

| What must you do before submitting or publishing your writing in English? |
| 1. Get answers to relevant questions before writing in English. |
| 2. Write about ideas that are relevant to the topic or issue. Make sure the writing is relevant to the topic or issue. |
| 3. Check all spelling. |
| 4. Use punctuation correctly. |
| 5. Capitalize correctly. Capitalization is not considered part of the punctuation. |
| 6. Write according to the presentation requirements, such as a question-and-answer presentation, a paragraph, a few paragraphs, or an incident report in a specific format. |
| 7. Write according to the document requirements. What are the types of documents in English language? Examples are a letter or a book. Here are further guidelines. |
| 8. Other issues relevant to writing in English. |
|
How many words or pages are to be written when 300 words equal 1 page? What is the topic or issue you need to write about in English? What type of document is to be written? What type of editing is required (for example, American English, non-American English)? Where will this document be used? Where must you forward the document? Whose perusal is required before displaying the document? Who are the audiences for this written document in English? When should the document in English be ready? Why do you have to write this document? What questions must you learn to write correctly in English? What questions must be answered before writing in English? Here are examples of questions with answers. What is the topic or issue you need to write about in English? English language writing skills. How many words or pages are to be written when 300 words equal 1 page? 300 words or 1 page is required. What type of document is to be written? Questions and answers are required. The questions and answers required should not be similar to what is displayed here. What type of editing is required (for example, American English, non-American English)? American English. Where will this document be used? Schools, colleges, universities, and executives of departments will benefit from these documents. Whose perusal is required before displaying the document? A review by an experienced editor of the English language is required. To whom does the writing need to be forwarded for further review before publishing or submitting? None. Why do you have to write this document? These documents will be education materials for others. Who are the audiences for this written document in English? School, college, and university students as well as current professionals are the audience. When should the document in English be ready? The document should be ready within the next 7 days. Where must you forward the document? The document must be forwarded to: admin@qureshiuniversity.com Questions you must know to write correctly in English. What questions must you learn to write correctly in English? Take a look at this. https://www.qureshiuniversity.org/techniques.html#English Here are further guidelines. https://qureshiuniversity.com/schoolworld.html |
|
We are here today so that I can teach you how to write in the English language. Do you know how to write in the English language? Do you know English words so that you can write in the English language? What English language documents can you write? What are various types of English language documents? How many different types of English language documents can you write? Can you write a research paper with questions and answers in the English language? Can you write a research paper of at least of 300 words (one page) with questions and answers in the English language on the topic of the English language? If no, these guidelines are for you. These guidelines are for those learning to write in the English language. Questions you must know to write correctly in English. What questions must you learn to write correctly in English? Take a look at this. https://www.qureshiuniversity.org/techniques.html#English |
Agendas
What does an agenda look like? Here are further guidelines. |
Books
How do you write a book? Here are further guidelines. |
Cover letter
What is a cover letter used for? Here are further guidelines. |
Documentation (Manuals)
Software Vehicles Construction Etc. Here are further guidelines. |
Dictionary
What is an encyclopedia? Here are further guidelines. |
Electronic mail
Write an electronic mail similar to a letter. Here are further guidelines. |
E-book
Here are further guidelines. |
Educational resources on the Internet
How do you measure usefulness of an educational resource on the Internet? Here are further guidelines. |
Hypertext document
Here are further guidelines. |
Instructions and procedures
Here are further guidelines. |
Interrogatories
Who writes most interrogatories? Here are further guidelines. |
Issues
What is the issue or issues? How many words or pages are to be written when 300 words equal 1 page? Here are further guidelines. |
Journals
What are the types of journal? Here are further guidelines. |
Literature reviews
Here are further guidelines. |
Letters
What are the different types of letters? Here are further guidelines. |
Linguistics
Here are further guidelines. |
Meeting documents
Here are further guidelines. |
| Memoranda |
Medical records
Here are further guidelines. |
| Notebooks |
| Newspapers |
News reports
Here are further guidelines. |
Oral Presentations
Here are further guidelines. |
| Proposals |
| Press releases |
Progress Report
Here are further guidelines. |
Profile/Résumés
Relevant skills, activities, and accomplishments. More questions can be asked to get more details. Here are further guidelines. |
Public Notice
Where should public notices be displayed? What questions should be answered before issuing a public notice? Here are further guidelines. |
Resume
How should you display your biodata? Here are further guidelines. |
Research Documents
Here are further guidelines. |
| Reports |
Recreational website
Here are further guidelines. |
| Specifications (Manufacturing) |
Statement of purpose
Here are further guidelines. |
Schools, colleges, and universities on the Internet
http//www.qureshiuniversity.com What can be displayed about schools, colleges, and universities on the Internet? Factual educational text, graphics, animation, and video. Here are further guidelines. |
|
Style guides
|
Theses
Here are further guidelines. |
|
What English language words should you know?
