic panel and metabolic panel 20 in human blood tests? |
Doctor Asif Qureshi’s lecture to first-year medical students during first class.
|
Who is the audience of this lecture? This is relevant to all principals of medical colleges in various states, medical students, and existing specific physicians. This is particularly relevant to government medical college principals in Srinagar and medical students who started their first class on August 21, 2017, in Srinagar government medical colleges. The profiles of 100 new medical students were not available. What do we start and where do we end? Assessment of a patient by a physician in various healthcare settings. Specific physicians required in every state at this point. Critical, emergency, and non-emergency medical complaints. Human diagnosis and treatment facts. Previous curriculum of specific physicians Assessment of a patient by a physician in various healthcare settings. Is this a critical, emergency, or non-emergency medical complaint? http://www.qureshiuniversity.org/assessment.html Previous curriculum of specific physicians What was the previous first-year medical college curriculum? Human anatomy Human biochemistry Human physiology Human cell biology Human embryology Human genetics Human behavior Human immunology Human neuroscience or neuroanatomy Some medical colleges are still teaching a historical or outdated curriculum. What was previously taught for 4 years in medical college? http://www.qureshiuniversity.org/medical.html In those days, there was no computer or Internet. In those days, there was not such advanced research. Critical, emergency, and non-emergency medical complaints. Questions you must be ready to answer. How many critical medical complaints are there? What are the critical medical complaints? How many emergency medical complaints are there? What are emergency medical complaints? How many non-emergency medical complaints are there? What are non-emergency medical complaints? What are examples of medical symptoms by human organ systems, age, and gender? What is on the list of all medical complaints? What must you do once you are placed for specific physician services? The 9 issues elaborated are critical. Any abnormality in vital signs, like consciousness, pulse, blood pressure, respiratory rate at rest, and high-grade temperature with complications. http://www.qureshiuniversity.org/criticalcareworld.html What issues need on-the-spot diagnosis and treatment? http://www.qureshiuniversity.org/onthespotemergency.html http://www.qureshiuniversity.org/symptoms.html What are various systems of medicine? Allopathic Osteopathic Unani medicine What types of guidelines for specific physicians are at these resources? Specific allopathic physician guidelines. What type of specific physician should you plan to be immediately? Select one of the specific specialties mentioned. Take a look at this. http://www.qureshiuniversity.org/physicians.html What type of specific physician should you plan to be later on due to the fact that fewer of them are required? Physician director of public health of the state. Physician director of health of the state. Governor of a state |