Alphabet Word Phrase Paragraph Line Sentence Punctuation Page Questions and answers What writing tools and materials should you be familiar with? Paper Pencil Eraser Scale/ruler Pen Ink Ballpoint pen Teaching tools and materials Chalk Blackboard Computer Word processor Internet Dictionary Printer Olden day tools of writing Quill pen (bird feather) Wooden writing board You can add more writing tools and materials if anything new comes up. What English language document do you plan to write? What is the detailed description of the English language document you plan to write? Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/englishworld.html What should you know about the English language? Semantics What do words and sentences mean? Lexicology How are words formed? Grammar and discourse studies How are words organized into larger structures? Language and culture, sociolinguistics How does language relate to the society we live in? Stylistics How is language used in literature? Phonetics and phonology How is English language pronounced? Orthography and graphology How is English language written? Onomastics How do names arise and what do they mean? Lexicography How do dictionaries and thesauruses work? Historical linguistics How and why has English changed in the last 1500 years? Old and Middle English literature What kind of literature survives from the medieval period? Study of manuscripts and olden printed materials/books. How is olden days literature transmitted? Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/englishworld.html What is writing? What is the best method of writing in English language? What is the difference between language and writing? What are the types of writing as per purpose? What are the types of writing as per type of document in the English language? What should you know about English language writing skills? What are excusable errors in writing English without a computer and editing? What is language? How should you select an English language writing topic? | |||||
|
What is writing?
If you ask this question of 10 different writers, you will get 10 different answers. Text/signs or symbols of a specific language are essential in writing. Letters of the alphabet or symbols are written or imprinted on a surface of material to represent the sounds or words of a language. English language writing English language writing is a skill. English language writing is an essential job skill. There are many languages that can be put in writing. English language writing is most popular. What is the best method of writing in English language? Write in question-and-answer format. In certain situations, you need to display only answers. What is the difference between language and writing? There are many languages in the world. The English language is most popular language. Language can be written or spoken. What are the types of writing as per purpose? Narrative. Expository. Persuasive (questions and answers). Descriptive. What are the types of writing as per type of document in the English language? What should you know about English language writing skills? It is very difficult to write an English language document without errors without having a computer and editing or editing software. What are excusable errors in writing English without a computer and editing? Occasional spelling error. Occasional punctuation error. If interrogative sentences (questions), declarative sentences, imperative sentences, and exclamaratory sentences are not differentiated in English language writing, that is not an excusable error. What is language? Language is a set of words or symbols used for communication. The words and symbols may be spoken or written. There also are sign languages. Speech is the verbal means of communicating. Language is a set of symbols being used mainly for communication. The symbols may be spoken or written. We use language to express inner thoughts and emotions, make sense of complex and abstract thought, to learn to communicate with others, to fulfill our wants and needs, as well as to establish rules and maintain our culture. | |||||
| Language Guide | |||||
| Writing in the English language | |||||
| Writing guidelines | |||||
|
English language writing topic How should you select an English language writing topic? There are more than 34 different kinds of English language documents. Writing a complaint letter is a common English language document. News report. Interrogatories. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. What should you do if teacher or any other person is asking you to write a fictional essay/story/composition in English language? If you are a school student and your teacher is asking you to write a fictional essay/story/composition in the English language, inform your teacher that this type of writing is not useful in the real world. This type of essay/story/composition is not relevant to the real world. You need to practice writing English language documents that are relevant and useful in real world. If you are a parent/guardian and your child/children is/are asked by a teacher to write a fictional essay/story/composition in the English language, inform the teacher that this type of writing is not useful in the real world. What are examples of English language documents that are relevant and useful in the real world? http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/englishworld.html This is in the context of English language Is there a difference between a phrase and a simple sentence? Yes, there is. What is the difference between a phrase and a simple sentence? Can you give some examples with declarative, interrogative, exclamatory, and imperative sentences? Do you know more than what has been included in these details? Do you agree that everything is correct in these details? What should you do if learning the English language seems difficult? You can start directly with questions and answers in the English language if other methods seem difficult. What are the types of documents in English language? Agendas Books Documentation (Manuals) Dictionary Electronic mail E-book Educational resources on the Internet Hypertext document Instructions and procedures Interrogatories Journals Literature reviews Letters Linguistics Meeting documents Memoranda Medical records Notebooks Newspapers News reports Oral Presentations Proposals Press releases Progress Report Profile/Résumés Public Notice Research Documents Reports Recreational website Specifications (Manufacturing) Statement of purpose Schools, colleges, and universities on the Internet Style guides Theses What should you not write? Fiction Dramas Poetry How should you write? In a questions-and-answer format. All the reports are written in question-and-answer format. A final presentation can vary from presenting a question-and-answer format to presenting answers only. Here are the questions you need to answer. Do you have proper writing tools? Do you need an editing service? Where will your writing be useful? How will your writing be useful? Writing in the English language What do you have to do to write better in the English language?
|
Here are further guidelines. 
|
|
Is there a difference between an announcement of death and a condolence? Yes. What is the difference between an announcement of death and a condolence? The announcement of death happens first, followed by condolences. Never hide a human death. You can be charged with a crime if you hide any human death. Condolence messages can be forwarded via media, postal mail, email, and telephone calls or in person. What should be included in a condolence press release? Was the death natural old age death or premature death? What was the day, date, time, location, profile, background, and circumstances of the individual’s death? How old was the individual? What do I remember about this individual? How did this individual enhance public services? Thank God healthcare services prolonged her life up to now. Sooner or later, everyone must go. I send my heartfelt condolences to your family. Thinking of you in your time of loss. |
| Obituary |
|
CONDOLENCE November 8, 2015 |
|
Aviation Emergency News. What are the day, date, time, location, and details of the incident? On Monday, January 26, 2015, at 1PM, a Greek fighter jet crashed in Spain, killing 10 people. The F-16 fighter jet is reported to have crashed shortly after taking off. What caused this air crash? The cause of the air crash is under investigation. Verification of News Report How do you verify a news report? I am calling to verify news report. On January 26, 2015, a Greek fighter jet crashed in Spain, killing 10 people: Is that correct? What are the sources of these facts? The air crash could not be verified because the phone number at the Barcelona Airport was unavailable. A call to 93 297 11 39 was answered: You have reached a nonworking number. How do you call from Chicago, Illinois, to Spain? 011 International code 34 regional code Airport Number 93 297 11 39 It rings but no one answers the telephone call. Email questions are awaiting a response. |
|
What are the human healthcare issues at this point? Stress is harming the residents. Substandard health care providers are harming residents. Healthcare Service quality assessment. How do you assess the quality of health care in an area? Answer these relevant questions. What area is been elaborated? Walkable distance from 5042 N. Winthrop Ave., Chicago, Illinois 60640. How is health care service in this area? Physicians are not competent. Counselors for stress are not available. Emergency medical professionals are not able to provide proper service. Healthcare facilities are available but competent staff, including competent physicians, is not available. Medication available is of good quality. This holds true from 1999-2015. |
|
From: Asif Qureshi, MD 5042 N. Winthrop Ave., Unit 237 Chicago, IL 60640 Telephone: 773-561-6102 Fax: 773-337-9107 Email: admin@qureshiuniversity.com Internet: www.qureshiuniversity.com/physicians.html Guide for 19 specific types of physicians. This is in addition to other executive professionals. To: Mario Treto, Jr. Acting Secretary Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation 100 West Randolph, 9th Floor Chicago, IL 60601 Cecilia Abundis Acting Director, Division of Professional Regulation Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation 100 West Randolph, 9th Floor Chicago, IL 60601 Subject: Issues Date of Circulation: July 6, 2021 Message: My name is Asif Qureshi. I am the founder of Global University. I am a qualified medical doctor. I am also a forensic psychiatrist. I am a problem solver. I can teach clients 60 categories of skills. I can guide 19 specific types of physicians. I can guide more than 1000 different professions, including teachers, lawyers, engineers, and physicians. I have 7 years of in-hospital experience as a doctor. I have 21 years of research experience in Chicago, Illinois. I have completed 1,181 academic projects since 1999. I have been doing this in Chicago, Illinois, since 1999. Professional Licensing Department Professional Licensing Issues Questions you need to answer. 1. What type of specific physician license will you offer to an individual like Dr. Asif Qureshi, who can guide 19 specific types of physicians, as demonstrated at https://qureshiuniversity.com/physicians.html? 2. What type of specific professional license at the executive level will you offer Dr. Asif Qureshi, who can guide so many professions at executive levels, including 19 specific physicians, lawyers, teachers, engineers, and administrators, as demonstrated at https://qureshiuniversity.com/professionsworld.html? 3. What do you understand by the alternative route to licensure for a person like Dr. Asif Qureshi, who can guide so many professions, including 19 specific types of physicians, lawyers, teachers, engineers, and administrators, as demonstrated at https://qureshiuniversity.com/professionsworld.html? What do you have to do? Answer the mentioned questions. Verify the findings at https://qureshiuniversity.com/professionsworld.html and www.qureshiuniversity.com/physicians.html, which document the research conducted by Dr. Asif Qureshi over the last 21 years, from 1999 to 2021, in Chicago, Illinois, United States, and forward the relevant professional license document to me relevant to the mentioned questions. Some of your questions and forms for professional licensing are not relevant to me. First understand my issues. One of the options is an executive-level job for Dr. Asif Qureshi at: Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation 100 West Randolph, 9th Floor Chicago, IL 60601 https://www.idfpr.com/About/About.asp What will my duties and responsibilities be at the executive level? 1. 19 specific types of physician licensing with alternative route options. 2. Educator license. Mandatory research presentation from educators for their licensing. 3. Lawyer license 4. Engineer license 5. Administrator license 6. Many more What did you understand after reading these facts? What is your answer to these questions? How do you plan to resolve these issues? How soon should I expect a response from you? |
|
How do you write incident reports in English language? Start with the day, date, time, harms, circumstances/scenario, and location inside or outside of the state. At least 6 points must be elaborated upon. Seven additional points have to be elaborated upon separately. What happened? On Tuesday, November 14, 2017, at 8 AM local time, at least 6 people were killed and 10 injured after a shooting in Rancho, Tehama County, California. The location is 125 northwest of Sacramento, California. Among the dead is the shooter. You can also write it like this. Circumstances of incident, day, date, time, harms, location inside/outside the state. What happened? Circumstances of incident: Shooting Day: Tuesday Date: November 14, 2017 Time: 8 AM local time Location: Rancho, Tehama County, California. Nearby location: Rancho Tehama School https://rts-corning-ca.schoolloop.com/newsletters Area zip code: 96021 Corning Tehama CA Assailant: Dead suspect was Kevin Janson Neal, 43. Harms: At least 6 dead and 10 injured. Weapons used: AR-type of weapon. A semi-automatic rifle and two handguns. The shooter was wearing the type of vest worn by soldiers carrying ammunition. Type: 223 Rem [AR-15] Motive: Further investigations are ongoing. Questions that need further answers. What was the motive behind this incident? How did this person get the weapons? Who is manufacturer of the weapons? Who must investigate the case? Local police. Investigators, including a forensic psychiatrist and forensic pathologist. Public health officials. Emergency Department Office of the Governor of California. Verification of facts of incident. November 14, 2017 Six dead after gunman opens fire on multiple sites, including a California elementary school. Is that correct? Who was asked to verify the facts? Lieutenant Yvette Borden email yborden@tehamaso.org internet address http://tehamaso.org/administration/. Did you get a verification email on November 14, 2017, at 5:35:10 PM local time? Laws relevant to this government department inside and outside the state. Emergency Management Department administrative laws inside and outside the state. Police Department administrative laws inside and outside the state. Can you elaborate on the administrative laws relevant to this government department inside and outside the state? How many laws are relevant to this government department inside and outside the state? What do you know about the administrative laws relevant to this government department inside and outside the state? Nevada What happened? On October 2, 2017, at Mandalay Bay, Las Vegas, Nevada, at least 59 were killed after a shooting. When the Nevada incident happened, the governor and director of this department did not know anything. These resources http://dem.nv.gov/ did not display anything for days after the incident. New York What happened? On November 1, 2017, at least 8 were killed after a truck attacked them in Manhattan, New York. When the New York incident happened, the governor and director of this department did not know anything. These resources www.semo.state.ny.us/ did not display anything for days after the incident. Texas What happened? On November 5, 2017, at least 28 people were killed after a shooting at a Texas church. Where is the situation or incident report from the emergency government department of Texas? http://www.dps.texas.gov/dem/ Situation Reports November 5, 2017 4.45 PM We are sorry, that page doesn't exist Who is responsible for uploading a situation or incident report from Texas to http://www.dps.texas.gov within 5 minutes of incident? Questions every director of the emergency department of a state must answer through the internet inside and outside the state. Incident Questions. What happened? When did this happen? Where did this happen? At which location? Who all was involved? Whom did you contact? Whose location is this? Why did this happen? How long did emergency responders take? How could this have been prevented? What needs to be accomplished immediately? What needs to be accomplished later on? Answers to these questions must be uploaded immediately to the mentioned resources within 5 minutes of an incident happening. http://www.qureshiuniversity.org/stateofficesemergencymanagement.html What human healthcare services are provided through a website, such as www.qureshiuniversity.org/health.html from Doctor Asif Qureshi? Patient care where face-to-face in-person meetings are not required. Medical research Medical education Issue-based advice Public health advice Administrative issues When should a specific physician provide human healthcare services through the internet? A specific physician with experience of more than 7 years in hospital patient care must provide healthcare services through the internet. Snowfall (Public health emergency) March 3, 2015, snowfall in Kashmir, Asia.
Meeting Report
Protest Report
Recommendations Report Recommendations on February 17, 2015
|
Present tenses
|
|
Quoted speech sentence in English language.
How do you write a quoted speech sentence in English language? “I will be investigating this case,†he said. Reported speech sentence in English language. How do you write a reported speech sentence in English language? He said that he would be investigating this case. There are many more examples. Statement of a person or persons
|
|
How should you do a presentation in English language? In a question-and-answer format in English language. Why should you do a question-and-answer presentation in English language? Findings can be utilized for investigation, research, and further research. |
|
|
Take a look at this. What is the word? Alphabet What do you have to do? How will you explain this word in the given parameters? Definition Usage Word origin English word class (part of speech) Pronunciation Synonyms Antonyms Names in other languages Inflections Homonyms (Yes / No) Derivations Length: 8 characters Syllables Example sentences What is the usage of this word? Can you make at least four different sentences using words you know? Definition What is the definition of this word? A set of symbols, components, or letters in a particular order that are used for writing a language. Word origin What is the etymology or origin of this word? Most lexicographers believe that the origin of English words is Latin. That is not correct. English language is the most evolved. Other languages develop from the most evolved languages. An English word can have an equivalent in Latin, Greek, or other languages. That does not mean it originated from that language. If any lexicographer presents the origin of an English word from Latin or any other language, ask them these questions: How did you verify that this English word originated from Latin or any other language? Did the English language exist first or did the Latin or other language exist first? What is the proof of these findings? Parts of speech What part of the speech does this word belong to? What is it? Noun Synonym What is the synonym of this word? Antonym What is the antonym of this word? Names in other languages What is this word in other languages? Spanish alphabetum Kashmiri alfaz Inflections Are inflections (prefix, suffix, plural, possessive) applicable to this word? What are the details of inflections of this word? Do all English words have inflections? No, they do not. Nouns, verbs, and adjectives have inflections. Now adverbs also have inflections. Pronunciation How is this word pronounced? The individual symbols or letters of alphabet are pronounced differently. Consonants Vowels Stress Derivative Are there any words derived from this word? Is there a difference between word inflection and a derived word in English grammar? Yes, there is. What is a derived word? In English grammar, it is a word that is formed from another word and that belongs to another class of word. Electronic (adjective) electronically (Adverb). Do all adjectives have derived adverbs? Example sentences. How many different patterns of sentences can you make with one word? You can make more than 30 different sentences from one word. How do you use this word in interrogative, declarative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences? When did the English alphabet come into existence? (Interrogative) The English alphabet has 26 letters. (Declarative) Memorize the English alphabet. (Imperative) What a nice photograph of the English alphabet! (Exclamatory) |
|
How does the English language have mathematical answers? What is a declarative sentence? What are the types of declarative sentences? What are the types of simple declarative sentences? How many types of declarative sentences are there? What are various examples? How many types of simple declarative sentence are there? How do you write a simple declarative sentence? What are various patterns of simple declarative sentence? What are the parts of a declarative sentence? What are some examples of declarative sentences? What are the different verb tenses? What should be goals of your English language learning? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
What are the types of declarative sentences?
Simple declarative sentence. Compound declarative sentence. Complex declarative sentence. Complex compound declarative sentence. How many types of simple declarative sentence are there? 9. What are the types of simple declarative sentences? What are various patterns of simple declarative sentence? A simple declarative sentence has following patterns.
      Basic Sentence Patterns Subject + Verb Subject + Verb + Object Subject + Verb + Adjective Subject + Verb + Adverb Subject + Verb + Noun Pattern 1 - Subject + Verb Pattern 2 - Subject + Verb + Direct Object Pattern 3 - Subject + Verb + Direct Object + Indirect Object Pattern 4 - Subject + Linking Verb + Noun Complement Pattern 5 - Subject + Linking Verb + Adjective Complement Subject-Verb-Complement Subject-Verb-Direct Object Subject-Verb-Indirect Object-Direct Object Subject-Verb-Direct Object-Complement Periodic Sentences Cumulative (Loose) Sentences Pattern 3 - Subject + Verb + Direct Object + Indirect Object Asif gives flower to Amy. Pattern 3 - Subject + Verb + Direct Object + Indirect Object Asif gave a book to Amy yesterday. Subject-Verb-Indirect Object-Direct Object Amy is baking a cake for her mother. There are more than nine types of simple declarative sentences. They are also called patterns of simple declarative sentences. Here are further guidelines. Subject + Verb + Object combine to make basic English sentences. Subject: who/what the sentence is about. Verb: What the subject does/is. Object: a person or thing that is affected by the action of a verb. Subject Verb Agreement 20 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement Singular subjects take singular verbs: Plural subjects take plural verbs: 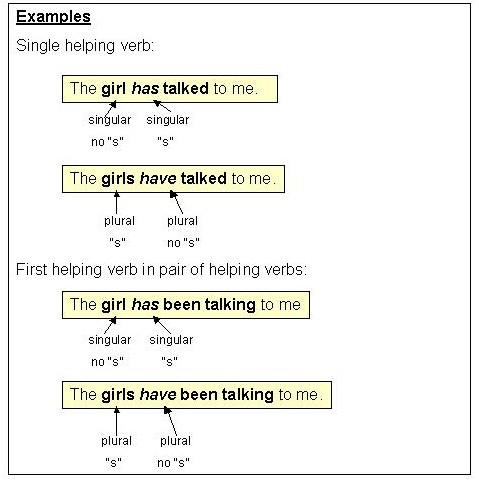 1 - The rain ___ flooding the village. are is Correct! is 2 - All the customers ___ left the shop. has have Correct! have 3 - A dog chased ___ all the way home! us we Correct! us 4 - Those girls ___ my students. is are Correct! are 5 - ___ has brown hair. He Him Correct! He 6 - The fireworks ___ beautiful. looks look Correct! look 7 - The pollution around here ___ awful. are is Correct! is 8 - Was __ looking at us? him he Correct! he 9 - We ___ reading when you called. were was Correct! were 10 - It ___ been snowing all day. has have Correct! has How do you write a simple declarative sentence? I, you, he, she, we, they, Asif (your name), my, their, all, a, an, the usually begins the simple declarative sentence. You can utilize other words also. What pattern or type of simple declarative sentence do you plan to write? 1. S + V 2. S + V + O 3. S + V + C 4. S + V + A 5. S + V + O + O 6. S + V + O + C 7. S + V + O + A 8. S + V + preposition + noun 9. S + V + preposition + verb(ing) gerund. What should be the pattern and tense of a simple declarative sentence? How many tenses can one pattern of simple declarative sentence have? Each pattern of a simple declarative sentence has 12 tenses. Here are simple declarative sentences with words beginning with I, you, he, she, we, they, Asif (your name), my, their, all, a, an, the. I will be investigating this case. What is the analysis of this English language sentence: "I will be investigating this case." I am writing to you to get answers to my questions. You did not precisely reply to my questions. He had no answers to my questions. She does not have any English language abilities. We must go ahead question by question. They are not enhancing the economy. Asif (your name) has many abilities and skills. My computer needs to be replaced. Their English language abilities are not good. Not all English language editors are of good quality. A, an, and the should be discarded from the English language. I have been harmed. I am being harmed. We have been harmed. We need to go ahead question by question. We need to go ahead issue by issue. Here are further guidelines. Here are further guidelines. I have few questions. English Grammar Rules for Simple Declarative Sentences. Subject + Predicate Simple declarative sentences in active and passive voice with tenses. What is the analysis of this English language sentence: "I will be investigating this case." Is this a declarative, imperative, exclamatory or interrogative sentence? Declarative sentence. Is it a simple declarative sentence, compound declarative sentence, complex declarative sentence, or compound complex declarative sentence? Simple declarative sentence. What is the pattern of this simple declarative sentence? Subject verb object pattern. What is the tense of this sentence? Future continuous tense Is this simple declarative sentence in active or passive format? Active voice (passive has to be determined. The case will be investigated by me.) Is it without quoted/unquoted format or in quoted/unquoted format? Without quoted/unquoted format. What will be the quoted and unquoted pattern of the sentence? Quoted and unquoted format of this sentence would be, He said,"I will be investigating this case." He said that I will be investigating this case. Which of these English language simple declarative sentences is correct? English language is the official language. An English language is the official language. The English language is the official language. A English language is the official language. Correct answer is: English language is the official language. Why is this simple declarative sentence correct? Which of these English language simple declarative sentences is correct? Understanding English language is essential. English language understanding is essential. The English language understanding is essential. An English language understanding is essential. Correct answer is: Understanding English language is essential. Why is this simple declarative sentence correct? Which of these English language declarative sentences is correct? The English language materials displayed at www.qureshiuniversity.com/english.html have been properly edited. English language materials displayed at www.qureshiuniversity.com/english.html have been properly edited. An English language materials displayed at www.qureshiuniversity.com/english.html have been properly edited. A English language materials displayed at www.qureshiuniversity.com/english.html have been properly edited. Correct answer is: The English language materials displayed at www.qureshiuniversity.com/english.html have been properly edited. Why is this declarative sentence correct? www.qureshiuniversity.com/declarativesentence.html What are examples of sentences in 12 tenses with the verb investigate and its conjugated forms?
|
|
At what age should career counseling start? Career counseling usually starts at the age of 14. Some prefer to start career counseling at the age of 10. What should be your first professional goal while seeking career counseling? Teacher, lawyer, engineer, or a physician in your original state. Take a look at this. www.qureshiuniversity.com/professionsworld.html Other options are elaborated. Here are further guidelines. http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/workcounseling.html What is career counseling? What is involved in career counseling? How long does career counseling take? What is the difference between Career Counseling and Coaching? Who needs Career Counseling? Questions you need to answer. Where is your biodata? Where are you now? What is your name? How old are you? What is your date of birth? What is the date today? What is your mailing address? What grade are you in? How do you like school? What subjects do you study? What would you like to be? Take a look at this. http://www.qureshiuniversity.org/occupations.html http://www.qureshiuniversity.com/workcounseling.html |
|
How many Classes of words or parts of speech are in English language? 9 What are the various classes of words in the English language?
Spelling
Descriptive adjectives
|
|
What is an example of an adverb in a simple declarative sentence in English language? Clearly the brilliant Doctor Asif Qureshi will be investigating this case. Clearly is an adverb. Here are further guidelines. |
|
What is a Conjunction? What do they do? What are coordinating and subordinating conjunctions? How many types of conjunctions are there? What are the different types of conjunctions? Can you name various subordinating conjunctions? How many subordinating conjunctions are there in English language? What are examples of subordinating conjunctions that begin complex declarative sentences in English language? What are examples of relative pronouns? What words start a noun clause in English language? What are examples of complex declarative sentences beginning with subordinating conjunctions in English language? What is a Conjunction? A conjunction is a word that joins two or more words, phrases, or clauses.  What do they do? Conjunctions join words or groups of words. How many types of conjunctions are there? 4 What are the different types of conjunctions? Coordinating conjunctions Subordinating conjunctions Correlative conjunctions Conjunctive adverbs Can you name various subordinating conjunctions? How many subordinating conjunctions are there in English language? There are more than 62. What are examples of subordinating conjunctions that begin complex declarative sentences in English language?
What are examples of relative pronouns?
What words start a noun clause in English language? Noun clauses usually start with relative pronouns. What are examples of complex declarative sentences beginning with subordinating conjunctions in English language? After lunch, I will be investigating this case. After we finish the discussion, I will investigate this case. After completing this lesson, I will be investigating this case. After (subordinator) they (subject) finish (verb) studying, I will be investigating this case. Although the gallery has closed for the day, I will be investigating this case. As you know, I will be investigating this case. As soon as the alarm goes off, I will be investigating this case. As far as I know, I will be investigating this case. As if harmed, I will be investigating this case. As long as I know, I will be investigating this case. As much as I know, I will be investigating this case. As soon as possible, I will be investigating this case. As though [need object of “as thoughâ€Â], I will be investigating this case. Because she lied on her application, I will investigate this case. Because she was lying, I will be investigating this case. Before she lies, I will be investigating this case. Before I go to bed, I will be investigating this case. Before I see the house, I will be investigating this case. Before we arrive at school, I will be investigating this case. Before you leave for school, I will be investigating this case. By the time you sleep, I will be investigating this case. Even if you win a million dollars, it doesn’t mean you’ll be happy. Even though I’d heard the song before, I didn’t know who sang it. Ever since I met her, I haven’t been able to think about anything else. Every time there is complaint, I will investigate this case. If you find out, please let us know. If you find out, I will investigate this case. If you want to speak to me, then learn English. If only harmed, I will be investigating this case. If harmed, then I will be investigating this case. If harmed, when will I be investigating this case? In case you are harmed, I will be investigating this case. In order that you are not harmed, I will be investigating this case. In that you were harmed, I will be investigating this case. Inasmuch as you were harmed, I will be investigating this case. Insofar as you were harmed, I will be investigating this case. Just as he was harmed, I started investigating this case. Lest harmed, I will be investigating this case. No matter how harmful, I will be investigating this case. Now healthy, I will be investigating this case. It’s been three years now since I was harmed, so I will be investigating this case. Now that he is harmed, I will be investigating this case. Now when someone is harmed, I investigate the case. Once this harm is known, I will investigate the case. Provided no one is harmed, I will be investigating this case. Provided that no one is harmed, I will be investigating this case. Rather than be harmed, I will be investigating this case. It isn’t that I will be harmed, but rather that I will be investigating this case. Since harmed, I have been investigating this case. So that no one is harmed, I will be investigating this case. Supposing that someone might be harmed, I will be investigating this case. So sure am I about potential harm that I will be investigating this case. So that I’m sure, I will be investigating this case. Since you are coming over anyway, I will be investigating this case. Though he harmed me, I will still be investigating this case. Than this harmed, I will be investigating this case. That no one is harmed, I will be investigating this case. The first time someone is harmed, I will be investigating this case. Though harmed, I will be investigating this case. Till you understand who was harmed, I will be investigating this case. Unless you’re willing to understand who was harmed, I will be investigating this case. Until spring arrives, I will be investigating this case. Unless this harms me, I will be investigating this case. Until I understand this harm, I will be investigating this case. Whenever he is harmed, I will investigate the case. Where this harm occurs, I will investigate the case. Where if this has been harmful, I will be investigating this case. Whereas this has been harmful, I will be investigating this case. Wherever harm occurs, I will be investigating the case. Whether he has been harmed or not, I will be investigating this case. Which issues has harmed, I will be investigating this case. While this has been harmful, I will still be investigating this case. To determine who may have been harmed, I will be investigating this case. Whoever harmed him, I will investigate the case to find you. To understand why he was harmed, I will be investigating this case. When Amy wrote an amazing paragraph, she earned an A+ in the course. When I read the story, I will investigate the case. When we’re done, let’s get some ice cream. When you get home, call me. Whether or not you agree, I will be investigating this case. While I’m there, I will be investigating this case. While we are on the way, I will be investigating this case. Wherever harm occurs, I will investigate the case. Relative pronouns. To determine that harms have occurred, I will be investigating this case. Whoever is harmed, I will be investigating this case. To know who may have been harmed, I will be investigating this case. To whom this may concern, I will be investigating this case. To help whomever he harmed, I will be investigating this case. To know which location may have been harmed, I will be investigating this case. To know whichever harms occurred, I will be investigating this case. Subordinating Conjunctions
|
| Here are further guidelines. |
|
What should you know about nouns if you are more than 18 years old? You must at least know common nouns (countable nouns, uncountable nouns) and proper nouns. Examples of countable nouns are book/books, table/tables, and window/windows. Examples of uncountable nouns are rice, milk, and water. Examples of proper nouns are Asif Qureshi, Illinois, Los Angeles, Tuesday, the Pacific Ocean, Jupiter, and the University of Qureshi. There are 10 categories of proper nouns. You should know this at least. At most there are 22 types of nouns. Here are further guidelines. |
What are various examples of pronouns?
1. Personal Pronouns / Subject Pronouns You already know subject pronouns, even if you didn't know that's what they were called. Subject pronouns are used to replace the subject in a sentence. You might also see them called "personal" pronouns, as they designate the person speaking (I, me, we, us), the person spoken to (you), or the person or thing spoken about (he, she, it, they, him, her, them). The following commonly used words are subject pronouns:
Personal pronoun examplesI will be leaving soon. You are welcome. She is the new teacher. He speaks three languages. They are very friendly neighbors. 2. Object PronounsObject pronouns are used as the object of a verb or a preposition.
Object pronoun examplesThey offered me a ride. ("Me" is the object of the verb "offered.") This letter is addressed to me. ("Me" is the object of the preposition "to.") They gave us free tickets to the show. ("Us" is the object of the verb "gave.") 3. Possessive PronounsA possessive pronoun designates ownership and can substitute for noun phrases.
Possessive pronoun examplesThe green gloves are mine. That cat is hers. The red house is theirs. Possessive Adjectives / Pronominal Adjectives"Pronominal" describes something that resembles a pronoun, as by specifying a person, place, or thing, while functioning primarily as another part of speech. A pronominal adjective is an adjective that resembles a pronoun. "Her" in "her car" is a pronominal adjective.
4. Reflexive PronounsReflexive pronouns might be the easiest group to remember because they all have one thing in common: the ending "self" or "selves." That's because reflexive pronouns show how the actions of an aforementioned person or group affects him or her (or them).
Reflexive pronoun examplesI bought myself a new car. That man thinks a great deal of himself. We may be deceiving ourselves. 5. Intensive PronounsIntensive and reflexive pronouns are actually the exact same words (ending with "self" or "selves"), but they function differently in a sentence. Intensive pronouns not only refer back to a previously mentioned person or people, but they also emphasize. As their name suggests, they intensify.
Intensive pronoun examplesI myself was certain of the facts. The trouble is in the machine itself. The cooks themselves eat after all the guests have finished. 6. Indefinite PronounsAs the word "indefinite" suggests, these pronouns do not specify the identity of their referents. They are more vague than other pronouns.
Indefinite pronouns examplesBoth were candidates. No one is home. Several of the workers went home sick. 7. Demonstrative PronounsDemonstrative pronouns specify a particular person or thing.
Demonstrative pronouns examplesI don't much care for these. Who's that? Such are the fortunes of war. 8. Interrogative PronounsThis group of pronouns question which individual referent or referents are intended by the rest of the sentence.
Interrogative pronoun examplesWho left? Which of these is yours? Do whatever you please. 9. Relative PronounsRelative pronouns introduce a dependent clause and refer to an antecedent (simply the word or phrase to which a pronoun refers). For instance, who in the child who is wearing a hat or that in the house that you live in.
Relative pronoun examplesThe car that has a flat tire needs to be towed. The visitor who came yesterday left his phone number. Do whatever you like. 10. Archaic PronounsThere are several pronouns that have fallen out of common usage but appear frequently in older texts, so there is still a good chance that you will encounter them. "Thee" is an old word for "you" used only when addressing one person, while "thy" is an old word for "your." "Thine" indicates the one or ones belonging to thee.
Archaic pronoun examplesThou shalt not kill. With this ring, I thee wed. Thy name is more hateful than thy face. To thine own self be true. List of all pronounsA full list of every word that can be considered a pronoun or pronominal adjective*:
Are there any pronouns we missed? Pronouns are words like I, me (personal pronouns) or my, mine (possessive pronouns).
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
What is a Preposition? What are various examples of prepositions? What does a prepositional phrase do in a sentence? Can you end a sentence with a preposition? What is a prepositional phrase? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
What is a Preposition? First, a quick recap of the basics: A preposition is a word such as with, by, on, in, at, to, or about. Prepositions are a class of word used to express the relationship between the elements of a sentence or clause. A preposition connects a verb, noun, or adjective to a noun or pronoun and is typically, but not always, found before the noun or pronoun in a sentence or clause. A preposition is a word such as after, in, to, on, and with. Prepositions are usually used in front of nouns or pronouns and they show the relationship between the noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and some other word in the sentence. Prepositions are words that help link either the noun, or the pronoun with another word in the sentence in order to describe their relationship. A preposition is a word, which is used to indicate different relations, such as place, time, reason and purpose, method, direction and motion, manner, and possession. It is usually placed before a noun, or pronoun. The most common examples of prepositions in grammar are on, in, at, to, with, up, etc. What are various examples of prepositions? One-word Prepositions
Complex Prepositions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Preposition List
What is a prepositional phrase? Subject + Verb + Object + Prepositional Phrase = Simple Sentence A prepositional phrase has two basic parts: a preposition plus a noun or a pronoun that serves as the object of the preposition. Remember the following rules for prepositional phrases and you will find that using them becomes much easier. •Prepositional phrases always consist of two basic parts at minimum: the object and the preposition. •In formal English, prepositions are almost always followed by objects. •Adjectives can be placed between the prepositions and objects in prepositional phrases. •Prepositional phrases can act as adverbs or adjectives. When they are used as adjectives, they modify nouns and pronouns in the same way single-word adjectives do. •When prepositional phrases are used as adverbs, they at the same way single-word adverbs and adverb clauses do, modifying adjectives, verbs, and other adverbs. If the sentence has an indirect object, it will always come between the verb and the direct object. If there is information after the direct object about who received it, that is most likely a prepositional phrase (Jeff threw the ball to Mark.). A prepositional phrase cannot be an indirect object. Examples of Prepositional PhrasesThe following sentences contain examples of prepositional phrases; the prepositional phrase in each sentence is italicized for easy identification. The cupcake with sprinkles is yours. The cupcake with colorful sprinkles is yours. We climbed up the hill . We climbed up the very steep hill . The rabbits hopped through the garden . The rabbits hopped through the perfectly manicured garden.
List of Prepositional Phrases While there are only about 150 prepositions in the English language, there are thousands of other words that can make their way into prepositional phrases. Learn to create a colorful prepositional phrase, and your writing will be wonderfully appealing. Down the tree Up the hill Around the mulberry bush Into the woods With chopped nuts Near a fast-flowing river Within the book’s pages Through the tunnel In spite of Instead of Any more On account of To the fact that Because of Prepositional phrases modify other parts of a sentence. They may be found in several other places in a sentence. Examples: (Initial) In the big house, Monica felt safe. (Medial) I was walking rapidly, through the snow, and I was getting cold. (Final) Ali slumped like a broken doll, after the fight. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Here are further guidelines. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Prepositions of Movement Prepositions of Place Prepositions of Time | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Questions and prepositions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Prepositions at the end of questions
Classes of Prepositions Simple Prepositions Double Prepositions Compound Prepositions Phrasal Prepositions Participial Prepositions Disguised Prepositions |
| Here are further guidelines. |
|
What are other names of helping verbs in the English language? Auxiliary verbs. What are the categories of helping verbs (also called auxiliary verbs) in the English language? Primary helping verbs, such as be (to be, be, is, am, are, was, were, been, being 9), do (do, did, does 3), and have (has, have, had 3). Modal helping verbs include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would. There are at least 15 modal helping verbs. What is a modal verb? What are modal verbs? What is the difference? “What is a modal verb†focuses on the definition of the modal verb concept. “What are modal verbs†focuses on all modal verbs. Answers to each question are different. Let me ask you a question. Can you name some modal verbs? What are examples of modal verbs in the English language? Can Could May Might Shall Should Will Would Must Ought to Must not/may not Need/Need not Used to Have to/has to/had to Some consider only the first ten in this list to be modal verbs. What are other terms for modal verbs in the English language? Modal verbs are also called modal auxiliary verbs and modal auxiliaries. Verbs in English Language. Investigate is a verb.
Types of Sentences in English Language
Simple declarative sentence in English language. Subject + Verb + Object What are examples of sentences in 12 tenses with the verb investigate and its conjugated forms?
Incident report Teaching investigators how to write incident reports in English language from Doctor Asif Qureshi.
Simple declarative sentence
Quoted speech sentence in English language. Reported speech sentence in English language.
Question-and-answer Presentation in English Language
|
| Best English language teachers around the world. |